Abstract
Introduction
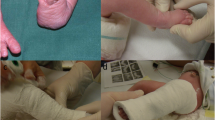
This study prospectively investigated the pain response and physiological parameters [heart rate (HR) and oxygen saturation (SpO2)] during sequential casting in bilateral clubfoot. Additionally, it explored the role of non-nutritive sucking and human care contact on the observed responses during casting.
Methods
Subjects were allotted to control group (Group A with no intervention) and two intervention groups (Group B: non-nutritive sucking intervention, Group C: human care contact intervention). Neonatal Infant Pain Score (NIPS), heart rate (HR), and oxygen saturation (SpO2) were used to assess the response.
Results
The three groups matched in age and gender characteristics of the participants. Pain response was noted across all groups. The left foot demonstrated a statistically significant preexisting tachycardia which rose further during casting (p < 0.01). Intergroup comparisons revealed that the alteration for NIPS during casting was in following sequence (Group A > C > B, p < 0.00001). The effect of interventions offered in Group B and C lasted in the post-cast period as well (B > C).
Conclusion
The clubfoot child exhibited moderate pain response during casting of both feet. A tachycardia was noted prior to initiation of second cast which further exaggerated with subsequent cast. Pacifier (non-nutritive sucking) intervention produced better control of pain response than human care contact during casting for both feet.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The dataset generated shall be available upon reasonable request to the corresponding author.
Change history
07 November 2023
This article has been retracted. Please see the Retraction Notice for more detail: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-023-05127-y
References
Pirani S, Staheli L, Naddumba E (2008) Ponseti clubfoot management: teaching manual for healthcare providers in Uganda, 1st edn. GHO Publications, Seattle
Milbrandt T, Kryscio R, Muchow R et al (2018) Oral sucrose for pain relief during clubfoot casting: a double-blinded randomized controlled trial. J Pediatr Orthop 38:430–435. https://doi.org/10.1097/BPO.0000000000000845
Upadhyay A, Barik S, Agarwal A, Patel Y (2023) Efficacy of 2 nonpharmaceutical (non-nutritive sucking and human care contact) pain relief measures for idiopathic clubfoot casted using ponseti technique. J Pediatr Orthop 43:e100–e105. https://doi.org/10.1097/BPO.0000000000002299
Hudson-Barr D, Capper-Michel B, Lambert S et al (2002) Validation of the pain assessment in neonates (PAIN) scale with the neonatal infant pain scale (NIPS). Neonatal Netw NN 21:15–21. https://doi.org/10.1891/0730-0832.21.6.15
Lawrence J, Alcock D, McGrath P et al (1993) The development of a tool to assess neonatal pain. Neonatal Netw NN 12:59–66
Fitri SYR, Lusmilasari L, Juffrie M, Rakhmawati W (2019) Pain in neonates: a concept analysis. Anesthesiol Pain Med 9:e92455. https://doi.org/10.5812/aapm.92455
de Sousa Freire NB, Garcia JBS, Lamy ZC (2008) Evaluation of analgesic effect of skin-to-skin contact compared to oral glucose in preterm neonates. Pain 139:28–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pain.2008.02.031
Okan F, Ozdil A, Bulbul A et al (2010) Analgesic effects of skin-to-skin contact and breastfeeding in procedural pain in healthy term neonates. Ann Trop Paediatr 30:119–128. https://doi.org/10.1179/146532810X12703902516121
Seo YS, Lee J, Ahn HY (2016) Effects of kangaroo care on neonatal pain in South Korea. J Trop Pediatr 62:246–249. https://doi.org/10.1093/tropej/fmv102
Funding
The authors declare that no funds, grants, or other support were received during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by AU and AA. The first draft of the manuscript was written by SB and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Ethics approval
This study was performed in line with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki. Approval was granted by the Institutional Ethics Committee of Chacha Nehru Bal Chikitsalaya (No). F.1/AEC/CNBC/15/02/2021/Protocol no. 92 /4256.
Consent to participate
Written informed consent was obtained from the parents.
Consent to publish
Written informed consent was obtained from the parents.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article has been retracted. Please see the retraction notice for more detail: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-023-05127-y"
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Agarwal, A., Barik, S., Upadhyay, A. et al. RETRACTED ARTICLE: Pain behavior of children with bilateral idiopathic clubfoot undergoing Ponseti casting and the effect of non-pharmaceutical pain-relieving agents. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 143, 5603–5608 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-023-04877-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-023-04877-z