Abstract
Objective
Controversy still exists in the relationship between p53 codon72 polymorphism and the risk of endometrial cancer.
Materials and methods
In order to figure out this inconsistency, database on HuGE Navigator, PubMed and Web of Science about the case–control studies were compiled in the present work. Statistic analysis was performed by STATA 12.0.
Results
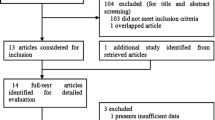
Total 11 eligible publications were selected in this meta-analysis including 1086 endometrial cancer and 1403 controls. There was no significant relationship between codon72 polymorphism of p53 gene and the risk of endometrial cancer under allele model [Pro versus Arg: OR 0.99, 95 % CI (0.87, 1.15)], dominant model [ArgPro + ProPro versus ArgArg: OR 0.88, 95 % CI (0.67, 1.15)], recessive model [ProPro versus ArgArg + ArgPro: OR 1.09, 95 % CI (0.84, 1.42)] and addictive model [ProPro versus ArgArg: OR 0.97, 95 % CI (0.72, 1.29)]. Samples from endometrial tissue with homozygous ArgArg have the increased risk of EC [allele model: OR 0.71, 95 % CI (0.53, 0.96); addictive model: OR 0.46, 95 % CI (0.24, 0.87)].
Conclusion
This meta-analysis revealed a weak association between the codon72 polymorphism of p53 gene and the risk of endometrial cancer. Women with homozygous Arg72 may be more susceptible to endometrial cancer than others with heterozygotes and homozygous Pro72.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sorosky JI (2008) Endometrial cancer. Obstet Gynecol 111(2 Pt 1):436–447. doi:10.1097/AOG.0b013e318162f690
Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A (2013) Cancer statistics. Ca Cancer J Clin 63(1):11–30
Cancer Research UK. Uterine cancer incidence statistics. http://www.cancerresearchuk.org/cancer-info/cancerstats/types/uterus/incidence/. Accessed 26 Apr 2015
Galaal K, Al Moundhri M, Bryant A, Lopes AD, Lawrie TA (2014) Adjuvant chemotherapy for advanced endometrial cancer. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 5:CD010681. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD010681.pub2
Murali R, Soslow RA, Weigelt B (2014) Classification of endometrial carcinoma: more than two types. Lancet Oncol 15(7):e268–e278. doi:10.1016/s1470-2045(13)70591-6
Fornasarig M, Campagnutta E, Talamini R, Franceschi S, Boz G, Scarabelli C, Andreaus CM, Scozzari G, Valentini M (1998) Risk factors for endometrial cancer according to familial susceptibility. Int J Cancer 77(1):29–32
Lorenzo Bermejo J, Buchner FL, Hemminki K (2004) Familial risk of endometrial cancer after exclusion of families that fulfilled Amsterdam, Japanese or Bethesda criteria for HNPCC. Ann Oncol 15(4):598–604
Win AK, Reece JC, Ryan S (2015) Family history and risk of endometrial cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Obstet Gynecol 125(1):89–98. doi:10.1097/AOG.0000000000000563
Britschgi C, Fey MF (2009) Tumor suppressor genes in myeloid differentiation and leukemogenesis. Future Oncol 5(2):245–257. doi:10.2217/14796694.5.2.245
Koshiyama M, Ueta M (2002) Two kinds of endometrial neoplasia arising from different origins in the uterine corpus: comparison of p53 expression and sex steroid receptor status. Eur J Obstet Gyn R B 104(2):167–170
Zajac A, Smolarz B, Stachowiak G, Wilczynski JR (2014) TP53 and MDM2 polymorphisms and the risk of endometrial cancer in postmenopausal women. Med Oncol 31(11):286. doi:10.1007/s12032-014-0286-z
Levine AJ, Oren M (2009) The first 30 years of p53: growing ever more complex. Nat Rev Cancer 9(10):749–758. doi:10.1038/nrc2723
Garcia PB, Attardi LD (2014) Illuminating p53 function in cancer with genetically engineered mouse models. Semin Cell Dev Biol 27:74–85
