Abstract
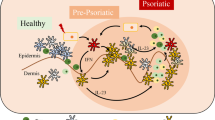
In psoriasis, leukocytes that infiltrate skin lesions have been shown to be involved in the pathogenesis of this disease. Previous investigations reporting the presence of CXCR3+ T lymphocytes in psoriatic lesional skin have suggested a role of this receptor in the recruitment of T cells into the lesion. The purpose of this study was to quantify the mRNA levels of CXCR3 and to perform a systematic analysis of the cell populations that express CXCR3 in human lesional and non-lesional psoriatic biopsies. We showed by real-time reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction that the mRNA levels of CXCR3 and its ligands, CXCL9-11, were significantly elevated in psoriatic lesions, as compared to non-lesional samples. Serial cryostat sections of psoriasis skin biopsies were evaluated by immunohistochemistry. The number of CXCR3+ cells was low in non-lesional tissues. Quantitative image analysis demonstrated significant increases in the number of both epidermal and dermal CXCR3+ cells in lesional compared with non-lesional biopsies. The majority of CXCR3+ cells were located in the dermis of the lesional skin and 74% were demonstrated to be CD3+ T lymphocytes. A small number of CXCR3+ cells were CD68+ myeloid cells. In addition, we found that nearly all BDCA-2+ plasmacytoid dendritic cells in the psoriatic biopsies were CXCR3+. These findings support and extend prior reports suggesting the potential role for CXCR3 in the pathophysiology of plaque psoriasis, by mediating the recruitment of plasmacytoid dendritic cells and T cells into the developing lesions.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albanesi C, Scarponi C, Pallotta S, Daniele R, Bosisio D, Madonna S, Fortugno P, Gonzalvo-Feo S, Franssen JD, Parmentier M, De Pita O, Girolomoni G, Sozzani S (2009) Chemerin expression marks early psoriatic skin lesions and correlates with plasmacytoid dendritic cell recruitment. J Exp Med 206:249–258. doi:10.1084/jem.20080129
Berry K, Friedrich M, Kersey K, Stempien MJ, Wagner F, van Lier JJ, Sabat R, Wolk K (2004) Evaluation of T0906487, a CXCR3 antagonist, in a phase 2 psoriasis trial. In: Inflammation research association annual meeting
Bjerke JR, Krogh HK, Matre R (1978) Characterization of mononuclear cell infiltrates in psoriatic lesions. J Invest Dermatol 71:340–343. doi:10.1111/1523-1747.ep12529841
Bovenschen HJ, Seyger MM, Van de Kerkhof PC (2005) Plaque psoriasis vs atopic dermatitis and lichen planus: a comparison for lesional T-cell subsets, epidermal proliferation and differentiation. Br J Dermatol 153:72–78. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.2005.06538.x
Boyman O, Hefti HP, Conrad C, Nickoloff BJ, Suter M, Nestle FO (2004) Spontaneous development of psoriasis in a new animal model shows an essential role for resident T cells and tumor necrosis factor-alpha. J Exp Med 199:731–736. doi:10.1084/jem.20031482
Chan JR, Blumenschein W, Murphy E, Diveu C, Wiekowski M, Abbondanzo S, Lucian L, Geissler R, Brodie S, Kimball AB, Gorman DM, Smith K, de Waal Malefyt R, Kastelein RA, McClanahan TK, Bowman EP (2006) IL-23 stimulates epidermal hyperplasia via TNF and IL-20R2-dependent mechanisms with implications for psoriasis pathogenesis. J Exp Med 203:2577–2587. doi:10.1084/jem.20060244
