Abstract
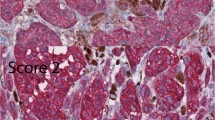
Survivin, a member of the inhibitors of apoptosis protein family, regulates both cellular proliferation and apoptotic cell death. While the human survivin gene is highly expressed in the developing fetus, in adults its expression is restricted to highly proliferating normal tissues and neoplastic tumors tissues. In the present study, we compared the expression of survivin in melanoma and benign melanocytic lesions such as junctional, compound, dermal, congenital, blue and spitz nevi. This analysis reveals a heterogeneous expression of survivin with respect to both the intensity, frequency and cellular localization. In junctional, compound and blue nevi, survivin was present in nuclear localization, whereas in spitz nevi survivin was detectable in the cytoplasm. In dermal and congenital nevi, survivin was present in both localizations with predominance of the nuclear compartment. Interestingly, this distribution was similar to that observed in primary melanoma; whereas in metastatic melanoma the predominance of the nuclear localization of survivin was lost. Our data demonstrate that although survivin is expressed in a large number of benign nevi, the balance between its cytoplasmic and nuclear expression was immensely heterogeneous between lesions with suspected different developmental origins.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kasof GM, Lu JJ, Liu D, Speer B, Mongan KN, Gomes BC, Lorenzi MV (2001) Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha Induces the Expression of DR6, a Member of the TNF Receptor Family, Through Activation of NF-KappaB. Oncogene 20(55):7965–7975
Ambrosini G, Adida C, Altieri DC (1997) A novel anti-apoptosis gene, Survivin, expressed in cancer and lymphoma. Nat Med 3(8):917–921
Koch CA, Vortmeyer AO, Diallo R, Poremba C, Giordano TJ, Sanders D, Bornstein SR, Chrousos GP, Pacak K (2002) Survivin: a novel neuroendocrine marker for pheochromocytoma. Eur J Endocrinol 146(3):381–388
Adida C, Haioun C, Gaulard P, Lepage E, Morel P, Briere J, Dombret H, Reyes F, Diebold J, Gisselbrecht C, Salles G, Altieri DC, Molina TJ (2000) Prognostic significance of survivin expression in diffuse large B-cell lymphomas. Blood 96(5):1921–1925
Grossman D, McNiff JM, Li F, Altieri DC (1999) Expression and targeting of the apoptosis inhibitor, survivin, in human melanoma. J Invest Dermatol 113(6):1076–1081
Grossman D, McNiff JM, Li F, Altieri DC (1999) Expression of the apoptosis Inhibitor, Survivin, in Nonmelanoma Skin Cancer and Gene Targeting in a keratinocyte cell line. lab invest 79(9):1121–1126
Bowen AR, Hanks AN, Allen SM, Alexander A, Diedrich MJ, Grossman D (2003) Apoptosis regulators and responses in human melanocytic and keratinocytic cells. J Invest Dermatol 120(1):48–55
Islam A, Kageyama H, Takada N, Kawamoto T, Takayasu H, Isogai E, Ohira M, Hashizume K, Kobayashi H, Kaneko Y, Nakagawara A (2000) High expression of survivin, mapped to 17q25, is significantly associated with poor prognostic factors and promotes cell survival in human neuroblastoma. oncogene 19(5):617–623
Swana HS, Grossman D, Anthony JN, Weiss RM, Altieri DC (1999) Tumor content of the antiapoptosis molecule survivin and recurrence of bladder cancer. N Engl J Med 341(6):452–453
Lee KH, Panelli MC, Kim CJ, Riker AI, Bettinotti MP, Roden MM, Fetsch P, Abati A, Rosenberg SA, Marincola FM (1998) Functional dissociation between local and systemic immune response during anti-melanoma peptide vaccination. J Immunol 161(8):4183–4194
Ambrosini G, Adida C, Sirugo G, Altieri DC. Induction of apoptosis and inhibition of cell proliferation by survivin gene targeting
Okada E, Murai Y, Matsui K, Isizawa S, Cheng C, Masuda M, Takano Y. Survivin expression in tumor cell nuclei is predictive of a favorable prognosis in gastric cancer patients
Fensterle J, Becker JC, Potapenko T, Heimbach V, Vetter CS, Brocker EB, Rapp UR (2004) B-Raf specific antibody responses in melanoma patients. BMC Cancer 4(1):62
Satyamoorthy K, Bogenrieder T, Herlyn M (2001) No longer a molecular black box—new clues to apoptosis and drug resistance in melanoma. Trends Mol Med 7(5):191–194
Thomas WD, Hersey P (1998) TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) induces apoptosis in Fas ligand-resistant melanoma cells and mediates CD4 T cell killing of target cells. J Immunol 161(5):2195–2200
Tang L, Tron VA, Reed JC, Mah KJ, Krajewska M, Li G, Zhou X, Ho VC, Trotter MJ (1998) Expression of apoptosis regulators in cutaneous malignant melanoma. Clin Cancer Res 4(8):1865–1871
Soengas MS, Capodieci P, Polsky D, Mora J, Esteller M, Opitz-Araya X, McCombie R, Herman JG, Gerald WL, Lazebnik YA, Cordon-Cardo C, Lowe SW (2001) Inactivation of the apoptosis effector Apaf-1 in malignant melanoma. Nature 409(6817):207–211
Vucic D, Stennicke HR, Pisabarro MT, Salvesen GS, Dixit VM (2000) ML-IAP, a novel inhibitor of apoptosis that is preferentially expressed in human melanomas. Curr Biol 10(21):1359–1366
