Abstract
Introduction
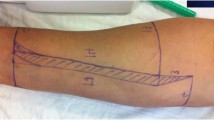
Few studies have been conducted to explore the utility of the Integra® dermal regeneration template (IDRT) combined with a delayed split-thickness skin graft (STSG) for reconstructing complex dorsal hand, digit, and thumb injuries. This study reports the indications and outcomes for 14 patients treated with this technique via a two-stage process.
Materials and methods
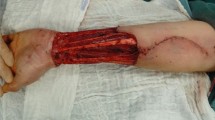
We retrospectively reviewed all patients treated by IDRT combined with STSG from May 2015 to October 2018. The inclusion criterion was traumatic or post-infectious soft tissue defects (STDs) of the dorsal hand, fingers, and thumb, not suitable for direct wound closure and requiring local, pedicle, or free flap reconstruction. After debridement, a two-stage procedure was applied, namely IDRT followed by STSG. Indications, functional outcomes, aesthetic results, complications, patient satisfaction, and the STSG take rate were evaluated over a 36-month follow-up using standardised instruments.
Results
A total of 14 patients with 15 reconstructions (average age = 48 years) were included. The dominant hand was involved in 50% of cases. Dorsal STDs involved the hand, fingers, thumb, and hand and thumb in 7, 3, 2 and 2 cases, respectively. The mean STD size was 35 cm2 (range: 3–150 cm2). The wound was associated with exposed tendons (without peritenon), bone (without periosteum), and joints (without a capsule) in eight cases (57%). The IDRT/STSG take rate was 97%. The average Vancouver Scar Scale score was 2 (1–4).
Conclusion
The 36-month follow-up demonstrated that IDRT is a safe and reliable technique that can be considered a viable alternative to flap reconstruction for the management of traumatic STDs in selected patients. The aesthetic outcomes are acceptable, functional recovery of the fingers is excellent, patient satisfaction is very high and the rate of complications is very low.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Burke JF, Yannas IV, Quinby WC Jr, Bondoc CC, Jung WK (1981) Successful use of a physiologically acceptable artificial skin in the treatment of extensive burn injury. Ann Surg 194(4):413–428. https://doi.org/10.1097/00000658-198110000-00005
Herlin C, Louhaem D, Bigorre M, Dimeglio A, Captier G (2007) Use of Integra in a paediatric upper extremity degloving injury. J Hand SurgEur 32(2):179–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JHSB.2006.11.013
Graham GP, Helmer SD, Haan JM, Khandelwal A (2013) The use of Integra® dermal regeneration template in the reconstruction of traumatic degloving injuries. J Burn Care Res 34(2):261–266. https://doi.org/10.1097/BCR.0b013e3182853eaf
Son JH, Bafus B, Khandelwal A, Chepla KJ (2018) Reconstruction of a circumferential upper extremity soft tissue defect with a dermal regeneration template and skin grafting. Tech Hand Up ExtremSurg 22(1):31–33. https://doi.org/10.1097/BTH.0000000000000185
Baryza MJ, Baryza GA (1995) Thevancouver scar scale: an administration tool and its interrater reliability. J Burn Care Rehabil 16(5):535–538. https://doi.org/10.1097/00004630-199509000-00013
Campbell DA, Kay SP (1996) The Hand Injury Severity Scoring System. J Hand Surg Br 21(3):295–298. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0266-7681(05)80187-1
Valerio IL, Masters Z, Seavay JG, Balazs GC, Ipsen D, Tintle SM (2016) Use of a dermal regeneration template wound dressing in the treatment of combat-related upper extremity soft tissue injuries. J Hand Surg Am 41(12):453–460. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhsa.2016.08.015
Carothers JT, Brigman BE, Lawson RD, Rizzo M (2005) Stacking of a dermal regeneration template for reconstruction of a soft-tissue defect after tumor excision from the palm of the hand: a case report. J Hand Surg Am 30(6):1322–1326. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhsa.2005.08.001
