Abstract
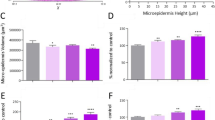
The family of human epidermal growth factor receptors (EGFR, HER2–4) exerts key functions in normal and malignant epithelial cells. Both EGFR and HER2 are valuable targets for anti-cancer drugs by interfering with ligand binding, receptor dimerization, or tyrosine kinase activity. A similar therapeutic strategy has been advocated for chronic psoriasis since plaque lesions overexpress EGFR and its ligands. Our aim was to characterize EGFR/HER2 protein expression in skin cultures and to evaluate the effects of tyrosine kinase inhibitors on epidermal outgrowth, morphology, and EGFR activation. Human skin explants were established on cell-free dermis and cultured at the air–liquid interface. The impact of small-molecule HER inhibitors on outgrowth was assayed by fluorescence-based image analysis and histometry. Effects of a dual EGFR/HER2 kinase inhibitor, PKI166, on neoepidermis were studied by immunohistochemistry and Western blot. Receptor immunostaining showed in vivo-like distributions with highest EGFR intensity in the proliferative layers whereas HER2 was mainly expressed by suprabasal keratinocytes. Reepithelialization was associated with EGFR autophosphorylation irrespective of exogenous ligand stimulation. PKI166 inhibited neoepidermal EGFR activation, keratinocyte proliferation, and outgrowth from normal and psoriatic skin explants. The rate of epidermalization in presence of other HER inhibitors varied suggesting that drug specificity, potency, and reversibility determine the dynamic outcome. Overall, agents predominantly targeting EGFR kinase were more efficient inhibitors of epidermal regeneration than an HER2-selective drug. The study illustrates the usefulness of a dynamic skin model and emphasizes the potential of HER-directed approaches to control epidermal growth in hyperproliferative skin disorders.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albanell J, Rojo F, Averbuch S, Feyereislova A, Mascaro JM, Herbst R, LoRusso P, Rischin D, Sauleda S, Gee J, Nicholson RI, Baselga J (2002) Pharmacodynamic studies of the epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitor ZD1839 in skin from cancer patients: histopathologic and molecular consequences of receptor inhibition. J Clin Oncol 20:110–124
Barbacci EG, Pustilnik LR, Rossi AM, Emerson E, Miller PE, Boscoe BP, Cox ED, Iwata KK, Jani JP, Provoncha K, Kath JC, Liu Z, Moyer JD (2003) The biological and biochemical effects of CP-654577, a selective erbB2 kinase inhibitor, on human breast cancer cells. Cancer Res 63:4450–4459
Baselga J (2002) Why the epidermal growth factor receptor? The rationale for cancer therapy. Oncologist 7(Suppl 4):2–8
Ben-Bassat H, Vardi DV, Gazit A, Klaus SN, Chaouat M, Hartzstark Z, Levitzki A (1995) Tyrphostins suppress the growth of psoriatic keratinocytes. Exp Dermatol 4:82–88
Ben-Bassat H, Klein BY (2000) Inhibitors of tyrosine kinases in the treatment of psoriasis. Curr Pharm Des 6:933–942
Bernard BA, Robinson SM, Vandaele S, Mansbridge JN, Darmon M (1985) Abnormal maturation pathway of keratinocytes in psoriatic skin. Br J Dermatol 112:647–653
Bertrand R, Solary E, O’Connor P, Kohn KW, Pommier Y (1994) Induction of a common pathway of apoptosis by staurosporine. Exp Cell Res 211:314–321
Bhushan M, McLaughlin B, Weiss JB, Griffiths CE (1999) Levels of endothelial cell stimulating angiogenesis factor and vascular endothelial growth factor are elevated in psoriasis. Br J Dermatol 141:1054–1060
Cook PW, Pittelkow MR, Keeble WW, Graves-Deal R, Coffey RJ Jr, Shipley GD (1992) Amphiregulin messenger RNA is elevated in psoriatic epidermis and gastrointestinal carcinomas. Cancer Res 52:3224–3227
Detmar M, Brown LF, Claffey KP, Yeo KT, Kocher O, Jackman RW, Berse B, Dvorak HF (1994) Overexpression of vascular permeability factor/vascular endothelial growth factor and its receptors in psoriasis. J Exp Med 180:1141–1146
Elder JT, Fisher GJ, Lindquist PB, Bennett GL, Pittelkow MR, Coffey RJ Jr, Ellingsworth L, Derynck R, Voorhees JJ (1989) Overexpression of transforming growth factor alpha in psoriatic epidermis. Science 243:811–814
Forsberg S, Saarialho-Kere U, Rollman O (2006) Comparison of growth-inhibitory agents by fluorescence imaging of human skin re-epithelialization in vitro. Acta Derm Venereol 86:292–299
