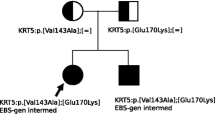
Abstract
Dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa (DEB) is caused by mutations in the gene encoding type VII collagen (COL7A1). Although most COL7A1 mutations are unique to individual families, small numbers of mutations are recurrent. The recurrent mutations R578X, 7786delG, and R2814X seem to be exclusive to a specific ethnic group, the British population. The mutations 5818delC, 6573+1G→C, and E2857X are present only in individuals of Japanese ethnic origin. On the other hand, the mutations 425A→G and G2043R have been found in several different ethnic groups. The purpose of this study was to clarify whether these recurrent mutations are also found in patients of other ethnic groups with DEB, mainly Asian patients. We demonstrated the absence of the recurrent mutations R578X, 7786delG, and R2814X in 42 non-British patients with DEB and detected the mutations 425A→G in a French patient and G2043R in Japanese and Chinese patients with DEB. The mutations 5818delC, 6573+1G→C, and E2857X were detected in 11 Japanese patients (13 alleles) with DEB. Our results confirm that R578X, 7786delG, and R2814X mutations are specifically limited to British patients, and the mutations 5818delC, 6573+1G→C, and E2857X are frequent in Japanese patients. On the other hand, the mutations 425A→G and G2043R can be found in different ethnic groups. In conclusion, our results further support the notion that recurrent mutations can be classified into two types, ethnic-specific mutation and worldwide mutation.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anton-Lamprecht I, Gedde-Dahl T Jr (2002) Epidermolysis bullosa. In: Rimoin DL, Connor JM, Pyeritz RE, Korf BR (eds) Emery and Rimoin’s principles and practice of medical genetics, 4th edn. Churchill Livingstone, London, pp 3810–3897
Bruckner-Tuderman L (1999) Hereditary skin diseases of anchoring fibrils. J Dermatol Sci 20:122–133
Christiano AM, Hoffman GG, Chung-Honet LC, Lee S, Cheng W, Uitto J, Greenspan DS (1994) Structural organization of the human type VII collagen gene (COL7A1), comprised of more exons than any previously characterized gene. Genomics 21:169–179
Christiano AM, Morricone A, Paradisi M, Angelo C, Mazzanti C, Cavalieri R, Uitto J (1995) A glycine-to-arginine substitution in the triple-helical domain of type VII collagen in a family with dominant dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa. J Invest Dermatol 104:438–440
Christiano AM, Suga Y, Greenspan DS, Ogawa H, Uitto J (1997) Strategy for identification of sequence variants in COL7A1, and a novel 2-bp deletion mutation in recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa. Hum Mutat 10:408–414
Cserhalmi-Friedman PB, Kárpáti S, Horvath A, Christiano AM (1997) Identification of the glycine-to-arginine substitution G2043R in type VII collagen in a family with dominant dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa from Hungary. Exp Dermatol 6:303–307
Cserhalmi-Friedman PB, Kárpáti S, Horvath A, Christiano AM (1997) Identification of a glycine substitution and a splice site mutation in the type VII collagen gene in a proband with mitis recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa. Arch Dermatol Res 289:640–645
Dunnill MGS, Richards AJ, Milana G, Mollica F, Eady RAJ, Pope FM (1994) A novel homozygous point mutation in the collagen VII gene (COL7A1) in two cousins with recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa. Hum Mol Genet 3:1693–1694
Fine JD, Eady RAJ, Bauer EA, Briggaman RA, Bruckner-Tuderman L, Christiano AM, Heggerty A, Hintner H, Jonkman MF, McGrath JA, McGuire J, Moshell A, Shimizu H, Tadini G, Uitto J (2000) Revised classification system for inherited epidermolysis bullosa: report of the second international consensus meeting on diagnosis and classification of epidermolysis bullosa. J Am Acad Dermatol 42:1051–1066
Gardella R, Belletti L, Zoppi N, Marini D, Barlati S, Colombi M (1996) Identification of two splicing mutations in the collagen type VII gene (COL7A1) of a patient affected by the localisata variant of recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa. Am J Hum Genet 59:292–300
