Abstract
Purpose
The purpose of this study was to examine the effects of atorvastatin in the treatment of experimental endometriosis.
Methods
Endometriosis was induced in 24 female rats. 4 weeks after the procedure dimensions of the foci were recorded. Rats were divided into three groups: in Group 1 (n = 8), a daily dose of 10 mg/kg atorvastatin was given for 14 days. In the second group (n = 8), a single dose of 1 mg/kg leuprolide acetate was injected intraperitoneally. The rats in Group 3 (n = 8) were received 1 mg/kg i.p. 0.9 % NaCl. At the end of the treatment, laparotomy was performed, and the dimensions of the endometriotic foci were recorded. Biochemical, histopathological and immunohistochemical studies were performed and nociception was compared in groups.
Results
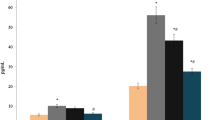
Atorvastatin treatment exhibited significant analgesic activity in hot plate model (P = 0.022). The serum hs-CRP and tumor necrosis TNF-α levels were similar between the Group 2 and Group 3 (P > 0.05); however atorvastatin caused significant decrease in both serum markers. The histological and immunohistochemical scores were also found to be markedly lower in Group 1 and Group 2 (P < 0.05).
Conclusion
Atorvastatin treatment may have a therapeutic potential in the treatment of endometriosis through its anti-inflammatory and anti-nociceptive properties.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vignali M, Infantino M, Matrone R, Chiodo I, Somigliana E, Busacca M, Viganò P (2002) Endometriosis: novel etiopathogenetic concepts and clinical perspectives. Fertil Steril 78(4):665–678
Giudice LC, Kao LC (2004) Endometriosis. Lancet 364(9447):1789–1799
Matarese G, De Placido G, Nikas Y, Alviggi C (2003) Pathogenesis of endometriosis: natural immunity dysfunction or autoimmune disease? Trends Mol Med 9(5):223–228
Olivares C, Bilotas M, Buquet R, Borghi M, Sueldo C, Tesone M, Meresman G (2008) Effects of a selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor on endometrial epithelial cells from patients with endometriosis. Hum Reprod 23(12):2701–2708. doi:10.1093/humrep/den315
Celik O, Hascalik S, Elter K, Tagluk ME, Gurates B, Aydin NE (2008) Combating endometriosis by blocking proteasome and nuclear factor-kappaB pathways. Hum Reprod 23(11):2458–2465. doi:10.1093/humrep/den246
Agic A, Xu H, Finas D, Banz C, Diedrich K, Hornung D (2006) Is endometriosis associated with systemic subclinical inflammation? Gynecol Obstet Invest 62(3):139–147
Kappou D, Matalliotakis M, Matalliotakis I (2010) Medical treatments for endometriosis. Minerva Ginecol 62(5):415–432
Jacobson TZ (2011) Potential cures for endometriosis. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1221:70–74. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.2010.05933.x
Wang F, He YL, Peng DX, Liu MB (2005) Expressions of nuclear factor-kappaB and intercellular adhesion molecule-1 in endometriosis. Di Yi Jun Yi Da Xue Xue Bao 25:703–705
Clearfield M, Whitney EJ, Weis S, Downs JR, Shapiro DR, Stein EA, Watson DJ, Langendörfer A, Beere PA, Stamler J, Gotto AM Jr (1998) Primary prevention of acute coronary events with lovastatin in men and women with average cholesterol levels: results of AFCAPS/TexCAPS. Air Force/Texas Coronary Atherosclerosis Prevention Study. JAMA 279:1615–1622
Ghaisas MM, Dandawate PR, Zawar SA, Ahire YS, Gandhi SP (2010) Antioxidant, antinociceptive and anti-inflammatory activities of atorvastatin and rosuvastatin in various experimental models. Inflammopharmacology 18(4):169–177. doi:10.1007/s10787-010-0044-6
Taubes G (2002) Does inflammation cut to the heart of the matter? Science 296:242–245
Schönbeck U, Libby P (2004) Inflammation, immunity, and HMGCoA reductase inhibitors: statins as antiinflammatory agents? Circulation 109:8–26
Grip O, Janciauskiene S, Bredberg A (2008) Use of atorvastatin as an anti-inflammatory treatment in Crohn’s disease. Br J Pharmacol 155:1085–1092. doi:10.1038/bjp.2008.369
Hogue JC, Lamarche B, Tremblay AJ, Bergeron J, Gagne C, Couture P (2008) Differential effect of atorvastatin and fenofibrate on plasma oxidized low-density lipoprotein, inflammation markers, and cell adhesion molecules in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Metabolism 57:380–386. doi:10.1016/j.metabol.2007.10.014
Gross GH (1977) A technique for sustained synchronization of hamster estrous cycles by hormonal means. Horm Behav 9:23–31
Vernon MW, Wilson EA (1985) Studies on the surgical induction of endometriosis in the rat. Fertil Steril 44:684–694