Conrad C, Boyman O, Tonel G, Tun-Kyi A, Laggner U, de Fougerolles A, Kotelianski V, Gardner H, Nestle FO (2007) Alpha 1 beta 1 integrin is crucial for accumulation of epidermal T cells and the development of psoriasis. Nat Med 13:836–842. doi:10.1038/nm1605
Cox MA, Jenh CH, Gonsiorek W, Fine J, Narula SK, Zavodny PJ, Hipkin RW (2001) Human interferon-inducible 10-kDa protein and human interferon-inducible T cell alpha chemoattractant are allotopic ligands for human CXCR3: differential binding to receptor states. Mol Pharmacol 59:707–715
Ellis CN, Fradin MS, Messana JM, Brown MD, Siegel MT, Hartley AH, Rocher LL, Wheeler S, Hamilton TA, Parish TG et al (1991) Cyclosporine for plaque-type psoriasis: results of a multidose, double-blind trial. N Engl J Med 324:277–284
Eriksen KW, Lovato P, Skov L, Krejsgaard T, Kaltoft K, Geisler C, Odum N (2005) Increased sensitivity to interferon-alpha in psoriatic T cells. J Invest Dermatol 125:936–944
Flier J, Boorsma DM, van Beek PJ, Nieboer C, Stoof TJ, Willemze R, Tensen CP (2001) Differential expression of CXCR3 targeting chemokines CXCL10, CXCL9, and CXCL11 in different types of skin inflammation. J Pathol 194:398–405. doi:10.1002/1096-9896(200108)194:4<397::AID-PATH899>3.0.CO;2-S
Garcia-Lopez MA, Sanchez-Madrid F, Rodriguez-Frade JM, Mellado M, Acevedo A, Garcia MI, Albar JP, Martinez C, Marazuela M (2001) CXCR3 chemokine receptor distribution in normal and inflamed tissues: expression on activated lymphocytes, endothelial cells, and dendritic cells. Lab Invest 81:409–418
Gilhar A, David M, Ullmann Y, Berkutski T, Kalish RS (1997) T-lymphocyte dependence of psoriatic pathology in human psoriatic skin grafted to SCID mice. J Invest Dermatol 109:283–288. doi:10.1111/1523-1747.ep12335758
Gilliet M, Conrad C, Geiges M, Cozzio A, Thurlimann W, Burg G, Nestle FO, Dummer R (2004) Psoriasis triggered by toll-like receptor 7 agonist imiquimod in the presence of dermal plasmacytoid dendritic cell precursors. Arch Dermatol 140:1490–1495. doi:10.1001/archderm.140.12.1490
Goedkoop AY, de Rie MA, Teunissen MB, Picavet DI, van der Hall PO, Bos JD, Tak PP, Kraan MC (2005) Digital image analysis for the evaluation of the inflammatory infiltrate in psoriasis. Arch Dermatol Res 297:51–59. doi:10.1007/s00403-005-0578-4
Gottlieb AB, Luster AD, Posnett DN, Carter DM (1988) Detection of a gamma interferon-induced protein IP-10 in psoriatic plaques. J Exp Med 168:941–948. doi:10.1084/jem.168.3.941
Gottlieb AB (2005) Psoriasis: emerging therapeutic strategies. Nat Rev Drug Discov 42:19–34. doi:10.1038/nrd1607
Gottlieb SL, Gilleaudeau P, Johnson R, Estes L, Woodworth TG, Gottlieb AB, Krueger JG (1995) Response of psoriasis to a lymphocyte-selective toxin (DAB389IL-2) suggests a primary immune, but not keratinocyte, pathogenic basis. Nat Med 1:442–447. doi:10.1038/nm0595-442
Horuk R (2009) Chemokine receptor antagonists: overcoming developmental hurdles. Nat Rev Drug Discov 8:23–33. doi:10.1038/nrd2734
Iijima W, Ohtani H, Nakayama T, Sugawara Y, Sato E, Nagura H, Yoshie O, Sasano T (2003) Infiltrating CD8+ T cells in oral lichen planus predominantly express CCR5 and CXCR3 and carry respective chemokine ligands RANTES/CCL5 and IP-10/CXCL10 in their cytolytic granules: a potential self-recruiting mechanism. Am J Pathol 163:261–268
