Abstract
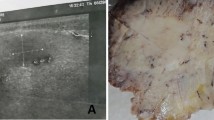
Tuberculosis is caused by a mycobacterium and is one of the most serious diseases in the world. Pulmonary involvement is the most common form of this condition. Primary tuberculosis of the parotid gland is rare. We report such a case in a 34-year-old man who presented with a painless preauricular mass on each side of his head. The clinical presentation, diagnosis, pathological findings and treatment are described.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Carmody TE (1914) Tuberculosis of the parotid gland. Laryngoscope 24:873
Chang KL, Arbor DA, Weis LM (2003) Lymph nodes. In: Cote W, Weiss S (eds) Modern surgical pathology, vol 2, 1st edn. Saunders, Philadelphia, pp 1477–1570
Donohue W, Bolden T (1961) Tuberculosis of the salivary glands. Oral Surg 14:576–588
Farnia P, Mohammadi F, Fadda G, et al (2001) Transmission pattern of tuberculosis using RFLP-based IS6110. Arch Irn Med 4:177–182
Hamdan AL, Hadi U, Shabb N (2002) Tuberculous parotitis: a forgotten entity. Head Neck Surg 126:581–582
Millar BG, Johnson PA, Leopard PJ (1989) Bilateral acinic cell carcinoma of the parotid. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg 3:192–197
Ohmori M, Aoki M (1997) Future prediction of tuberculosis incidence rates by prefecture. Nippon Koshu Eisei Zasshi 44:741–748
Pust RE (1992) Tuberculosis in the 1990s: resurgence, regimens and resources. South Med J 85:584–593
Singh B, Maharaj TJ (1992) Tuberculosis of the parotid gland: clinically indistinguishable from a neoplasm. J Laryngol Otol 106:929–931
Stanley RB, Fernandez JA, Peppard SB (1983) Cervicofacial mycobacterial infections presenting as major salivary gland disease. Laryngoscope 93:1271–1275
Tveteras K, Kristensen S (1986) Warthin’s tumour with bilateral synchronous presentation. Survey of the literature and a new case. J Laryngol Otol 100:487–492
Walsted A, Peitersen E (1988) Bilateral pleomorphic adenomas of the parotid glands. Ugeskr Laeger 150:170–171
Weiner GM, Pahor AL (1996) Tuberculosis parotitis: limiting the role of surgery. J Laryngol Otol 110:96–97
Yaniv E, Avedillo H (1985) Facial paralysis due to primary tuberculosis of the parotid gland. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 9:195–196
Zumla A, Squire SB, Chintu C, Grange JM (1999) The tuberculosis pandemic implications for health in the tropics. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 93:113–117
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This case report was presented as a poster at the Turkish Ear, Nose and Throat and Head Neck Surgery Association 2nd Academy Congress, 15–18 April 2004, in Adana, Turkey.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Erkan, A.N., Çakmak, Ö., Kayaselçuk, F. et al. Bilateral parotid gland tuberculosis. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 263, 487–489 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-005-1021-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-005-1021-3