Abstract
Purpose
Intraoperative injury to the popliteal artery (PA) should be avoided during total knee arthroplasty (TKA). This study was performed to clarify the preoperative localization of the PA and the patient factors that impact its localization as a preventive measure.
Methods
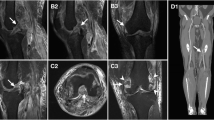
Ninety-seven patients (110 knees; 18 men, 79 women) with osteoarthritis who underwent primary TKA were retrospectively reviewed. Preoperative sagittal magnetic resonance imaging was used to measure the distance between the PA and the closest point at three levels: the femoral epicondyle (DPF), the tibial articular surface (DPAS), and the posterior tibial cortex (DPT). All variables are expressed in millimeters as median (interquartile range).
Results
The median distance was 10.35 (7.90–12.34) mm for DPF, 6.32 (5.12–8.57) mm for DPAS, and 3.76 (2.28–5.26) mm for DPT. Body height and weight showed weak correlations with DPF (r = 0.324, p < 0.001 and r = 0.207, p = 0.03, respectively). DPF was smaller in women [9.82 (7.64–12.23) mm] than in men [11.27 (10.26–12.75) mm] (p = 0.004). A larger flexion angle and range of motion showed a weak negative correlation with DPT (r = − 0.282, p = 0.003 and r = − 0.236, p = 0.016, respectively). Multiple regression analysis revealed that DPF was related to body height (β = 0.341, p < 0.001) and that DPT was related to the flexion angle (β = − 0.264, p = 0.005).
Conclusions
Special attention should be paid to women with a small physique on the femoral side and/or patients with a large flexion angle on the tibial side as a strategy to prevent PA-related complications.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Ninomiya JT, Dean JC, Goldberg VM (1999) Injury to the popliteal artery and its anatomic location in total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 14:803–809
O’Connor JV, Stocks G, Crabtree JD Jr, Galasso P, Wallsh E (1998) Popliteal pseudoaneurysm following total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 13:830–832
Dua A, Zepeda R, Hernanez FC, Igbadumhe AA, Desai SS (2015) The national incidence of iatrogenic popliteal artery injury during total knee replacement. Vascular 23:455–458
Ko L, DeHart M, Yoo J, Huff T (2014) Popliteal artery injury associated with total knee arthroplasty: trends, costs and risk factors. J Arthroplasty 29:1181–1184
Slick GS, Davis Iii CM, Elfar JC, Nikkel LE (2021) Process mapping total knee arthroplasty: a comparison of instrument designs. J Arthroplasty 36:941–945
Kumar SN, Chapman J, Rawlins I (1998) Vascular injuries in total knee arthroplasty. A review of the problem with special reference to the possible effects of the tourniquet. J Arthroplasty 13:211–216
Eriksson K, Bartlett J (2010) Popliteal artery-tibial plateau relationship before and after total knee replacement: a prospective ultrasound study. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 18:967–970
Keyurapan E, Phoemphunkunarak W, Lektrakool N (2016) Location of the neurovascular bundle of the knee during flexed and extended position: an MRI study. J Med Assoc Thai 99:1102–1109
Kimura Y, Takahashi T, Ae R, Takeshita K (2022) Proximal branching of the anterior tibial artery from the popliteal artery increases the risk of vascular injury during total knee arthroplasty: a retrospective analysis using preoperative magnetic resonance imaging and intraoperative findings. Geriatr Orthop Surg Rehabil 13:1–7
Smith PN, Gelinas J, Kennedy K, Thain L, Rorabeck CH, Bourne RB (1999) Popliteal vessels in knee surgery. A magnetic resonance imaging study. Clin Orthop Relat Res 367:158–164
Farrington WJ, Charnley GJ, Harries SR, Fox BM, Sharp R, Hughes PM (1999) The position of the popliteal artery in the arthritic knee. J Arthroplasty 14:800–802
Shetty AA, Tindall AJ, Qureshi F, Divekar M, Fernando KW (2003) The effect of knee flexion on the popliteal artery and its surgical significance. J Bone Joint Surg Br 85:218–222
Takeda M, Ishii Y, Noguchi H, Sato J (2011) Change in the position of the popliteal artery with knee flexion after TKA. AAOS exhibit selection. J Bone Joint Surg Am 93:e1231-1236
