Abstract
Introduction
The purpose of the present study was to determine which factors affect the positional accuracy of iliosacral screws inserted using 3D fluoroscopic navigation. Specifically, we asked: (1) does the screw insertion angle in the coronal and axial planes affect the positional accuracy of iliosacral screw insertion using 3D fluoroscopic navigation? (2) Is the positional accuracy of iliosacral screw insertion using 3D fluoroscopic navigation affected by the type of screw (transsacral versus standard iliosacral), site of screw insertion (S1 versus S2), patient position (supine versus prone), presence of a dysmorphic sacrum, or AO/OTA classification (type B versus C)?
Materials and methods
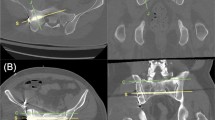
Twenty-seven patients with AO/OTA type B or C pelvic ring fracture were treated by percutaneous iliosacral screw fixation. A total of 55 screws were inserted into S1 or S2 using 3D fluoroscopic navigation combined with preoperative CT-based planning. The positional accuracy of screw placement was assessed by matching postoperative CT images with preoperative CT images. The distance between the central axis of the inserted screw and that of the planned screw placement was measured in the sagittal plane passing through the center of the vertebral body.
Results
The mean deviation between the planned and the inserted screw position was 2.9 ± 1.7 mm (range 0–8.5 mm) at the vertebral body center. Multiple regression analysis showed that the screw insertion angle relative to the vertical line of the bone surface in the axial plane (β = 0.354, p = 0.013) and the use of a transsacral screw (β = 0.317, p = 0.017) were correlated with the positional accuracy of screw placement (adjusted R2 = 0.276, p = 0.002).
Conclusions
A greater screw insertion angle relative to the vertical line on the bone surface and the use of transsacral screws increases the positional error of iliosacral screws inserted using 3D fluoroscopic navigation.
Level of evidence
Level IV, therapeutic study.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vanderschot PM, Broens PM, Vermeire JI, Broos PL (1999) Trans iliac-sacral-iliac bar stabilization to treat bilateral sacro-iliac joint disruptions. Injury 30(9):637–640
Matta JM, Saucedo T (1989) Internal fixation of pelvic ring fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res 242:83–97
Routt ML Jr, Kregor PJ, Simonian PT, Mayo KA (1995) Early results of percutaneous iliosacral screws placed with the patient in the supine position. J Orthop Trauma 9(3):207–214
Gardner MJ, Morshed S, Nork SE, Ricci WM, Chip Routt ML Jr (2010) Quantification of the upper and second sacral segment safe zones in normal and dysmorphic sacra. J Orthop Trauma 24(10):622–629. https://doi.org/10.1097/BOT.0b013e3181cf0404
van den Bosch EW, van Zwienen CM, van Vugt AB (2002) Fluoroscopic positioning of sacroiliac screws in 88 patients. J Trauma 53(1):44–48
Grossterlinden L, Rueger J, Catala-Lehnen P, Rupprecht M, Lehmann W, Rucker A, Briem D (2011) Factors influencing the accuracy of iliosacral screw placement in trauma patients. Int Orthop 35(9):1391–1396. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-010-1092-7
Takao M, Nishii T, Sakai T, Sugano N (2013) CT-3D-fluoroscopy matching navigation can reduce the malposition rate of iliosacral screw insertion for less-experienced surgeons. J Orthop Trauma 27(12):716–721. https://doi.org/10.1097/BOT.0b013e31828fc4a5
Zwingmann J, Hauschild O, Bode G, Sudkamp NP, Schmal H (2013) Malposition and revision rates of different imaging modalities for percutaneous iliosacral screw fixation following pelvic fractures: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 133(9):1257–1265. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-013-1788-4
Marsh JL, Slongo TF, Agel J, Broderick JS, Creevey W, DeCoster TA, Prokuski L, Sirkin MS, Ziran B, Henley B, Audige L (2007) Fracture and dislocation classification compendium—2007: orthopaedic trauma association classification, database and outcomes committee. J Orthop Trauma 21(10 Suppl):S1–S133
Takao M, Nishii T, Sakai T, Sugano N (2014) Navigation-aided visualization of lumbosacral nerves for anterior sacroiliac plate fixation: a case report. Int J Med Robot + Comput Assist Surg: MRCAS 10(2):230–236. https://doi.org/10.1002/rcs.1556
Routt ML Jr, Simonian PT, Agnew SG, Mann FA (1996) Radiographic recognition of the sacral alar slope for optimal placement of iliosacral screws: a cadaveric and clinical study. J Orthop Trauma 10(3):171–177
Takao M, Nishii T, Sakai T, Yoshikawa H, Sugano N (2014) Iliosacral screw insertion using CT-3D-fluoroscopy matching navigation. Injury 45(6):988–994. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.injury.2014.01.015
Smith HE, Yuan PS, Sasso R, Papadopolous S, Vaccaro AR (2006) An evaluation of image-guided technologies in the placement of percutaneous iliosacral screws. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 31(2):234–238
Zwingmann J, Konrad G, Kotter E, Sudkamp NP, Oberst M (2009) Computer-navigated iliosacral screw insertion reduces malposition rate and radiation exposure. Clin Orthop Relat Res 467(7):1833–1838. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-008-0632-6
Zwingmann J, Konrad G, Mehlhorn AT, Sudkamp NP, Oberst M (2010) Percutaneous iliosacral screw insertion: malpositioning and revision rate of screws with regards to application technique (navigated vs. Conventional). J Trauma 69(6):1501–1506. https://doi.org/10.1097/TA.0b013e3181d862db
Matityahu A, Kahler D, Krettek C, Stockle U, Grutzner PA, Messmer P, Ljungqvist J, Gebhard F (2014) Three-dimensional navigation is more accurate than two-dimensional navigation or conventional fluoroscopy for percutaneous sacroiliac screw fixation in the dysmorphic sacrum: a randomized multicenter study. J Orthop Trauma 28(12):707–710. https://doi.org/10.1097/bot.0000000000000092
Thakkar SC, Thakkar RS, Sirisreetreerux N, Carrino JA, Shafiq B, Hasenboehler EA (2017) 2D versus 3D fluoroscopy-based navigation in posterior pelvic fixation: review of the literature on current technology. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg 12(1):69–76. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-016-1465-5
Richter PH, Gebhard F, Dehner C, Scola A (2016) Accuracy of computer-assisted iliosacral screw placement using a hybrid operating room. Injury 47(2):402–407. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.injury.2015.11.023
Grossterlinden L, Nuechtern J, Begemann PG, Fuhrhop I, Petersen JP, Ruecker A, Rupprecht M, Lehmann W, Schumacher U, Rueger JM, Briem D (2011) Computer-assisted surgery and intraoperative three-dimensional imaging for screw placement in different pelvic regions. J Trauma 71(4):926–932. https://doi.org/10.1097/TA.0b013e31820333dd
Acknowledgements
We thank Prof. Hideki Yoshikawa from Osaka University for his advice and criticism and Kelly Zammit, BVSc, from Edanz Group (http://www.edanzediting.com/ac), for editing a draft of this manuscript.
Funding
No funding was received for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
For this type of study, formal consent is not required.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Takao, M., Hamada, H., Sakai, T. et al. Factors influencing the accuracy of iliosacral screw insertion using 3D fluoroscopic navigation. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 139, 189–195 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-018-3055-1
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-018-3055-1