Abstract
Introduction
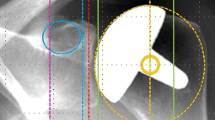
Proximal humeral bone loss in total shoulder arthroplasty (TSA) is more frequent than in hemiarthroplasty. Factors such as age, gender, inclination angle, and radiolucent lines may also contribute. Additionally, current bone loss grading systems are often not sensitive enough to detect slight bone changes, especially at the medial calcar where bone loss is commonly observed. This study uses a new, more detailed bone loss grading system to evaluate factors that could influence bone loss at the proximal humerus.
Materials and methods
In this single-center prospective study, patients underwent hemiarthroplasty or TSA with an anatomic stemless prosthesis. Bone loss was measured at the proximal humerus using the new grading system. The effect of treatment type, age, gender, radiolucent lines, and inclination angle on bone loss was evaluated. The Constant-Murley score of patients was assessed and complications recorded.
Results
Ninety-one shoulders were available for the final follow-up examination at a median of 85.0 months (range 82.6–121.1 months). Bone loss was found at the proximal humerus in approximately one-third of shoulders, and significantly more shoulders had bone loss in TSA than in hemiarthroplasty (P = 0.03). However, this difference was no longer significant after stratifying by gender and age (P > 0.05). Bone loss significantly correlated with gender (P = 0.03) but not with treatment type, radiolucent lines, and the postoperative inclination angle (P > 0.05). Most Constant–Murley score components did not differ significantly between shoulders with and without bone loss (P > 0.05). Lastly, six complications and four revisions were reported.
Conclusions
Results showed gender had the greatest influence on bone loss after stemless shoulder arthroplasty. Furthermore, both patients with or without bone loss can expect similar clinical outcomes with the stemless prosthesis used in this study. Lastly, the new grading system is simple and straightforward to use.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bell SN, Christmas M, Coghlan JA (2020) Proximal humeral osteolysis and glenoid radiolucent lines in an anatomic shoulder arthroplasty: a comparison of a ceramic and a metal humeral head component. J Shoulder Elb Surg 29(5):913–923
Brabston EW, Fehringer EV, Owen MT, Ponce BA (2020) Stemless humeral implants in total shoulder arthroplasty. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 28(7):e277–e287
Denard PJ, Raiss P, Gobezie R, Edwards TB, Lederman E (2018) Stress shielding of the humerus in press-fit anatomic shoulder arthroplasty: review and recommendations for evaluation. J Shoulder Elb Surg 27(6):1139–1147
DeVito P, Judd H, Malarkey A et al (2019) Medial calcar bone resorption after anatomic total shoulder arthroplasty: does it affect outcomes? J Shoulder Elb Surg 28(11):2128–2138
Favard L, Berhouet J, Walch G, Chaoui J, Lévigne C (2017) Superior glenoid inclination and glenoid bone loss: definition, assessment, biomechanical consequences, and surgical options. Der Orthopade 46(12):1015–1021
Greiner S, Berth A, Kääb M, Irlenbusch U (2013) Glenoid morphology affects the incidence of radiolucent lines around cemented pegged polyethylene glenoid components. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 133(10):1331–1339
Habermeyer P, Lichtenberg S, Tauber M, Magosch P (2015) Midterm results of stemless shoulder arthroplasty: a prospective study. J Shoulder Elb Surg 24(9):1463–1472
Huguet D, DeClercq G, Rio B, Teissier J, Zipoli B (2010) Results of a new stemless shoulder prosthesis: radiologic proof of maintained fixation and stability after a minimum of three years’ follow-up. J Shoulder Elb Surg 19(6):847–852
Irlenbusch U, Kaab MJ, Kohut G, Proust J, Reuther F, Joudet T (2015) Reversed shoulder arthroplasty with inversed bearing materials: 2-year clinical and radiographic results in 101 patients. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 135(2):161–169
Jordan R, Kelly C, Pap G et al (2021) Mid-term results of a stemless ceramic on polyethylene shoulder prosthesis—a prospective multicentre study. Should Elb 13(1):67–77
Karssiens TJ, Gill JR, Sunil Kumar KH, Sjolin SU (2021) Clinical results and survivorship of the Mathys Affinis Short, Short Stem Total Shoulder Prosthesis. Bone Jt Open 2(1):58–65
Peduzzi L, Goetzmann T, Wein F et al (2019) Proximal humeral bony adaptations with a short uncemented stem for shoulder arthroplasty: a quantitative analysis. JSES Open Access 3(4):278–286
Raiss P, Bruckner T, Rickert M, Walch G (2014) Longitudinal observational study of total shoulder replacements with cement: fifteen to twenty-year follow-up. J Bone Jt Surg Am Vol 96(3):198–205
Raiss P, Edwards TB, Deutsch A et al (2014) Radiographic changes around humeral components in shoulder arthroplasty. J Bone Jt Surg Am Vol 96(7):e54
Santos B, Quental C, Folgado J, Sarmento M, Monteiro J (2018) Bone remodelling of the humerus after a resurfacing and a stemless shoulder arthroplasty. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon) 59:78–84
Upfill-Brown A, Satariano N, Feeley B (2019) Stemless shoulder arthroplasty: review of short and medium-term results. JSES Open Access 3(3):154–161
Uschok S, Magosch P, Moe M, Lichtenberg S, Habermeyer P (2017) Is the stemless humeral head replacement clinically and radiographically a secure equivalent to standard stem humeral head replacement in the long-term follow-up? A prospective randomized trial. J Shoulder Elb Surg 26(2):225–232
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. Dominik Pfluger at numerics data GmbH for statistical analysis and Medical Minds GmbH for providing medical writing and editorial support.
Funding
The author(s) received no financial support for research, authorship, and/or publication of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors have substantially contributed to the conception and design of the study, the acquisition, analysis interpretation of data, and drafting of the manuscript. All authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript and also read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Financial interests: the authors declare they have no financial interests. Non-financial interests: U.I. is a medical advisor for Mathys Ltd Bettlach.
Ethical approval
This study was approved by The Comité intercantonal d’éthique (Jura, Fribourg, Neuchatel) in February 2012 (number 012/10770). It is compliant with the Declaration of Helsinki.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Greis, M., Heubach, K., Hoberg, M. et al. Proximal humeral bone loss in stemless shoulder arthroplasty: potential factors influencing bone loss and a new classification system. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 143, 3085–3090 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-022-04493-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-022-04493-3