Abstract
Objective
To investigate the value of spatiotemporal image correlation (STIC) technique in the ventricular septal defect diagnosis.
Methods
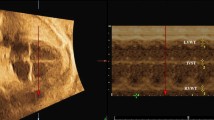
A total of 1,163 fetuses were enrolled in this study, diagnosed by fetal echocardiography and analyzed by STIC technique. We obtained effective STIC volumes from the fetus according to the Goncalves’ report, and judged fetal cardiac structure from STIC volume information again with a double-blind method. Another echocardiography was obtained during neonatal or infant period as follow-up.
Results
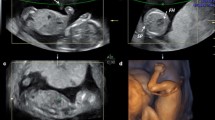
(1) As much as 1,062 cases were diagnosed to have normal fetal heart by fetal echocardiography, 43 cases had congenital heart disease without VSD, and 58 cases had VSD [21 cases (36.2%) were simple VSD and 37 cases (63.8%)were VSD with other heart malformation]. (2) Three fetal VSD cases (0.26%) were missed and one normal case was diagnosed as VSD after two-dimensional (2D) echocardiography. STIC technique corrected the diagnosis for two cases: one case of VSD after fetal 2D echocardiography was confirmed to be normal with STIC and neonatal heart examination; one case that was diagnosed as normal by fetal 2D echocardiography was confirmed to have VSD with STIC and neonatal heart examination.
Conclusions
The special value of STIC technique in the diagnosis of VSD had been confirmed by this study, and it had been proved as the best additional method to fetal echocardiography.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Came E, Stoll M, Clementi M (2001) Evaluation of prenatal diagnosis of congenital heart diseases by ultrasound: experience from 20 European registries. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 17:386–391
Paladini D, Palmieri S, Lamberti A et al (2000) Characterization and natural history of ventricular septal defects in the fetus. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 16:118–122
Benacerraf BR, Sanders SP (1990) Fetal echocardiography. Radiol Clin North Am 28:131–147
Li H, Wei J, Ma Y et al (2005) Prenatal diagnosis of congenital fetal heart abnormalities and clinical analysis. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B 6:903–906
Allan LD (1994) Fetal congenital heart disease: diagnosis and management. Curr Opin Obstet Gynecol 6:45–49
Rizzo G, Capponi A, Vendola M et al (2008) Role of tomographic ultrasound imaging with spatiotemporal image correlation for identifying fetal ventricular septal defects. J Ultrasound Med 27:1071–1075
DeVore GR, Falkensammer P, Sklansky MS et al (2003) Spatio-temporal image correlation (STIC): new technology for evaluation of the fetal heart. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 22:380–387
Shih JC, Chen CP (2005) Spatio-temporal image correlation (STIC): innovative 3D/4D technique for illustrating unique and independent information and diagnosing complex congenital heart diseases. Croat Med J 46:812–820
Gonçalves LF, Lee W, Espinoza J et al (2006) Examination of the fetal heart by four-dimensional (4D) ultrasound with spatio-temporal image correlation (STIC). Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 27:336–348
Yagel S, Benachi A, Bonnet D et al (2006) Rendering in fetal cardiac scanning: the intracardiac septa and the coronal atrioventricular valve planes. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 28:266–274
Li H, Meng T, Shang T et al (2007) Fetal heart screening in twins for congenital heart malformation. Chin Med J 120:1391–1394
Goncalves LF, Lee W, Chaiworaponsa T et al (2003) Four-dimensional ultrasonography of the fetal heart with spatiotemporal image correlation. Am J Obstet Gynecol 189:1792–1802
Espinoza J, Hassan SS, Gotsch F et al (2007) A systematic approach to the use of the multiplanar display in evaluation of abnormal vascular connections to the fetal heart using 4-dimensional ultrasonography. J Ultrasound Med 26:1461–1467
Espinoza J, Romero R, Kusanovic JP et al (2007) The role of the sagittal view of the ductal arch in identification of fetuses with conotruncal anomalies using 4-dimensional ultrasonography. J Ultrasound Med 26:1181–1188
Wanitpongpan P, Kanagawa T, Kinugasa Y et al (2008) Spatio-temporal image correlation (STIC) used by general obstetricians is marginally clinically effective compared to 2D fetal echocardiography scanning by experts. Prenat Diagn 28:923–928
Goncalves LF, Romero R, Espinoza J et al (2004) Four-dimensional ultrasonography of the fetal heart using color Doppler spatiotemporal image correlation. J Ultrasound Med 23:473–481
Chaoui R, Hoffmann J, Heling KS (2004) Three-dimensional (3D) and 4D color Doppler fetal echocardiography using spatio-temporal image correlation (STIC). Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 23:535–545
Yagel S, Valsky DV, Messing B (2005) Detailed assessment of fetal ventricular septal defect with 4D color Doppler ultrasound using spatio-temporal image correlation technology. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 25:97–98
Lee W, Goncalves LF, Espinoza J et al (2005) Inversion mode: a new volume analysis tool for 3-dimensional ultrasonography. J Ultrasound Med 24:201–207
Ghi T, Cera E, Segata M et al (2005) Inversion mode spatio-temporal image correlation (STIC) echocardiography in three-dimensional rendering of fetal ventricular septal defects. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 26:679–686
Acknowledgments
The study was supported by fundings from the Chinese National Key Technologies R&D Program, No. 2006BAI05A04. The name of the project is Research of prenatal imaging screening and new diagnostic technologies for major fetal structural anomalies. Many thanks are due to our colleagues in the ultrasound department and obstetrical department.
Conflict of interest statement
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dan-dan, W., Xiao-peng, D., Wei, C. et al. The value of spatiotemporal image correlation technique in the diagnosis of fetal ventricular septal defect. Arch Gynecol Obstet 283, 965–969 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00404-010-1493-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00404-010-1493-2