Gottlieb AB, Chang CK, Posnett DN, Fanelli B, Tam JP (1988) Detection of transforming growth factor alpha in normal, malignant, and hyperproliferative human keratinocytes. J Exp Med 167:670–675
Hudson LG, McCawley LJ (1998) Contributions of the epidermal growth factor receptor to keratinocyte motility. Microsc Res Tech 43:444–455
Jiang CK, Magnaldo T, Ohtsuki M, Freedberg IM, Bernerd F, Blumenberg M (1993) Epidermal growth factor and transforming growth factor alpha specifically induce the activation- and hyperproliferation-associated keratins 6 and 16. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:6786–6790
Johnson I (1998) Fluorescent probes for living cells. Histochem J 30:123–140
Jost M, Class R, Kari C, Jensen PJ, Rodeck U (1999) A central role of Bcl-X(L) in the regulation of keratinocyte survival by autocrine EGFR ligands. J Invest Dermatol 112:443–449
King LE Jr, Gates RE, Stoscheck CM, Nanney LB (1990) Epidermal growth factor/transforming growth factor alpha receptors and psoriasis. J Invest Dermatol 95:10S–12S
Krahn G, Leiter U, Kaskel P, Udart M, Utikal J, Bezold G, Peter RU (2001) Coexpression patterns of EGFR, HER2, HER3 and HER4 in non-melanoma skin cancer. Eur J Cancer 37:251–259
Lee E, Jeon SH, Yi JY, Jin YJ, Son YS (2001) Calcipotriol inhibits autocrine phosphorylation of EGF receptor in a calcium-dependent manner, a possible mechanism for its inhibition of cell proliferation and stimulation of cell differentiation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 284:419–425
Lee MW, Seo CW, Kim SW, Yang HJ, Lee HW, Choi JH, Moon KC, Koh JK (2004) Cutaneous side effects in non-small cell lung cancer patients treated with Iressa (ZD1839), an inhibitor of epidermal growth factor. Acta Derm Venereol 84:23–26
Leigh IM, Navsaria H, Purkis PE, McKay IA, Bowden PE, Riddle PN (1995) Keratins (K16 and K17) as markers of keratinocyte hyperproliferation in psoriasis in vivo and in vitro. Br J Dermatol 133:501–511
Levitzki A, Gazit A (1995) Tyrosine kinase inhibition: an approach to drug development. Science 267:1782–1788
Lu H, Rollman O (2004) Fluorescence imaging of reepithelialization from skin explant cultures on acellular dermis. Wound Repair Regen 12:575–586
Mascia F, Mariani V, Girolomoni G, Pastore S (2003) Blockade of the EGF receptor induces a deranged chemokine expression in keratinocytes leading to enhanced skin inflammation. Am J Pathol 163:303–312
Maubec E, Duvillard P, Velasco V, Crickx B, Avril MF (2005) Immunohistochemical analysis of EGFR and HER-2 in patients with metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the skin. Anticancer Res 25:1205–1210
Mils V, Basset-Seguin N, Moles JP, Tesniere A, Leigh I, Guilhou JJ (1994) Comparative analysis of normal and psoriatic skin both in vivo and in vitro. Differentiation 58:77–86
Miyagawa S, Fujimoto H, Ko S, Hirota S, Kitamura Y (2002) Improvement of psoriasis during imatinib therapy in a patient with a metastatic gastrointestinal stromal tumour. Br J Dermatol 147:406–407
Nanney LB, McKanna JA, Stoscheck CM, Carpenter G, King LE (1984) Visualization of epidermal growth factor receptors in human epidermis. J Invest Dermatol 82:165–169
Nanney LB, Stoscheck CM, Magid M, King LE Jr (1986) Altered [125I]epidermal growth factor binding and receptor distribution in psoriasis. J Invest Dermatol 86:260–265
Peus D, Hamacher L, Pittelkow MR (1997) EGF-receptor tyrosine kinase inhibition induces keratinocyte growth arrest and terminal differentiation. J Invest Dermatol 109:751–756
Piepkorn M (1996) Overexpression of amphiregulin, a major autocrine growth factor for cultured human keratinocytes, in hyperproliferative skin diseases. Am J Dermatopathol 18:165–171
Piepkorn M, Pittelkow MR, Cook PW (1998) Autocrine regulation of keratinocytes: the emerging role of heparin-binding, epidermal growth factor-related growth factors. J Invest Dermatol 111:715–721
Piepkorn M, Predd H, Underwood R, Cook P (2003) Proliferation–differentiation relationships in the expression of heparin-binding epidermal growth factor-related factors and erbB receptors by normal and psoriatic human keratinocytes. Arch Dermatol Res 295:93–101
Pinheiro JC, Bates DM (2000) Mixed-effects models in S and S-PLUS. Springer, New York
Plowman GD, Culouscou JM, Whitney GS, Green JM, Carlton GW, Foy L, Neubauer MG, Shoyab M (1993) Ligand-specific activation of HER4/p180erbB4, a fourth member of the epidermal growth factor receptor family. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:1746–1750
