Abstract.
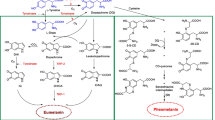
Skin wrinkling and xerosis associated with aging result from decreases in dermal collagen and stratum corneum ceramide content. This study demonstrated that ursolic acid incorporated into liposomes (URA liposomes) increases both the ceramide content of cultured normal human epidermal keratinocytes (NHEK), and the collagen content of cultured normal human dermal fibroblasts. In addition, URA liposomes increased the ceramide content of the skin of human subjects, with increases in hydroxy ceramides occurring after only 3 days of treatment. Both URA liposomes and retinoic acid decreased markers of keratinocyte differentiation (keratin 1, keratin 10 and involucrin) in cultured NHEK. Thus, URA liposomes have effects on keratinocyte differentiation and dermal fibroblast collagen synthesis similar to those of retinoids. However, this study showed that URA liposomes increase ceramides in NHEK, in contrast to the decreases previously shown to be caused by retinoids. URA liposomes have the potential to be used alone or in combination with other agents to restore or maintain skin ceramide and collagen content.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Both, D.M., Goodtzova, K., Yarosh, D.B. et al. Liposome-encapsulated ursolic acid increases ceramides and collagen in human skin cells. Arch Dermatol Res 293, 569–575 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00403-001-0272-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00403-001-0272-0