Abstract
Introduction
Although metallosis is a well-known complication after total hip arthroplasty, little is known about this phenomenon after total (TKA) or unicompartmental knee arthroplasty (UKA). The aim of the present work was to review the current knowledge about the reasons and the diagnostic as well as therapeutic management of metallosis after knee arthroplasty.
Materials and methods
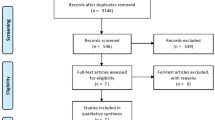
A literature search was performed through PubMed until April 2019. Search terms were “metallosis” in combination with “knee”, “knee prosthesis”, “knee arthroplasty” and “knee replacement”, respectively. All publications were analyzed regarding publication year, level of evidence, number of knees/patients treated, type of prosthesis, metallosis cause, time period between primary implantation and metallosis emergence, laboratory examination, treatment, complications and follow up.
Results
A total of 38 studies reporting on a total of 97 knees were identified. 29 studies reported on metallosis after TKA, 8 after UKA, and one study after both procedures. The time period between the primary implantation and metallosis emergence ranged between 6 weeks and 26 years. The most common reason was the failure of a metal-backed patellar component in 40%, followed by implant/structural- and PE failure (wear/dislocation) in 27% and 18% of the cases, respectively. Complete blood cell count, serum chemistry, erythrocyte sedimentation rate or C-reactive protein serum values were not indicative to diagnose metallosis. The diagnosis was confirmed by histopathological analyses and macroscopic evaluation during surgery. Depending on the particular cause various surgical procedures have been performed. Complete prosthesis exchange was the most common one showing no complications in 89.4% of the cases.
Conclusions
Metallosis after knee arthroplasty is a rare and perhaps underestimated or under published complication. A systematic diagnostic approach is necessary for the timely and correct diagnosis. A thorough debridement as well as a (sub)total synovectomy should be always performed. In cases with a damaged component, a partial/complete prosthesis exchange leads to the best results. Should a malalignment be the cause of the metallosis, then it should be corrected within the revision surgery.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fehring KA, Fehring TK (2015) Modes of failure in metal-on-metal total hip arthroplasty. Orthop Clin N Am 46:185–192
Bayley JC, Scott RD, Ewald FC, Holmes GB Jr (1988) Failure of the metal-backed patellar component after total knee replacement. J Bone Jt Surg Am 70:668–674
Wolff M, Haasper C, Zahar A, Gauck C, Gehrke T, Citak M (2017) Severe metallosis and elevated chromium in serum following implantation of the joint unloading implant system. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 137:1751–1754
Mahendra G, Pandit H, Kliskey K, Murray D, Gill HS, Athanasou N (2009) Necrotic and inflammatory changes in metal-on-metal resurfacing hip arthroplasties. Acta Orthop 80:653–659
Matsushita I, Morita Y, Gejo R, Kimura T (2007) Severe bone defects and reduced mineralization caused by massive metallosis after total knee arthroplasty: histopathologic and bone morphometric findings. Mod Rheumatol 17:507–510
Heffernan EJ, Alkubaidan FO, Nielsen TO, Munk PL (2008) The imaging appearances of metallosis. Skelet Radiol 37:59–62
Schiavone Panni A, Vasso M, Cerciello S, Maccauro G (2011) Metallosis following knee arthroplasty: a histological and immunohistochemical study. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol 24:711–719