Gardella R, Zoppi N, Ferraboli S, Marini D, Tadini G, Barlati S, Colombi M (1999) Three homozygous PTC mutations in the collagen type VII gene of patients affected by recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa: analysis of transcript levels in dermal fibroblasts. Hum Mutat 13:439–452
Gardella R, Castiglia D, Posteraro P, Bernardini S, Zoppi N, Paradisi M, Tadini G, Barlati S, McGrath JA, Zambruno G, Colombi M (2002) Genotype-phenotype correlation in Italian patients with dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa. J Invest Dermatol 119:1456–1462
Järvikallio A, Pulkkinen L, Uitto J (1997) Molecular basis of dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa: mutations in the type VII collagen gene (COL7A1). Hum Mutat 10:338–347
Mellerio JE, Dunnill MG, Allison W, Ashton GH, Christiano AM, Uitto J, Eady RA, McGrath JA (1997) Recurrent mutations in the type VII collagen gene (COL7A1) in patients with recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa. J Invest Dermatol 109:246–249
Mellerio JE, Salas-Alanis JC, Talamantes ML, Horn H, Tidman MJ, Ashton GHS, Eady RAJ, McGrath JA (1998) A recurrent glycine substitution mutation, G2043R, in the type VII collagen gene (COL7A1) in dominant dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa. Br J Dermatol 139:730–737
Mohammedi R, Mellerio JE, Ashton GH, Eady RAJ, McGrath JA (1999) A recurrent COL7A1 mutation, R2814X, in British patients with recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa. Clin Exp Dermatol 24:37–39
Rouan F, Pulkkinen L, Jonkman MF, Bauer JW, Cserhalmi-Friedman PB, Christiano AM, Uitto J (1998) Novel and de novo glycine substitution mutations in the type VII collagen gene (COL7A1) in dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa: implications for genetic counseling. J Invest Dermatol 111:1210–1213
Tamai K, Murai T, Mayama M, Kon A, Nomura K, Sawamura D, Hanada K, Hashimoto I, Shimizu H, Masunaga T, Nishikawa T, Mitsuhashi Y, Ishida-Yamamoto A, Ikeda S, Ogawa H, McGrath JA, Pulkkinen L, Uitto J, the Japanese Collaborative Study Group on Epidermolysis Bullosa (1999) Recurrent COL7A1 mutations in Japanese patients with dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa: positional effects of premature termination codon mutations on clinical severity. J Invest Dermatol 112:991–993
Uitto J, Pulkkinen L, Christiano AM (1999) The molecular basis of the dystrophic form of epidermolysis bullosa. In: Fine JD, Bauer EA, McGuire J, Moshell A (eds) Epidermolysis bullosa. John Hopkins University Press, Baltimore, pp 326–350
Wessagowit V, Ashton GHS, Mohammedi R, Salas-Alanis JC, Denyer JE, Mellerio JE, Eady RAJ, McGrath JA (2001) Three cases of de novo dominant dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa associated with the mutation G2043R in COL7A1. Clin Exp Dermatol 26:97–99
Whittock NV, Ashton GHS, Mohammedi R, Mellerio JE, Mathew CG, Abbs SJ, Eady RAJ, McGrath JA (1999) Comparative mutation detection screening of the type VII collagen gene (COL7A1) using the protein truncation test, fluorescent chemical cleavage of mismatch, and conformation sensitive gel electrophoresis. J Invest Dermatol 113:673–686
Winberg J-O, Hammami-Hauasli N, Nilssen O, Anton-Lamprecht I, Naylor SL, Kerbacher K, Zimmermann M, Krajci P, Gedde-Dahl T Jr, Bruckner-Tuderman L (1997) Modulation of disease severity of dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa by a splice site mutation in combination with a missense mutation in the COL7A1 gene. Hum Mol Genet 6:1125–1135
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Dr. John A. McGrath for providing genomic DNA with the respective recurrent mutation and Ms. Yuriko Okuno for her technical assistance with the mutation analysis. This work was supported by Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research (nos. 05404036 and 07457191) from the Ministry of Education, Science, Sports, and Culture of Japan and by Keio Gijuku Academic Development Funds to Hiroshi Shimizu.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Murata, T., Masunaga, T., Ishiko, A. et al. Differences in recurrent COL7A1 mutations in dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa: ethnic-specific and worldwide recurrent mutations. Arch Dermatol Res 295, 442–447 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00403-003-0444-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00403-003-0444-1