Abstract
Objective
To compare the efficacy and side effects of 0.2 mg methyl-ergometrine IM, 400 μg misoprostol sublingual and 125 μg 15 methyl PGF2α IM in active management of third stage of labor.
Method
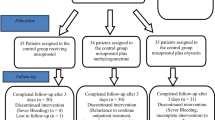
Two hundred low risk pregnant women with induced or spontaneous labor were randomized to receive either 400 μg misoprostol sublingually or 0.2 mg methyl-ergometrine intramuscularly or 125 μg 15-methyl PGF2α intramuscularly, after the delivery of anterior shoulder of baby. The main outcome measures were: blood loss more than 500 ml, need for additional oxytoxic drug, change in hemoglobin level and side effects due to drugs.
Results
The median estimated blood loss, blood loss more than 500 ml, need for additional oxytocic drug and change in hemoglobin levels were similar in all three groups. The significant side effects in the misoprostol group were shivering, pyrexia (temperature > 38°C) and vomiting, which were self-limiting. Diarrhea was significantly more in the 15 methyl PGF2α group. Three women in methyl-ergometrine group underwent manual removal of placenta. One woman in misoprostol group received blood transfusion.
Conclusion
Sublingual misoprostol appears to be as effective as intramuscular methyl-ergometrine and intramuscular 15-methyl PGF2α in the prevention of postpartum hemorrhage. It can be a good alternative in resource poor setting.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
World Health Organisation (1998) Postpartum care of the mother and the newborn: a practical guide. Safe Motherhood Unit WHO, Geneva
Prendiville WJ, Elbourne D, McDonald S (2000) Active versus expectant management in the third stage of labour. Cochrane Database Syst Rev (3):CD000007
World Health Organisation (1989) The prevention and management of postpartum hemorrhage: report of a technical working group. Safe Motherhood Unit WHO, Geneva
Hogerzeil HV, Waker GJA (1996) Instability of methylergometrine in tropical climate: an overview. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 69:25–29. doi:10.1016/0301-2115(95)02530-8
Tang OS, Chan CC, Kan AS, Ho PC (2005) A prospective randomized comparison of sublingual and oral misoprostol when combined with mifepristone for medical abortion at 12–20 weeks gestation. Hum Reprod 20(11):3062–3066. doi:10.1093/humrep/dei196
Souza AS, Amorim MM, Feitosa FE (2008) Comparison of sublingual versus vaginal misoprostol for the induction of labour: a systematic review. BJOG 115(11):1340–1349. doi:10.1111/j.1471-0528.2008.01872.x
El-Refaey H, O’Brien P, Morafa W, Walder J, Rodeck C (1997) Use of oral misoprostol in the prevention of postpartum haemorrhage. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 104(3):336–339
Hofmeyr GJ, Nikodem VC, de Jager M, Gelbart BR (1998) A randomised placebo controlled trial of oral misoprostol in the third stage of labour. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 105(9):971–975
Kundodyiwa TW, Majoko F, Rusakaniko S (2001) Misoprostol versus oxytocin in the third stage of labor. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 75(3):235–241. doi:10.1016/S0020-7292(01)00498-2
Amant F, Spitz B, Timmerman D, Corremans A, Van Assche FA (1999) Misoprostol compared with methylergometrine for the prevention of postpartum haemorrhage: a double-blind randomised trial. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 106(10):1066–1070
Joy SD, Sanchez-Ramos L, Kaunitz AM (2003) Misoprostol use in third stage of labor. Int J Obstet Gynecol 82:143–152. doi:10.1016/S0020-7292(03)00146-2
Gulmezoglu AM, Forna F Villar J, Hofmeyr GJ (2007) Prostaglandins for prevention of poatpartum hemorrhage. Cochrane Database Syst Rev (3):CD 000494
Garg P, Batra S, Gandhi G (2005) Oral misoprostol versus injectable methylergometrine in management of the third stage of labor. Int J Gynecol Obstet 91(2):160–161
Enakpene CA, Morhason-Bello IO, Enakpene EO, Arowojolu AO, Omigbodun AO (2007) Oral misoprostol for the prevention of primary post-partum hemorrhage during third stage of labor. J Obstet Gynaecol Res 33(6):810–817. doi:10.1111/j.1447-0756.2007.00661.x
Vimala N, Mittal S, Kumar S, Dadhwal V, Mehta S (2004) Sublingual misoprostol versus methylergometrine for active management of the third stage of labor. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 87(1):1–5. doi:10.1016/j.ijgo.2004.05.016
Vimala N, Mittal S, Kumar S (2006) Sublingual misoprostol versus oxytocin infusion to reduce blood loss at cesarean section. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 92(2):106–110. doi:10.1016/j.ijgo.2005.10.008
Hoj L, Cardoso P, Nielsen BB, Hvidman L, Nielsen J, Aaby P (2005) Effect of sublingual misoprostol on severe postpartum haemorrhage in a primary health centre in Guinea-Bissau: randomised double blind clinical trial. BMJ 331(7519):723. doi:10.1136/bmj.331.7519.723
Chhabra S, Tickoo C (2008) Low-dose sublingual misoprostol versus methylergometrine for active management of the third stage of labor. J Obstet Gynaecol Res 34(5):820–823. doi:10.1111/j.1447-0756.2008.00843.x
Lam H, Tang OS, Lee CP, Ho PC (2004) A pilot-randomized comparison of sublingual misoprostol with syntometrine on the blood loss in third stage of labor. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 83(7):647–650. doi:10.1111/j.0001-6349.2004.00572.x
Bais J, Eskes M, Pel M, Bonsel G, Bleker O (2004) Postpartum haemorrhage in nulliparous women: incidence and risk factors in low and high risk women. A Dutch population-based cohort study on standard (≥ 500 ml) and severe (≥ 1,000 ml) postpartum haemorrhage. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 115(2):166–172
Singh N, Singh U (2005) Methylergometrine and carboprost tromethamine prophylaxis for postpartum hemorrhage. J Obstet Gynaecol India 55(4):325–328
Nagaria T, Ekka M (2006) Intramuscular PGF Fα 125μg intramuscular versus intravenous methylergometrine 0.2 mg in active management of third stage of labor. J Obstet Gynaecol India 56(5):396–398
Abdel-Aleem H, Abol-Oyoun EM, Moustafa SA, Kamel HS, Abdel-Wahab HA (1993) Carboprost trometamol in the management of the third stage of labor. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 42(3):247–250. doi:10.1016/0020-7292(93)90219-M
Kushtagi P, Verghese LM (2006) Evaluation of two uterotonics drug in the management of the third stage of labor. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 94:47–48. doi:10.1016/j.ijgo.2006.04.011
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vaid, A., Dadhwal, V., Mittal, S. et al. A randomized controlled trial of prophylactic sublingual misoprostol versus intramuscular methyl-ergometrine versus intramuscular 15-methyl PGF2α in active management of third stage of labor. Arch Gynecol Obstet 280, 893–897 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00404-009-1019-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00404-009-1019-y