Zajac A, Stachowiak G, Smolarz B, Wilczynski JR (2013) Polymorphisms of codon 72 of the TP53 gene in endometrial carcinoma of postmenopausal women. Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online) 67:1312–1318
Kataoka M, Okabayashi T, Johira H, Nakatani S, Nakashima A, Takeda A, Nishizaki M, Orita K, Tanaka N (2000) Aberration of p53 and DCC in gastric and colorectal cancer. Oncol Rep 7(1):99–103
Higgins JP, Thompson SG (2002) Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat Med 21(11):1539–1558. doi:10.1002/sim.1186
Zubor P, Hatok J, Moricova P, Kajo K, Kapustova I, Mendelova A, Racay P, Danko J (2015) Gene expression abnormalities in histologically normal breast epithelium from patients with luminal type of breast cancer. Mol Biol Rep 42(5):977–988
Brachova P, Mueting SR, Carlson MJ, Goodheart MJ, Button AM, Mott SL, Dai DH, Thiel KW, Devor EJ, Leslie KK (2015) TP53 oncomorphic mutations predict resistance to platinum- and taxane-based standard chemotherapy in patients diagnosed with advanced serous ovarian carcinoma. Int J Oncol 46(2):607–618
Bellini MF, Cadamuro ACT, Succi M, Proenca MA, Silva AE (2012) Alterations of the TP53 gene in gastric and esophageal carcinogenesis. J Biomed Biotechnol 2012:891961
Bergamaschi D, Samuels Y, Sullivan A, Zvelebil M, Breyssens H, Bisso A, Del Sal G, Syed N, Smith P, Gasco M, Crook T, Lu X (2006) iASPP preferentially binds p53 proline-rich region and modulates apoptotic function of codon 72 polymorphic p53. Nat Genet 38(10):1133–1141
Thomas M, Kalita A, Labrecque S, Pim D, Banks L, Matlashewski G (1999) Two polymorphic variants of wild-type p53 differ biochemically and biologically. Mol Cell Biol 19(2):1092–1100
Dumont P, Leu JIJ, Della Pietra AC, George DL, Murphy M (2003) The codon 72 polymorphic variants of p53 have markedly different apoptotic potential. Nat Genet 33(3):357–365
Pim D, Banks L (2004) p53 polymorphic variants at codon 72 exert different effects on cell cycle progression. Int J Cancer 108(2):196–199
Storey A, Thomas M, Kalita A, Harwood C, Gardiol D, Mantovani F, Breuer J, Leigh IM, Matlashewski G, Banks L (1998) Role of a p53 polymorphism in the development of human papillomavirus-associated cancer. Nature 393(6682):229–234. doi:10.1038/30400
Malisic E, Jankovic R, Brotto K, Radulovic S (2013) TP53 codon 72 polymorphism and risk of cervical carcinoma in Serbian women. Arch Gynecol Obstet 288(3):621–625. doi:10.1007/s00404-013-2783-2
Kafshdooz T, Tabrizi AD, Ardabili SMM, Kafshdooz L, Ghojazadeh M, Gharesouran J, Abdii A, Alizadeh H (2014) Polymorphism of p53 Gene Codon 72 in endometrial cancer: correlation with tumor grade and histological type. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 15(22):9603–9606. doi:10.7314/apjcp.2014.15.22.9603
Roh JW, Kim JW, Park NH, Song YS, Park IA, Park SY, Kang SB, Lee HP (2004) p53 and p21 genetic polymorphisms and susceptibility to endometrial cancer. Gynecol Oncol 93(2):499–505. doi:10.1016/j.ygyno.2004.02.005
Gu Y, Zhou X, Zhang SL (2011) Meta-analysis of an association of codon 72 polymorphisms of the p53 gene with increased endometrial cancer risk. Genet Mol Res 10(4):3609–3619. doi:10.4238/2011.October.31.11
Khan MH, Khalil A, Rashid H (2015) Evaluation of the p53 Arg72Pro polymorphism and its association with cancer risk: a HuGE review and meta-analysis. Genet Res (Camb) 97:e7. doi:10.1017/S0016672315000075
Mitchell AA, Cutler DJ, Chakravarti A (2003) Undetected genotyping errors cause apparent overtransmission of common alleles in the transmission/disequilibrium test. Am J Hum Genet 72(3):598–610. doi:10.1086/368203
