Abstract
Objectives
Chronic intervillositis of unknown etiology (CIUE) is characterized by an intervillous infiltrate of mononuclear cells and a high recurrence rate of adverse obstetrical outcomes. The aim was to describe obstetrical history in patients with at least one event characterized by CIUE, and the possible impact of systematic investigation of an underlying autoimmune disease on the obstetrical outcome of subsequent pregnancies.
Methods
We retrospectively reviewed all pregnancies in patients having experienced at least one adverse obstetric outcome associated with chronic intervillositis of unknown etiology diagnosed by placental histological analysis between 2004 and 2011 in our university hospital. For each patient, data pertaining to obstetrical history, treatments during pregnancies, the results of systematic investigation of an underlying autoimmune disease, and treatments as well as obstetrical outcome in subsequent pregnancies, were collected.
Results
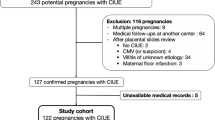
Twelve patients with 38 pregnancies were included [median age 30 (22; 40 years)]. Autoimmune disease or autoimmune antibodies (AID group) were found in 7/12 patients: primary antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) (n = 4), Sjögren’s syndrome (n = 1), pernicious anemia (n = 1) and celiac disease (n = 1). When comparing pregnancies of patients with and without AID, there was no difference with regard to the type of obstetrical events or live-born babies, in spite of appropriate treatment. Corticosteroids (prednisone 10 mg/day) were used in only 2 cases with AID (Sjögren’s syndrome and APS; n = 1 each), and these 2 pregnancies resulted in live-born babies.
Conclusion
This study shows that the immunological assessment in patients with CIUE raises the possibility of a specific severity when AID or obstetrical APS is associated with CIUE, since conventional treatment did not improve obstetrical outcome in these patients as compared to those without autoimmune diseases. The benefit of immunosuppressant agents in this subset of patients needs further evaluation.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Labarrere C, Mullen E (1987) Fibrinoid and trophoblastic necrosis with massive chronic intervillositis: an extreme variant of villitis of unknown etiology. Am J Reprod Immunol Microbiol 15:85–91
Boyd TK, Redline RW (2000) Chronic histiocytic intervillositis: a placental lesion associated with recurrent reproductive loss. Hum Pathol 31:1389–1396
Ordi J, Ismail MR, Ventura PJ, Kahigwa E, Hirt R, Cardesa A, Alonso PL, Menendez C (1998) Massive chronic intervillositis of the placenta associated with malaria infection. Am J Surg Pathol 22:1006–1011
Parant O, Capdet J, Kessler S, Aziza J, Berrebi A (2009) Chronic intervillositis of unknown etiology (CIUE): relation between placental lesions and perinatal outcome. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 143:9–13
Marchaudon V, Devisme L, Petit S, Ansart-Franquet H, Vaast P, Subtil D (2011) Chronic histiocytic intervillositis of unknown etiology: clinical features in a consecutive series of 69 cases. Placenta 32:140–145
Miyakis S, Lockshin MD, Atsumi T, Branch DW, Brey RL, Cervera R et al (2006) International consensus statement on an update of the classification criteria for definite antiphospholipid syndrome (APS). J Thromb Haemost 4:295–306
Rota C, Carles D, Schaeffer V, Guyon F, Saura R, Horovitz J (2006) Perinatal prognosis of pregnancies complicated by placental chronic intervillitis. J Gynecol Obstet Biol Reprod 35:711–719
Doss BJ, Greene MF, Hill J, Heffner LJ, Bieber FR, Genest DR (1995) Massive chronic intervillositis associated with recurrent abortions. Hum Pathol 26:1245–1251
Boog G, Le Vaillant C, Alnoukari F, Jossic F, Barrier J, Muller JY (2006) Combining corticosteroid and aspirin for the prevention of recurrent villitis or intervillositis of unknown etiology. J Gynecol Obstet Biol Reprod 35:396–404
Traeder J, Jonigk D, Feist H, Bröcker V, Länger F, Kreipe H, Hussein K (2010) Pathological characteristics of a series of rare chronic histiocytic intervillositis of the placenta. Placenta 31:1116–1119
Contro E, deSouza R, Bhide A (2010) Chronic intervillositis of the placenta: a systematic review. Placenta 31:1106–1110
Dollmann A, Schmitz-Moormann P (1972) Recurrent placental insufficiency due to villous placentitis with extreme growth retardation. Geburtshilfe Frauenheilkd 32:795–801
Kaandorp S, Di Nisio M, Goddijn M, Middeldorp S (2009) Aspirin or anticoagulants for treating recurrent miscarriage in women without antiphospholipid syndrome. Cochrane Database Syst Rev (1):CD004734. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD004734
Mekinian A, Revaux A, Bucourt M, Cornelis F, Carbillon L, Fain O (2012) Fetal death in primary SS associated with chronic intervillositis. Rheumatology 51:1136–1137
Jindal P, Regan L, Fourkala EO, Rai R, Moore G, Goldin RD, Sebire NJ (2007) Placental pathology of recurrent spontaneous abortion: the role of histopathological examination of products of conception in routine clinical practice: a mini review. Hum Reprod 22:313–316
Mekinian A, Costedoat-Chalumeau N, Masseau A, Botta A, Chudzinski A, Theulin A, on the behalf of the SNFMI and the European Forum of APS et al (2014) Chronic histiocytic intervillositis: outcome, associated diseases and treatment in a multicenter prospective study. Autoimmunity 16:1–6
Acknowledgments
We thank Pierre Pothier for English review of the manuscript.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
A. Revaux and A. Mekinian contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Revaux, A., Mekinian, A., Nicaise, P. et al. Antiphospholipid syndrome and other autoimmune diseases associated with chronic intervillositis. Arch Gynecol Obstet 291, 1229–1236 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00404-014-3536-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00404-014-3536-6