Powell TJ, Ben-Bassat H, Klein BY, Chen H, Shenoy N, McCollough J, Narog B, Gazit A, Harzstark Z, Chaouat M, Levitzki R, Tang C, McMahon J, Shawver L, Levitzki A (1999) Growth inhibition of psoriatic keratinocytes by quinazoline tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Br J Dermatol 141:802–810
Press MF, Cordon-Cardo C, Slamon DJ (1990) Expression of the HER-2/neu proto-oncogene in normal human adult and fetal tissues. Oncogene 5:953–962
Prigent SA, Lemoine NR, Hughes CM, Plowman GD, Selden C, Gullick WJ (1992) Expression of the c-erbB-3 protein in normal human adult and fetal tissues. Oncogene 7:1273–1278
Regnier M, Asselineau D, Lenoir MC (1990) Human epidermis reconstructed on dermal substrates in vitro: an alternative to animals in skin pharmacology. Skin Pharmacol 3:70–85
Rikimaru K, Moles JP, Watt FM (1997) Correlation between hyperproliferation and suprabasal integrin expression in human epidermis reconstituted in culture. Exp Dermatol 6:214–221
Segaert S, Van Cutsem E (2005) Clinical signs, pathophysiology and management of skin toxicity during therapy with epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors. Ann Oncol 16:1425–1433
Slichenmyer WJ, Elliott WL, Fry DW (2001) CI-1033, a pan-erbB tyrosine kinase inhibitor. Semin Oncol 28:80–85
Srinivasan R, Poulsom R, Hurst HC, Gullick WJ (1998) Expression of the c-erbB-4/HER4 protein and mRNA in normal human fetal and adult tissues and in a survey of nine solid tumour types. J Pathol 185:236–245
Stoll SW, Kansra S, Peshick S, Fry DW, Leopold WR, Wiesen JF, Sibilia M, Zhang T, Werb Z, Derynck R, Wagner EF, Elder JT (2001) Differential utilization and localization of ErbB receptor tyrosine kinases in skin compared to normal and malignant keratinocytes. Neoplasia 3:339–350
Traxler P, Bold G, Buchdunger E, Caravatti G, Furet P, Manley P, O’Reilly T, Wood J, Zimmermann J (2001) Tyrosine kinase inhibitors: from rational design to clinical trials. Med Res Rev 21:499–512
Traxler P (2003) Tyrosine kinases as targets in cancer therapy—successes and failures. Expert Opin Ther Targets 7:215–234
Traxler P, Allegrini PR, Brandt R, Brueggen J, Cozens R, Fabbro D, Grosios K, Lane HA, McSheehy P, Mestan J, Meyer T, Tang C, Wartmann M, Wood J, Caravatti G (2004) AEE788: a dual family epidermal growth factor receptor/ErbB2 and vascular endothelial growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor with antitumor and antiangiogenic activity. Cancer Res 64:4931–4941
Varani J, Lateef H, Fay K, Elder JT (2005) Antagonism of epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase ameliorates the psoriatic phenotype in organ-cultured skin. Skin Pharmacol Physiol 18:123–131
Wakeling AE, Guy SP, Woodburn JR, Ashton SE, Curry BJ, Barker AJ, Gibson KH (2002) ZD1839 (Iressa): an orally active inhibitor of epidermal growth factor signaling with potential for cancer therapy. Cancer Res 62:5749–5754
Watanabe S, Wagatsuma K, Ichikawa E, Takahashi H (1991) Abnormal distribution of epidermal protein antigens in psoriatic epidermis. J Dermatol 18:143–151
Wierzbicka E, Tourani JM, Guillet G (2006) Improvement of psoriasis and cutaneous side-effects during tyrosine kinase inhibitor therapy for renal metastatic adenocarcinoma. A role for epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) inhibitors in psoriasis? Br J Dermatol 155:213–214
Wilgus TA, Matthies AM, Radek KA, Dovi JV, Burns AL, Shankar R, DiPietro LA (2005) Novel function for vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-1 on epidermal keratinocytes. Am J Pathol 167:1257–1266
Acknowledgments
We thank Inger Pihl-Lundin for skillful technical assistance and Lisa Wernroth at Uppsala Clinical Research Centre (UCR) for statistical expertise. The Department of Plastic Surgery, University Hospital, Uppsala, is acknowledged for supplying us with skin samples. Thanks are due to Pfizer, Novartis and AstraZeneca for generous supply of tyrosine kinase inhibitors. This study was supported by the Finsen Welander Foundation and the Swedish Psoriasis Association.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Forsberg, S., Östman, A. & Rollman, O. Regeneration of human epidermis on acellular dermis is impeded by small-molecule inhibitors of EGF receptor tyrosine kinase. Arch Dermatol Res 300, 505–516 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00403-008-0853-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00403-008-0853-2