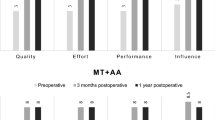
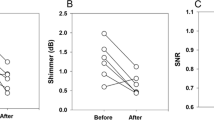
Abstract
The aim of this study was to objectively evaluate the voices of patients suffering from unilateral vocal cord paralysis, before and after endoscopic augmentation and thyroplasty. In the past, we used injectable Teflon to treat this condition; later techniques included collagen injection and Isshiki thyroplasty. In the last 7 years, preferred treatment methods have included Bioplastique injection and lipoaugmentation of the vocal cords as well as medialization thyroplasty using a titanium implant according to Friedrich. Pre- and postoperative data was evaluated and compared to 25 patients. Appropriate glottic closure of the vocal cords was achieved in every case, in most cases after the first intervention. We used voice range profile measurements to evaluate the results. An objective evaluation was performed using the Friedrich dysphonia index. Significant improvements were found: the dysphonia index decreased in every case, from an average of 2.47, preoperatively, to an average of 1.18 postoperatively. In agreement with earlier studies, voice pitch range was the only parameter that not significantly improved. There was no statistical difference between the lipoaugmentation and thyroplasty according to Friedrich. We concluded that both endoscopic methods and thyroplasty can be used to achieve an optimal result. Cases must be evaluated individually so that the best technique, or combination of methods can be determined.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnold GE (1955) Vocal rehabilitation of paralytic dysphonia: I. Cartilage injection into a paralysed vocal cord. Arch Otolaryngol 62:1
Arnold GE (1962) Vocal rehabilitation of paralytic dysphonia. IX. Technique of intracordal injection. Arch Otolaryngol 76:358–368
Brandenburg JH Danna Koschkee MA (1996) Lipoinjection laryngoplasty. Abstract of The second international symposium on laryngeal and tracheal reconstruction May 22–26, 1996, Monte-Carlo
Brünings W (1911) Über eine neue Behandlungsmethode der Rekurrenslähmung. 18. Verhandl. Ver. Deutsch. Laryng., pp 93 (525), 151 (583)
Cummings CW, Purcell LL, Flint PW (1993) Hydroxylapatite laryngeal implants for medialization. Preliminary report. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 102:843–851
Desrosiers M, Ahmarani C, Bettez M (1993) Precise vocal cord medialization using an adjustable laryngeal implant: a preliminary study. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 109:1014–1019
Ford CN, Martin DW, Warner TF (1984) Injectable collagen in laryngeal rehabilitation. Laryngoscope 94:513–518
Friedrich G (1996) Qualitätssicherung in der Phoniatrie. Vorschlag zur Standardisierung der Klinischen Stimmprüfung HNO 44:401–416
Friedrich G (1998) Externe Stimmlippenmedialisation: Funktionelle Ergebnisse. Laryngorhinootologie 77:18–26
Friedrich G (1999) Titanium vocal fold medializing implant: introducing a novel implant system for external vocal fold medialization. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 108:79–86
Goff WF (1960) Laryngeal adductor paralysis treated by vocal cord injection of bone paste: a preliminary investigation. Trans Pac Coast Otoophtalmol Soc 41:77–88
Höfler H, Duman M (1993) Stimmlippenunterfütterung mit Bioplastique: erste Ergebnisse. Zentralbl. HNO 577–577
Isshiki N, Morita H, Okamura H, Hiramoto M (1974) Thyroplasty as a new Phonosurgical technique. Acta Otolaryngol 78:451–457
Isshiki N, Okamura H, Ishikawa T (1975) Thyroplasty type I (lateral compression) for dysphonia due to vocal cord paralysis or atrophy. Acta Otolaryngol (Stockh) 80:465–473
Kleinsasser O, Schroeder HG, Glanz H (1982) Medianverlagerung gelähmter Stimmlippen mittels Knorpelspanimplantation und Türflügelthyreoplastic. HNO 30:275–279
Kresa Z, Rems J, Wichterle O (1973) Hydron gel implants in vocal cords. Acta Otolaryngol (Stockh) 76:360
Lichtenberger G (2000) Diagnostik und Therapie ein- und beidseitiger Rekurrensparesen. Laryngo Rhino Otol 79:682–683
Mahieu HF, Schutte HK (1989) New surgical techniques for voice improvement. Arch Otorhinolaryngol 246:397–402
McCulloch TM, Hoffman HT (1998) Medialization laryngoplasty with expanded polytetrafluoroethylene. Surgical technique and preliminary results. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 107:427–432
Montgomery MM, Blaugrund SM, Varvares MA (1993) Thyroplasty: a new approach. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 102:571–579
Montgomery MM, Montgomery SK (1997) Montgomery thyroplasty implant system. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol Suppl 170:1–16
Payr E (1915) Plastik am Schildknorpel zur Behebung der Folgen einseitiger Stimmbandlähmung. Dtsch Med Wochenschr 43:1265–1270
Remacle MJM, Marbaix E, Bertrand BMG (1986) The value of injectable collagen in vocal and glottic rehabilitation. Arch Otorhinolaryngol 243:233–237
Rubin HJ (1965) Intracordal injection of silicone in selected dysphonias. Arch Otol 81:604
Schramm Jr VL, May M, Lavorato AS (1978) Gelfoam paste injection for vocal cord paralysis: temporary rehabilitation of glottic incompetence. Laryngoscope 88:1268–1273
Sittel C, Thumfart WF, Pototschnig C, Wittekindt C, Eckel HE (2000) Textured polymethylsiloxane elastomers in the human larynx: safety and efficiency of use. J Biomed Mater Res 53:646–650
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Presented at the 5th ELS Congress in Lisbon on 10-13 July 2004
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bihari, A., Mészáros, K., Reményi, A. et al. Voice quality improvement after management of unilateral vocal cord paralysis with different techniques. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 263, 1115–1120 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-006-0116-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-006-0116-9