Yoo JH, Chang CB (2009) The location of the popliteal artery in extension and 90 degree knee flexion measured on MRI. Knee 16:143–148
Zaidi SH, Cobb AG, Bentley G (1995) Danger to the popliteal artery in high tibial osteotomy. J Bone Joint Surg Br 77:384–386
Simons M, Schraut N, Moretti V, Klazura G, Chuang D, Parekh A, Gonzalez M (2018) Location of the popliteal artery in knee extension on magnetic resonance imaging. J Surg Orthop Adv 27:325–328
de Araujo Goes RF, Filho AC, de Oliveira Castro GN, Loures FB, Da Palma IM, Kinder A, Labronici PJ (2015) Magnetic resonance study on the anatomical relationship between the posterior proximal region of the tibia and the popliteal artery. Rev Bras Ortop 50:422–429
No author listed. stem. http://www.asahq.org/resources/clinical-information/asa-physical-statusclassification-system. Accessed 24 Mar 2022
Kellgren JH, Lawrence JS (1957) Radiographical assessment of osteo-arthrosis. Ann Rheum Dis 16:494–502
Alicea J (2001) Scoring systems and their validation for the arthritic knee. In: Insall JN, Scott WN (eds) Surgery of the knee, vol 2, 3rd edn. Churchill Livingstone, New York, pp 1507–1515
Lombardi AV Jr, Berend KR (2006) Posterior cruciate ligament retaining, posterior stabilized, and varus/valgus posterior stabilized constrained articulations in total knee arthroplasty. Instr Course Lect 55:419–427
Berend KR, Lombardi AV Jr, Adams JB (2006) Total knee arthroplasty in patients with greater than 20 degrees flexion contracture. Clin Orthop Relat Res 452:83–87
Lombardi AV Jr, Mallory TH, Fada RA, Hartman JF, Capps SG, Kefauver CA, Adams JB (2001) An algorithm for the posterior cruciate ligament in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 392:75–87
Robinson WH, Lepus CM, Wang Q, Raghu H, Mao R, Lindstrom TM, Sokolove J (2016) Low-grade inflammation as a key mediator of the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol 12:580–592
Tarasevicius S, Kesteris U, Gelmanas A, Smailys A, Wingstrand H (2007) Intracapsular pressure and elasticity of the hip joint capsule in osteoarthritis. J Arthroplasty 22:596–600
Pinter Z, Staggers R, Lee S, Bergstresser S, Shah A, Naranje S (2019) Open posterior capsular release with an osteotome in total knee arthroplasty does not place important neurovascular structures at risk. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 27:2120–2123
Qiao Y, Li F, Zhang L, Song X, Yu X, Yang W, Zhou S, Zhang H (2023) Clinical effects of interspace between the popliteal artery and capsule of the posterior knee block with multimodal analgesia for total knee arthroplasty: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-023-04798-x
Li H, Zhang M, Li Y, Wang H (2021) Comparison of clinical outcomes associated with arthroscopic cyst wall preservation or resection in the treatment of popliteal cyst: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 141:1741–1752
Nha KW, Kim SJ, Park JH, Bae JH, Jang KM, Kim SG (2023) Arthroscopic cystectomy for Baker’s cysts with and without one-way valve lesions: incidence of one-way valve lesion, associated pathologies, and clinical outcomes. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 143:287–294
Acknowledgements
We thank Edanz Group (https://en-author-services.edanz.com/ac), for editing a draft of this manuscript.
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Each author certifies that he or she has no commercial associations (e.g., consultancies, stock ownership, equity interest, patent/licensing arrangements) that might pose a conflict of interest in connection with the submitted article.
Ethical approval
The local institutional review board approved this study. All patients provided informed consent.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ishii, Y., Noguchi, H., Sato, J. et al. Patient factors impacting localization of popliteal artery before total knee arthroplasty. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 143, 6353–6360 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-023-04896-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-023-04896-w