Williams GT (1991) Programmed cell death: apoptosis and oncogenesis. Cell 65(7):1097–1098
Raff MC (1992) Social controls on cell survival and cell death. Nature 356(6368):397–400
Williams GT, Smith CA (1993) Molecular regulation of apoptosis: genetic controls on cell death. Cell 74(5):777–779
Gilchrest BA, Eller MS, Geller AC, Yaar M (1999) The pathogenesis of melanoma induced by ultraviolet radiation. N Engl J Med 340(17):1341–1348
Alanko T, Rosenberg M, Saksela O (1999) FGF expression allows nevus cells to survive in three-dimensional collagen gel under conditions that induce apoptosis in normal human melanocytes. J Invest Dermatol 113(1):111–116
Li G, Tang L, Zhou X, Tron V, Ho V (1998) Chemotherapy-induced apoptosis in melanoma cells is P53 dependent. melanoma Res 8(1):17–23
Mooney EE, Ruis Peris JM, O’Neill A, Sweeney EC (1995) Apoptotic and mitotic indices in malignant melanoma and basal cell carcinoma. J Clin Pathol 48(3):242–244
Bastian BC (2003) Understanding the progression of melanocytic neoplasia using genomic analysis: from fields to cancer. Oncogene 22(20):3081–3086
Frost M, Jarboe EA, Orlicky D, Gianani R, Thompson LC, Enomoto T, Shroyer KR (2002) Immunohistochemical localization of survivin in benign cervical mucosa, cervical dysplasia, and invasive squamous cell carcinoma. Am J Clin Pathol 117(5):738–744
Herlyn M, Berking C, Li G, Satyamoorthy K (2000) Lessons from melanocyte development for understanding the biological events in naevus and melanoma formation. melanoma Res 10(4):303–312
Ito T, Shiraki K, Sugimoto K, Yamanaka T, Fujikawa K, Ito M, Takase K, Moriyama M, Kawano H, Hayashida M, Nakano T, Suzuki A (2000) Survivin promotes cell proliferation in human hepatocellular carcinoma. hepatology 31(5):1080–1085
Yoshida H, Ishiko O, Sumi T, Matsumoto Y, Ogita S (2001) Survivin, Bcl-2 and matrix metalloproteinase-2 enhance progression of clear cell- and serous-type ovarian carcinomas. Int J Oncol 19(3):537–542
Grabowski P, Kuhnel T, Muhr-Wilkenshoff F, Heine B, Stein H, Hopfner M, Germer CT, Scherubl H (2003) Prognostic value of nuclear survivin expression in oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Br J Cancer 88(1):115–119
Marusawa H, Matsuzawa S, Welsh K, Zou H, Armstrong R, Tamm I, Reed JC (2003) HBXIP functions as a cofactor of survivin in apoptosis suppression. EMBO J22(11):2729–2740
Meier F, Satyamoorthy K, Nesbit M, Hsu MY, Schittek B, Garbe C, Herlyn M (1998) Molecular events in melanoma development and progression. front biosci 3:D1005–D1010
Li G, Herlyn M (2000) Dynamics of intercellular communication during melanoma development. Mol Med Today 6(4):163–169
Morales-Ducret CR, van de Rijn M, Smoller BR (1995) Bcl-2 expression in melanocytic nevi. Insights into the biology of dermal maturation. Arch Dermatol 131(8):915–918
Sprecher E, Bergman R, Meilick A, Kerner H, Manov L, Reiter I, Shafer Y, Maor G, Friedman-Birnbaum R (1999) Apoptosis, Fas and Fas-ligand expression in melanocytic tumors. J Cutan Pathol 26(2):72–77
Boni R, Wellmann A, Man YG, Hofbauer G, Brinkmann U (1999) Expression of the proliferation and apoptosis-associated CAS protein in benign and malignant cutaneous melanocytic lesions. Am J Dermatopathol 21(2):125–128
Shennan MG, Badin AC, Walsh S, Summers A, From L, McKenzie M, Goldstein AM, Tucker MA, Hogg D, Lassam N (2000) Lack of germline CDK6 mutations in familial melanoma. Oncogene 19(14):1849–1852
Badie C, Itzhaki JE, Sullivan MJ, Carpenter AJ, Porter AC (2000) Repression of CDK1 and other genes with CDE and CHR promoter elements during DNA damage-induced G(2)/M arrest in human cells. Mol Cell Biol 20(7):2358–2366
Zhao J, Tenev T, Martins LM, Downward J, Lemoine NR (2000) The Ubiquitin-proteasome pathway regulates survivin degradation in a cell cycle-dependent manner. J Cell Sci 113(Pt23):4363–4371
O’Connor DS, Wall NR, Porter AC, Altieri DCA (2002) P34(Cdc2) survival checkpoint in cancer. Cancer Cell 2(1):43–54
Fukuda S, Foster RG, Porter SB, Pelus LM (2002) The antiapoptosis protein survivin is associated with cell cycle entry of normal cord blood CD34(+) cells and modulates cell cycle and proliferation of mouse hematopoietic progenitor cells. Blood 100(7):2463–2471
Shen Y, Devgan G, Darnell JE Jr, Bromberg JF (2001) Constitutively activated stat3 protects fibroblasts from serum withdrawal and UV-induced apoptosis and antagonizes the proapoptotic effects of Activated Stat1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 98(4):1543–1548
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vetter, C.S., Müller-Blech, K., Schrama, D. et al. Cytoplasmic and nuclear expression of survivin in melanocytic skin lesions. Arch Dermatol Res 297, 26–30 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00403-005-0572-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00403-005-0572-x