Urban RM, Jacobs JJ, Tomlinson MJ, Gavrilovic J, Black J, Peoc'h M (2000) Dissemination of wear particles to the liver, spleen, and abdominal lymph nodes of patients with hip or knee replacement. J Bone Jt Surg Am 82:457–476
Tower SS (2012) Arthroprosthetic cobaltism associated with metal on metal hip implants. BMJ 344:e430
Sharareh B, Phan DL, Goreal W, Schwarzkopf R (2015) Metallosis presenting as knee pain 26 years after primary total knee arthroplasty. J Orthop Case Rep 5:62–65
Luyet A, Fischer JF, Jolles BM, Lunebourg A (2015) Unexpected wear of an unicompartimental knee arthroplasty in oxidized zirconium. Acta Orthop Belg 81:790–795
Barba T, Wach J, Lustig S, Laurent F, Devouassoux-Shisheboran M, Valour F, Chidiac C, Ferry T (2015) Metallosis-associated prosthetic joint infection. Med Mal Infect 45:484–487
Helito CP, Buarque de Gusmao CV, Angelini FJ, Tirico LE, Pecora JR (2014) Severe metallosis following total knee arthroplasty: a case report and review of radiographic signs. Skelet Radiol 43:1169–1173
Apostolopoulos AP, Katsougrakis I, Fanous R, Harrison A, Saavedra E (2014) Severe metallosis following polyethylene dislocation in a mobile-bearing medial unicompartmental knee replacement. J Long Term Effects Med Implants 24:147–150
Bonutti PM, Pivec R, Issa K, Kapadia BH, Banerjee S, Harwin SF, Mont MA, Bauer TW (2013) Delamination of tantalum porous coating from a TKA due to regional dissemination of debris. Orthopedics 36:600–604
Breen DJ, Stoker DJ (1993) Titanium lines: a manifestation of metallosis and tissue response to titanium alloy megaprostheses at the knee. Clin Radiol 47:274–277
Buechel FF Sr (2002) Long-term followup after mobile-bearing total knee replacement. Clin Orthop Relat Res 404:40–50
Callender VD, Cardwell LA, Munhutu MN, Bigby U, Rodney IJ (2015) Cutaneous metallosis in patient with knee prosthesis composed of cobalt-chromium molybdenum alloy and titanium–aluminium–vanadium alloy. JAAD Case Rep 1:36–37
Chew FS, Ramsdell MG, Keel SB (1998) Metallosis after total knee replacement. AJR Am J Roentgenol 170:1556
Engh GA, Koralewicz LM, Pereles TR (2000) Clinical results of modular polyethylene insert exchange with retention of total knee arthroplasty components. J Bone Jt Surg Am 82:516–523
Foran JR, Brown NM, Della Valle CJ, Berger RA, Galante JO (2013) Long-term survivorship and failure modes of unicompartmental knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 471:102–108
Greco N, Berend K (2018) Polyethylene liner dislocation of fixed-bearing medial oxinium unicompartmental arthroplasty with severe metallosis. Knee 25:341–345
Ho J, Mahajan J, Taylor M, Byers A, Arauz P, Kwon YM (2018) Metallosis in cemented titanium alloy total knee arthroplasty without apparent metal-on-metal articulation. Knee 25:728–731
Jayasekera N, Gouk C, Patel A, Eyres K (2015) Apparent skin discoloration about the knee joint: a rare sequela of metallosis after total knee replacement. Case Rep Orthop 2015:891904
Kharrazi FD, Busfield BT, Khorshad DS, Hornicek FJ, Mankin HJ (2008) Knee mass from severe metallosis after failure of a metal-backed patellar component total knee arthroplasty. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ) 37:E38–41
Klontz KC, Smith WI, Jonathan CK (2014) Acute metallosis following total knee replacement—a case report. J Orthop Case Rep 4:21–23
La Verde L, Fenga D, Spinelli MS, Campo FR, Florio M, Rosa MA (2017) Catastrophic metallosis after tumoral knee prosthesis failure: a case report. Int J Surg Case Rep 30:9–12
Mavrogenis AF, Nomikos GN, Sakellariou VI, Karaliotas GI, Kontovazenitis P, Papagelopoulos PJ (2009) Wear debris pseudotumor following total knee arthroplasty: a case report. J Med Case Rep 3:9304