Jones D, Benjamin RJ, Shahsafaei A, Dorfman DM (2000) The chemokine receptor CXCR3 is expressed in a subset of B-cell lymphomas and is a marker of B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 95:627–632
Kallinich T, Schmidt S, Hamelmann E, Fischer A, Qin S, Luttmann W, Virchow JC, Kroczek RA (2005) Chemokine-receptor expression on T cells in lung compartments of challenged asthmatic patients. Clin Exp Allergy 35:26–33. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2222.2004.02132.x
Kazazi F, Mathijs JM, Foley P, Cunningham AL (1989) Variations in CD4 expression by human monocytes and macrophages and their relationships to infection with the human immunodeficiency virus. J Gen Virol 70(Pt 10):2661–2672. doi:10.1099/0022-1317-70-10-2661
Kohrgruber N, Groger M, Meraner P, Kriehuber E, Petzelbauer P, Brandt S, Stingl G, Rot A, Maurer D (2004) Plasmacytoid dendritic cell recruitment by immobilized CXCR3 ligands. J Immunol 173:6592–6602
Kunkel EJ, Boisvert J, Murphy K, Vierra MA, Genovese MC, Wardlaw AJ, Greenberg HB, Hodge MR, Wu L, Butcher EC, Campbell JJ (2002) Expression of the chemokine receptors CCR4, CCR5, and CXCR3 by human tissue-infiltrating lymphocytes. Am J Pathol 160:347–355
Lande R, Gregorio J, Facchinetti V, Chatterjee B, Wang YH, Homey B, Cao W, Su B, Nestle FO, Zal T, Mellman I, Schroder JM, Liu YJ, Gilliet M (2007) Plasmacytoid dendritic cells sense self-DNA coupled with antimicrobial peptide. Nature 449:564–569. doi:10.1038/nature06116
Langrish CL, Chen Y, Blumenschein WM, Mattson J, Basham B, Sedgwick JD, McClanahan T, Kastelein RA, Cua DJ (2005) IL-23 drives a pathogenic T cell population that induces autoimmune inflammation. J Exp Med 201:233–240. doi:10.1084/jem.20041257
Leigh IM, Navsaria H, Purkis PE, McKay IA, Bowden PE, Riddle PN (1995) Keratins (K16 and K17) as markers of keratinocyte hyperproliferation in psoriasis in vivo and in vitro. Br J Dermatol 133:501–511. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.1995.tb02696.x
Li J, Li D, Tan Z (2004) The expression of interleukin-17, interferon-gamma, and macrophage inflammatory protein-3 alpha mRNA in patients with psoriasis vulgaris. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technol Med Sci 24:294–296
Lowes MA, Chamian F, Abello MV, Fuentes-Duculan J, Lin SL, Nussbaum R, Novitskaya I, Carbonaro H, Cardinale I, Kikuchi T, Gilleaudeau P, Sullivan-Whalen M, Wittkowski KM, Papp K, Garovoy M, Dummer W, Steinman RM, Krueger JG (2005) Increase in TNF-alpha and inducible nitric oxide synthase-expressing dendritic cells in psoriasis and reduction with efalizumab (anti-CD11a). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:19057–19062. doi:10.1073/pnas.0509736102
Lowes MA, Kikuchi T, Fuentes-Duculan J, Cardinale I, Zaba LC, Haider AS, Bowman EP, Krueger JG (2008) Psoriasis vulgaris lesions contain discrete populations of Th1 and Th17 T cells. J Invest Dermatol 128:1207–1211. doi:10.1038/sj.jid.5701213