Jongen VHWM, Briet JM, de Jong RA, Joppe E, ten Hoor KA, Boezen HM, Evans DB, Hollema H, van der Zee AGJ, Nijman HW (2009) Aromatase, cyclooxygenase 2, HER-2/neu, and P53 as prognostic factors in endometrioid endometrial cancer. Int J Gynecol Cancer 19(4):670–676
Ashton KA, Proietto A, Otton G, Symonds I, McEvoy M, Attia J, Gilbert M, Hamann U, Scott RJ (2009) Polymorphisms in TP53 and MDM2 combined are associated with high grade endometrial cancer. Gynecol Oncol 113(1):109–114. doi:10.1016/j.ygyno.2008.12.036
Janiec-Jankowska A, Konopka B, Goluda C, Najmola U (2010) TP53 mutations in endometrial cancers: relation to PTEN gene defects. Int J Gynecol Cancer 20(2):196–202
Garcia-Dios DA, Lambrechts D, Coenegrachts L, Vandenput I, Capoen A, Webb PM, Ferguson K, Akslen LA, Claes B, Vergote I, Moerman P, Van Robays J, Marcickiewicz J, Salvesen HB, Spurdle AB, Amant F (2013) High-throughput interrogation of PIK3CA, PTEN, KRAS, FBXW7 and TP53 mutations in primary endometrial carcinoma. Gynecol Oncol 128(2):327–334. doi:10.1016/j.ygyno.2012.11.037
Esteller M, GarcÃa A, MartÃnez-Palone JM, Xercavin J, Reventà J (1997) Susceptibility to endometrial cancer: influence of allelism at p53, glutathione S-transferase (GSTM1 and GSTT1) and cytochrome P-450 (CYP1A1) loci. Br J Cancer 75(9):1385–1388
Peller Shoshana, Halperin Rehuvit, Schneider D (1999) Polymorphisms of the p53 gene in women with ovarian or endometrial carcinoma. Oncol Rep 6:193–197
Agorastos T, Masouridou S, Lambropoulos AF, Chrisafi S, Miliaras D, Pantazis K, Constantinides TC, Kotsis A, Bontis I (2004) P53 codon 72 polymorphism and correlation with ovarian and endometrial cancer in Greek women. Eur J Cancer Prev 13(4):277–280
Niwa Y, Hirose K, Matsuo K, Tajima K, Ikoma Y, Nakanishi T, Nawa A, Kuzuya K, Tamakoshi A, Hamajima N (2005) Association of p73 G4C14-to-A4T14 polymorphism at exon 2 and p53 Arg72Pro polymorphism with the risk of endometrial cancer in Japanese subjects. Cancer Lett 219(2):183–190. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2004.10.018
Ueda M, Terai Y, Kanda K, Kanemura M, Takehara M, Yamaguchi H, Nishiyama K, Yasuda M, Ueki M (2006) Germline polymorphism of p53 codon 72 in gynecological cancer. Gynecol Oncol 100(1):173–178. doi:10.1016/j.ygyno.2005.08.015
Nunobiki O, Ueda M, Yamamoto M, Toji E, Sato N, Izuma S, Okamoto Y, Torii K, Noda S (2009) Polymorphisms of p53 codon 72 and MDM2 promoter 309 and the risk of endometrial cancer. Hum Cell 22(4):101–106. doi:10.1111/j.1749-0774.2009.00075.x
Zubor P, Stanclova A, Kajo K, Hatok J, Klobusiakova D, Visnovsky J, Danko J (2009) The p53 codon 72 exon 4 BstUI polymorphism and endometrial cancer in Caucasian women. Oncology 76(3):173–183. doi:10.1159/000201570
Ghasemi N, Karimi-Zarchi M, Mortazavi-Zadeh MR, Atash-Afza A (2010) Evaluation of the frequency of TP53 gene codon 72 polymorphisms in Iranian patients with endometrial cancer. Cancer Genet Cytogenet 196(2):167–170. doi:10.1016/j.cancergencyto.2009.09.013
Yoneda T, Kuboyama A, Kato K, Ohgami T, Okamoto K, Saito T, Wake N (2013) Association of MDM2 SNP309 and TP53 Arg72Pro polymorphisms with risk of endometrial cancer. Oncol Rep 30(1):25–34. doi:10.3892/or.2013.2433
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, X., Hou, D., Huang, C. et al. The association between codon72 polymorphism of p53 gene and the risk of endometrial cancer: an updating meta-analysis. Arch Gynecol Obstet 294, 353–359 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00404-015-4005-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00404-015-4005-6