Meding JB, Ritter MA, Faris PM (2001) Total knee arthroplasty with 4.4 mm of tibial polyethylene: 10-year followup. Clin Orthop Relat Res 388:112–117
Mineta K, Okada M, Matsumoto S, Hamada D, Goto T, Sairyo K (2017) Fracture of the tibial baseplate 16 years after Miller-Galante II total knee arthroplasty. Case Rep Orthop 2017:4080816
Nasser S, Campbell PA, Kilgus D, Kossovsky N, Amstutz HC (1990) Cementless total joint arthroplasty prostheses with titanium-alloy articular surfaces. A human retrieval analysis. Clin Orthop Relat Res 261:171–185
Ottaviani G, Catagni MA, Matturri L (2005) Massive metallosis due to metal-on-metal impingement in substitutive long-stemmed knee prosthesis. Histopathology 46:237–238
Papagelopoulos PJ, Mavrogenis AF, Karamitros AE, Zahos KA, Nomikos G, Soucacos PN (2007) Distal leg wear debris mass from a rotating hinged knee prosthesis. J Arthroplasty 22:909–915
Pescador D, Calero-Paniagua I, Sánchez-González MD, Montilla C (2016) Metallosis as a cause of pain and inflammation in a patient with a knee replacement: a case description. Reumatol Clin 12:112–113
Rader CP, Lohr J, Wittmann R, Eulert J (1996) Results of total knee arthroplasty with a metal-backed patellar component: a 6-year follow-up study. J Arthroplasty 11:923–930
Rajgopal A, Panda I, Tyagi VC (2018) Early failure with massive metallosis and posteromedial wear following atraumatic anterior cruciate ligament rupture after medial unicompartmental knee arthroplasty. Arthroplasty Today 4:15–19
Romesburg JW, Wasserman PL, Schoppe CH (2010) Metallosis and metal-induced synovitis following total knee arthroplasty: review of radiographic and CT findings. J Radiol Case Rep 4:7–17
Saad AI, Shahban SA, Fernandes R (2018) Metallosis following a clip breakage in a total knee arthroplasty implant: a case report. World J Orthop 9:300–303
Sanchis-Alfonso V (2007) Severe metallosis after unicompartmental knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 15:361–364
Sivananthan S, Pirapat R, Goodman SB (2015) A rare case of pseudotumor formation following total knee arthroplasty. Malays Orthop J 9:44–46
Tan GM, Lynne G, Sarbjit S (2008) Osteolysis and wear debris after total knee arthroplasty presenting with extra-articular metallosis in the calf. J Arthroplasty 23:775–780
Vecchini E, Ditta A, Gelmini M, Maluta T, Valentini R, Ricci M, Magnan B (2019) Rupture of the femoral component and severe metallosis of the knee 10 years after unicompartmental knee arthroplasty (UKA): a case report. Acta Biomed 90:198–202
Vivegananthan B, Shah R, Karuppiah AS, Karuppiah SV (2014) Metallosis in a total knee arthroplasty. BMJ Case Rep 2014:bcr2013202801
Willis-Owen CA, Keene GC, Oakeshott RD (2011) Early metallosis-related failure after total knee replacement: a report of 15 cases. J Bone Jt Surg Br 93:205–209
Worland RL, Arredondo J, Angles F, Jessup DE (1998) Scintigraphic evaluation in total knee failure secondary to severe metallosis. J Arthroplasty 13:116–119
Niimi R, Hasegawa M, Sudo A, Uchida A (2007) A large metallic cyst caused by wear particles after total knee arthroplasty. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 127:51–54
Friesenbichler J, Schwarzkopf R, Sadoghi P, Marwin SE, Glehr M, Maurer-Ertl W, Leithner A (2012) Failure rate of a rotating hinge knee design due to yoke fracture of the hinged tibial insert: a retrospective data analysis and review of the literature. Int Orthop 36:993–998
Doorn PF, Mirra JM, Campbell PA, Amstutz HC (1996) Tissue reaction to metal on metal total hip prostheses. Clin Orthop Relat Res 329:S187–S205
Campbell P, Ebramzadeh E, Nelson S, Takamura K, De Smet K, Amstutz HC (2010) Histological features of pseudotumor-like tissues from metal-on-metal hips. Clin Orthop Relat Res 468:2321–2327