Meller S, Winterberg F, Gilliet M, Muller A, Lauceviciute I, Rieker J, Neumann NJ, Kubitza R, Gombert M, Bunemann E, Wiesner U, Franken-Kunkel P, Kanzler H, Dieu-Nosjean MC, Amara A, Ruzicka T, Lehmann P, Zlotnik A, Homey B (2005) Ultraviolet radiation-induced injury, chemokines, and leukocyte recruitment: an amplification cycle triggering cutaneous lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 52:1504–1516. doi:10.1002/art.21034
Muehlinghaus G, Cigliano L, Huehn S, Peddinghaus A, Leyendeckers H, Hauser AE, Hiepe F, Radbruch A, Arce S, Manz RA (2005) Regulation of CXCR3 and CXCR4 expression during terminal differentiation of memory B cells into plasma cells. Blood 105:3965–3971. doi:10.1182/blood-2004-08-2992
Nestle FO, Conrad C, Tun-Kyi A, Homey B, Gombert M, Boyman O, Burg G, Liu YJ, Gilliet M (2005) Plasmacytoid pre-dendritic cells initiate psoriasis through interferon-alpha production. J Exp Med 202:135–143. doi:10.1084/jem.20050500
Nickoloff BJ, Wrone-Smith T (1999) Injection of pre-psoriatic skin with CD4+ T cells induces psoriasis. Am J Pathol 155:145–158
Ocana E, Delgado-Perez L, Campos-Caro A, Munoz J, Paz A, Franco R, Brieva JA (2007) The prognostic role of CXCR3 expression by chronic lymphocytic leukemia B cells. Haematologica 92:349–356. doi:10.3324/haematol.10649
Oppmann B, Lesley R, Blom B, Timans JC, Xu Y, Hunte B, Vega F, Yu N, Wang J, Singh K, Zonin F, Vaisberg E, Churakova T, Liu M, Gorman D, Wagner J, Zurawski S, Liu Y, Abrams JS, Moore KW, Rennick D, de Waal-Malefyt R, Hannum C, Bazan JF, Kastelein RA (2000) Novel p19 protein engages IL-12p40 to form a cytokine, IL-23, with biological activities similar as well as distinct from IL-12. Immunity 13:715–725. doi:10.1016/S1074-7613(00)00070-4
Piskin G, Sylva-Steenland RM, Bos JD, Teunissen MB (2006) In vitro and in situ expression of IL-23 by keratinocytes in healthy skin and psoriasis lesions: enhanced expression in psoriatic skin. J Immunol 176:1908–1915
Prinz JC, Gross B, Vollmer S, Trommler P, Strobel I, Meurer M, Plewig G (1994) T cell clones from psoriasis skin lesions can promote keratinocyte proliferation in vitro via secreted products. Eur J Immunol 24:593–598. doi:10.1002/eji.1830240315
Qin S, Rottman JB, Myers P, Kassam N, Weinblatt M, Loetscher M, Koch AE, Moser B, Mackay CR (1998) The chemokine receptors CXCR3 and CCR5 mark subsets of T cells associated with certain inflammatory reactions. J Clin Invest 101:746–754. doi:10.1172/JCI1422
Rottman JB, Smith TL, Ganley KG, Kikuchi T, Krueger JG (2001) Potential role of the chemokine receptors CXCR3, CCR4, and the integrin alpha Ebeta7 in the pathogenesis of psoriasis vulgaris. Lab Invest 81:335–347
Schmid P, Itin P, Cox D, McMaster GK, Horisberger MA (1994) The type I interferon system is locally activated in psoriatic lesions. J Interferon Res 14:229–234
Skrzeczynska-Moncznik J, Wawro K, Stefanska A, Oleszycka E, Kulig P, Zabel BA, Sulkowski M, Kapinska-Mrowiecka M, Czubak-Macugowska M, Butcher EC, Cichy J (2009) Potential role of chemerin in recruitment of plasmacytoid dendritic cells to diseased skin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 380:323–327. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2009.01.071
Teraki Y, Miyake A, Takebayashi R, Shiohara T (2004) Homing receptor and chemokine receptor on intraepidermal T cells in psoriasis vulgaris. Clin Exp Dermatol 29:658–663. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2230.2004.01638.x