Murray RC, Gordin EA, Saigal K, Leventhal D, Krein H, Heffelfinger RN (2011) Reconstruction of the radial forearm free flap donor site using integra artificial dermis. Microsurgery 31(2):104–108. https://doi.org/10.1002/micr.20833
Ellis CV, Kulber DA (2012) Acellular dermal matrices in hand reconstruction. PlastReconstrSurg 130(5 Suppl 2):256S–S269. https://doi.org/10.1097/PRS.0b013e318265a5cf
Weigert R, Choughri H, Casoli V (2011) Management of severe hand wounds with Integra® dermal regeneration template. J Hand SurgEur 36(3):185–193. https://doi.org/10.1177/1753193410387329
Moiemen NS, Vlachou E, Staiano JJ, Thawy Y, Frame JD (2006) Reconstructive surgery with Integra dermal regeneration template: histologic study, clinical evaluation, and current practice. PlastReconstrSurg 117(7 Suppl):160S–174S. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.prs.0000222609.40461.68
Arner M, Möller K (1994) Morbidity of the pedicled groin flap. A retrospective study of 44 cases. J PlastReconstr 28(2):143–146. https://doi.org/10.3109/02844319409071192
Heimbach DM, Warden GD, Luterman A, Jordan MH, Ozobia N, Ryan CM et al (2003) Multicenterpostapproval clinical trial of Integra dermal regeneration template for burn treatment. J Burn Care Rehabil 24(1):42–48. https://doi.org/10.1097/00004630-200301000-00009
Yeong EK, Yu YC, Chan ZH, Roan TL (2013) Is artificial dermis an effective tool in the treatment of tendon-exposed wounds? J Burn Care Res 34(1):161–167. https://doi.org/10.1097/BCR.0b013e3182685f0a
Stern R, McPherson M, Longaker MT (1990) Histologic study of artificial skin used in the treatment of full-thickness thermal injury. J Burn Care Rehabil 11(1):7–13. https://doi.org/10.1097/00004630-199001000-00003
Bache SE, Watson SB (2011) Bedside application of integra debridement of necrotising fasciitis. J PlastReconstrAesthetSurg 64(4):559–560. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjps.2010.07.032
Akhtar S, Hasham S, Abela C, Phipps AR (2006) The use of Integra in necrotizing fasciitis. Burns 32(2):251–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.burns.2005.06.009
Foucher G, Dallaserra M, Tilquin B, Lenoble E, Sammut D (1994) The Hueston flap in reconstruction of fingertip skin loss: results in a series of 41 patients. J Hand Surg Am 19(3):508–515. https://doi.org/10.1016/0363-5023(94)90072-8
Verbelen J, Hoeksema H, Pirayesh A, Van Landuyt K, Monstrey S (2016) Exposed tibial bone after burns: flap reconstruction versus dermal substitute. Burns 42(2):e31–e37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.burns.2015.08.013
Alet JM, Weigert R, Castede JC, Casoli V (2014) Management of traumatic soft tissue defects with dermal regeneration template: a prospective study. Injury 45(7):1042–1048. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.injury.2013.11.034
Taras JS, Sapienza A, Roach JB, Taras JP (2010) Acellular dermal regeneration template for soft tissue reconstruction of the digits. J Hand Surg Am 35(3):415–421. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhsa.2009.12.008
Seavay JG, Masters ZA, Balazs GC, Tintle SM, Sabino J, Fleming ME, Valerio IL (2016) Use of bioartificial dermal regeneration template for skin restoration in combat casualty injuries. Regen Med 11(1):81–90. https://doi.org/10.2217/rme.15.83
Abai B, Thayer D, Glat PM (2004) The use of dermal regeneration template (Integra) for acute resurfacing and reconstruction of defects created by excision of giant hairy nevi. PlastReconstrSurg 114(1):162–168. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.prs.0000129078.41960.92
Dantzer E, Queruel P, Salinier L, Palmier B, Quinot JF (2003) Dermal regeneration template for deep hand burns: clinical utility for both early grafting and reconstructive surgery. Br J PlastSurg 56(8):764–774. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0007-1226(03)00366-7