Magone K, Luckenbill D, Goswami T (2015) Metal ions as inflammatory initiators of osteolysis. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 135:683–695
Al SaffarRevell NPA (1994) Interleukin-1 production by activated macrophages surrounding loosened orthopaedic implants: a potential role in osteolysis. Br J Rheumatol 33:309–316
Kim KJ, Kobayashi Y, Itoh T (1998) Osteolysis model with continuous infusion of polyethylene particles. Clin Orthop Relat Res 352:46–52
Harris WH (1995) The problem is osteolysis. Clin Orthop Relat Res 311:46–53
Merritt K, Brown SA (1996) Distribution of cobalt chromium wear and corrosion products and biologic reactions. Clin Orthop Relat Res 329:S233–S243
Hozack WJ, Cole PA, Gardner R, Corces A (1990) Popliteal aneurysm after total knee arthroplasty. Case reports and review of the literature. J Arthroplasty 5:301–305
Akimoto M, Hara H, Suzuki H (2003) Metallosis of the skin mimicking malignant skin tumour. Br J Dermatol 149:653
Devlin JJ, Pomerleau AC, Brent J, Morgan BW, Deitchman S, Schwartz M (2013) Clinical features, testing, and management of patients with suspected prosthetic hip-associated cobalt toxicity: a systematic review of cases. J Med Toxicol 9:405–415
Su EP, Callander PW, Salvati EA (2003) The bubble sign: a new radiographic sign in total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 18:110–112
Ghanem E, Parvizi J, Burnett RS, Sharkey PF, Keshavarzi N, Aggarwal A, Barrack RL (2008) Cell count and differential of aspirated fluid in the diagnosis of infection at the site of total knee arthroplasty. J Bone Jt Surg Am 90:1637–1643
Jeong JH, Kang H, Ha YC, Jang EC (2012) Incarceration of a dislocated mobile bearing to the popliteal fossa after unicompartmental knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 27(323):e325–3327
Parks NL, Engh GA, Topoleski LD, Emperado J (1998) The Coventry Award. Modular tibial insert micromotion: a concern with contemporary knee implants. Clin Orthop Relat Res 356:10–15
Thienpont E (2013) Failure of tibial polyethylene insert locking mechanism in posterior stabilized arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 21:2685–2688
Bartel DL, Burstein AH, Santavicca EA, Insall JN (1982) Performance of the tibial component in total knee replacement. J Bone Jt Surg Am 64:1026–1033
Zambianchi F, Digennaro V, Giorgini A, Grandi G, Fiacchi F, Mugnai R, Catani F (2015) Surgeon's experience influences UKA survivorship: a comparative study between all-poly and metal back designs. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 23:2074–2080
Arredondo J, Worland RL, Jessup DE, Angles F (1997) Midterm results in metal-backed patella revisions for metallosis. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ) 26:598–600
Friesenbichler J, Sadoghi P, Maurer-Ertl W, Szkandera J, Glehr M, Ogris K, Wolf M, Weger C, Leithner A (2014) Serum metal ion concentrations in paediatric patients following total knee arthroplasty using megaprostheses. Biomed Res Int 2014:817257
Kurmis AP, Herman A, McIntyre AR, Masri BA, Garbuz DS (2019) Pseudotumors and high-grade aseptic lymphocyte-dominated vasculitis-associated lesions around total knee replacements identified at aseptic revision surgery: findings of a large-scale histologic review. J Arthroplasty 34:2434–2438
Funding
There is no funding source.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sahan, I., Anagnostakos, K. Metallosis after knee replacement: a review. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 140, 1791–1808 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-020-03560-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-020-03560-x