Birnbaum Y, Lin Y, Ye Y, Merla R, Perez-Polo JR, Uretsky BF (2008) Pretreatment with high-dose statin, but not low-dose statin, ezetimibe, or the combination of low-dose statin and ezetimibe, limits infarct size in the rat. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol Ther 13(1):72–79. doi:10.1177/1074248407312839
Dogan E, Saygili U, Posaci C, Tuna B, Caliskan S, Altunyurt S, Saatli B (2004) Regression of endometrial explants in rats treated with the cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor rofecoxib. Fertil Steril 82(Suppl 3):1115–1120
Porreca F, Mosberg HI, Hurst R, Hruby VJ, Burks TF (1984) Roles of mu, delta and kappa opioid receptors in spinal and supraspinal mediation of gastrointestinal transit effects and hot-plate analgesia in the mouse. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 230(2):341–348
Forster MJ, Lal H (1999) Estimating age-related changes in psychomotor function: influence of practice and of level of caloric intake in different genotypes. Neurobiol Aging 20(2):167–176
Yucel A, Aydogan MS, Parlakpinar H, Erdogan MA, Kurt A, Ucar M, Durmus M (2012) Effects of propofol and dexmedetomidine on motor coordination and analgesia: a comparative analysis. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther 50(9):678–682. doi:10.5414/CP201696
Simsek Y, Celik O, Karaer A, Gul M, Yılmaz E, Koc O, Colak C, Zengin S, Aydin NE (2012) Therapeutic efficiency of Atosiban, an oxytocin receptor blocking agent in the treatment of experimental endometriosis. Arch Gynecol Obstet 286(3):777–783. doi:10.1007/s00404-012-2390-7
Kianpour M, Nematbakhsh M, Ahmadi SM (2012) C-reactive protein of serum and peritoneal fluid in endometriosis. Iran J Nurs Midwifery Res 17(2 Suppl 1):S115–S119
Lermann J, Mueller A, Körber F, Oppelt P, Beckmann MW, Dittrich R, Renner SP (2010) Evaluation of high-sensitivity C-reactive protein in comparison with C-reactive protein as biochemical serum markers in women with endometriosis. Fertil Steril. 93(7):21–2129. doi:10.1016/j.fertnstert.2009.01.072
Xavier P, Belo L, Beires J, Rebelo I, Martinez-de-Oliveira J, Lunet N, Barros H (2006) Serum levels of VEGF and TNF-alpha and their association with C-reactive protein in patients with endometriosis. Arch Gynecol Obstet 273(4):227–231
Jialal I, Devaraj S, Venugopal SK (2004) C-reactive protein: risk marker or mediator in atherothrombosis? Hypertension 44:6–11
Scholl B, Bersinger NA, Kuhn A, Mueller MD (2009) Correlation between symptoms of pain and peritoneal fluid inflammatory cytokine concentrations in endometriosis. Gynecol Endocrinol 25(11):701–706. doi:10.3109/09513590903159680
Lee GH, Choi YM, Kim SH, Hong MA, Oh ST, Lim YT, Moon SY (2008) Association of tumor necrosis factor-{alpha} gene polymorphisms with advanced stage endometriosis. Hum Reprod 23(4):977–981. doi:10.1093/humrep/den016
Eisermann J, Gast MJ, Pineda J, Odem RR, Collins JL (1988) Tumor necrosis factor in peritoneal fluid of women undergoing laparoscopic surgery. Fertil Steril 50(4):573–579
Iwabe T, Harada T, Terakawa N (2002) Role of cytokines in endometriosis-associated infertility. Gynecol Obstet Invest 53(Suppl 1):19–25
Oktem M, Esinler I, Eroglu D, Haberal N, Bayraktar N, Zeyneloglu HB (2007) High-dose atorvastatin causes regression of endometriotic implants: a rat model. Hum Reprod 22(5):1474–1480
Rodriguez AL, Wojcik BM, Wrobleski SK, Myers DD Jr, Wakefield TW, Diaz JA (2012) Statins, inflammation and deep vein thrombosis: a systematic review. J Thromb Thrombolysis 33(4):371–382. doi:10.1007/s11239-012-0687-9
Garcia GG, Miranda HF, Noriega V, Sierralta F, Olavarría L, Zepeda RJ, Prieto J (2011) Antinociception induced by atorvastatin in different pain models. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 100(1):125–129. doi:10.1016/j.pbb.2011.08.007
Santodomingo-Garzón T, Cunha TM, Verri WA Jr, Valério DA, Parada CA, Poole S, Ferreira SH, Cunha FQ (2006) Atorvastatin inhibits inflammatory hypernociception. Br J Pharmacol 149(1):14–22
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Simsek, Y., Gul, M., Yilmaz, E. et al. Atorvastatin exerts anti-nociceptive activity and decreases serum levels of high-sensitivity C-reactive protein and tumor necrosis factor-α in a rat endometriosis model. Arch Gynecol Obstet 290, 999–1006 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00404-014-3295-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00404-014-3295-4