Teunissen MB, Koomen CW, de Waal Malefyt R, Wierenga EA, Bos JD (1998) Interleukin-17 and interferon-gamma synergize in the enhancement of proinflammatory cytokine production by human keratinocytes. J Invest Dermatol 111:645–649. doi:10.1046/j.1523-1747.1998.00347.x
Thomas SY, Banerji A, Medoff BD, Lilly CM, Luster AD (2007) Multiple chemokine receptors, including CCR6 and CXCR3, regulate antigen-induced T cell homing to the human asthmatic airway. J Immunol 179:1901–1912
van der Fits L, van der Wel LI, Laman JD, Prens EP, Verschuren MC (2004) In psoriasis lesional skin the type I interferon signaling pathway is activated, whereas interferon-alpha sensitivity is unaltered. J Invest Dermatol 122:51–60. doi:10.1046/j.0022-202X.2003.22113.x
Vanbervliet B, Bendriss-Vermare N, Massacrier C, Homey B, de Bouteiller O, Briere F, Trinchieri G, Caux C (2003) The inducible CXCR3 ligands control plasmacytoid dendritic cell responsiveness to the constitutive chemokine stromal cell-derived factor 1 (SDF-1)/CXCL12. J Exp Med 198:823–830. doi:10.1084/jem.20020437
Wenzel J, Uerlich M, Haller O, Bieber T, Tueting T (2005) Enhanced type I interferon signaling and recruitment of chemokine receptor CXCR3-expressing lymphocytes into the skin following treatment with the TLR7-agonist imiquimod. J Cutan Pathol 32:257–262. doi:10.1111/j.0303-6987.2005.00297.x
Wenzel J, Wiechert A, Merkel C, Bieber T, Tuting T (2007) IP10/CXCL10–CXCR3 interaction: a potential self-recruiting mechanism for cytotoxic lymphocytes in lichen Sclerosus atrophicus. Acta Derm Venereol 87:112–117. doi:10.2340/00015555-0194
Wenzel J, Peters B, Zahn S, Birth M, Hofmann K, Kusters D, Tomiuk S, Baron JM, Merk HF, Mauch C, Krieg T, Bieber T, Tuting T, Bosio A (2008) Gene expression profiling of lichen planus reflects CXCL9+-mediated inflammation and distinguishes this disease from atopic dermatitis and psoriasis. J Invest Dermatol 128:67–78. doi:10.1038/sj.jid.5700945
Wijtmans M, Verzijl D, Leurs R, de Esch IJ, Smit MJ (2008) Towards small-molecule CXCR3 ligands with clinical potential. Chem Med Chem 3:861–872. doi:10.1002/cmdc.200700365
Wrone-Smith T, Nickoloff BJ (1996) Dermal injection of immunocytes induces psoriasis. J Clin Invest 98:1878–1887. doi:10.1172/JCI118989
Yamamoto J, Adachi Y, Onoue Y, Adachi YS, Okabe Y, Itazawa T, Toyoda M, Seki T, Morohashi M, Matsushima K, Miyawaki T (2000) Differential expression of the chemokine receptors by the Th1- and Th2-type effector populations within circulating CD4+ T cells. J Leukoc Biol 68:568–574
Acknowledgment
We thank Dr. Jason Simon for sharing with us the microarray data of the skin biopsies, which led to the subsequent RT-PCR analysis described in this report. We are grateful to Dr. Daniel Lundell for his critical reading and comments to this manuscript.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, SC., de Groot, M., Kinsley, D. et al. Expression of chemokine receptor CXCR3 by lymphocytes and plasmacytoid dendritic cells in human psoriatic lesions. Arch Dermatol Res 302, 113–123 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00403-009-0966-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00403-009-0966-2