Shores JT, Hiersche M, Gabriel A, Gupta S (2012) Tendon coverage using artificial skin substitute. J PlastReconstrAesthetSurg 65(11):1544–1550. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjps.2012.05.021
Hulsen J, Diederich R, Neumeister MW, Bueno RA Jr (2014) Integra® dermal regeneration template application on exposed tendon. Hand 9(4):539–542. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11552-014-9630-1
Weigert R, Leclere FM, Delia G, De Luca L, Al Mutairi K, Casoli V (2015) Long-term patient-reported functional and cosmetic outcomes following severe traumatic foot and ankle wound reconstruction with acellular dermal matrix. J Cosmet Laser Ther 17(6):321–329. https://doi.org/10.3109/14764172.2015.1027231
Wolter TP, Noah EM, Pallua N (2005) The use of Integra in an upper extremity avulsion injury. Br J PlastSurg 58(3):416–418. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjps.2004.04.008
Gravvanis AI, Tsoutsos DA, Iconomou T et al (2007) The use of integra artificial dermis to minimize donor-site morbidity after suprafascial dissection of the radial forearm flap. Microsurgery 27(7):583–587. https://doi.org/10.1002/micr.20406
Watt AJ, Friedrich JB, Huang JI (2012) Advances in treating skin defects of the hand: skin substitutes and negative-pressure wound therapy. Hand Clin 28(4):519–528. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hcl.2012.08.010
Niu XF, Yi JH, Zha GQ, Hu J, Liu YJ, Xiao LB (2017) Vacuum sealing drainage as a pre-surgical adjunct in the treatment of complex (open) hand injuries: Report of 17 cases. OrthopTraumatolSurg Res 103(3):461–464. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.otsr.2017.01.008
Menn ZK, Lee E, Klebuc MJ (2012) Acellular dermal matrix and negative pressure wound therapy: a tissue-engineered alternative to free tissue transfer in the compromised host. J ReconstrMicrosurg 28(2):139–144. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0031-1289167
Unglaub F, Ulrich D, Pallua N (2005) Reconstructive surgery using an artificial dermis (Integra): results with 19 grafts. ZentralblChir 130(2):157–161. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2005-836367
Schiavon M, Francescon M, Drigo D, Sallom G, Baraziol R, Tesei J, Fraccalanza E, Barbone F (2016) The use of Integra dermal regeneration template versus flaps for reconstruction of full-thickness scalp defects involving the calvaria: a cost-benefit analysis. AesthPlastSurg 40(6):901–907. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-016-0768-9
Kim TG, Choi MK (2018) Secondary contouring of flaps. Arch PlastSurg 45(4):319–324. https://doi.org/10.5999/aps.2018.00542
Elliot D, Adani R, Woo SH, Tang JB (2018) Repair of soft tissue defects in finger, thumb and forearm: less invasive methods with similar outcomes. J Hand SurgEur 43(10):1019–1029. https://doi.org/10.1177/1753193418805698
Rehim SA, Singhal M, Chung KC (2014) Dermal skin substitutes for upper limb reconstruction: current status, indications and contraindications. Hand Clin 30(2):239–252. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hcl.2014.02.001
Acknowledgements
None specific.
Funding
This research did not receive any grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethics approval
Not required.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary file1 (MP4 281335 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choughri, H., Weigert, R., Heron, A. et al. Indications and functional outcome of the use of integra® dermal regeneration template for the management of traumatic soft tissue defects on dorsal hand, fingers and thumb. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 140, 2115–2127 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-020-03615-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-020-03615-z