Abstract
Objective
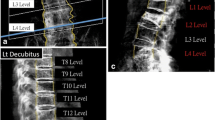
Radiologic parameters are important factors for planning the treatment for thoracolumbar fracture. However, we noted that measurements of the degree of kyphosis by lateral decubitus plain radiography were greater than supine CT. The cause of this discrepancy is unclear.
Methods
We retrospectively reviewed the plain radiographs and CT scans of 90 patients with thoracolumbar fractures (fracture group). We measured the segmental sagittal angle (SSA) on lateral decubitus plain radiographs and in the median sagittal plane on CT scans obtained in the supine position. The method agreement (plain radiography versus CT) was determined by utilizing Bland–Altman plots. For the purpose of comparison, the same analyses were performed in a group of age and sex-matched controls (normal group). After establishing the method disagreement in the fracture group, the factors that contributed to the difference in the SSA between plain radiography and CT, as well as their threshold values, were determined.
Results
On Bland–Altman plots for the fracture group, the mean difference was 4.53° [95% confidence interval (CI) − 4.87° to 13.93°]. For the normal group, the mean difference was − 0.64° (95% CI − 5.87° to 4.58°). On univariate analysis, male sex, thoracolumbar level, and SSA(X) were significant factors associated with ∆SSA (P = 0.03, 0.002, and 0.000, respectively). Multivariable regression analysis showed that SSA(X) was the only significant factor. Receiver operating characteristic curve analysis indicated that the optimal threshold of SSA(X) was 17° with a sensitivity of 78% and a specificity of 75% (area under curve: 0.752).
Conclusions
The mean SSA determined on lateral decubitus plain radiographs indicated significantly more kyphosis than that determined on CT images obtained in supine position. When the SSA on plain radiography is more than 17°, there might be a significant discrepancy between the two imaging modalities. This discrepancy seems to be mainly attributable to the difference in patient positioning (lateral decubitus position for plain radiography versus supine position for CT imaging).







Similar content being viewed by others
References
el-Khoury GY, Kathol MH, Daniel WW (1995) Imaging of acute injuries of the cervical spine: value of plain radiography, CT, and MR imaging. Am J Roentgenol 164:43–50. https://doi.org/10.2214/ajr.164.1.7998567
Stewart BG, Rhea JT, Sheridan RL, Novelline RA (2002) Is the screening portable pelvis film clinically useful in multiple trauma patients who will be examined by abdominopelvic CT? Experience with 397 patients. Emerg Radiol 9:266–271. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10140-002-0232-9
McCulloch PT, France J, Jones DL, Krantz W, Nguyen T-P, Chambers C et al (2005) Helical computed tomography alone compared with plain radiographs with adjunct computed tomography to evaluate the cervical spine after high-energy trauma. J Bone Jt Surg Am 87:2388–2394. https://doi.org/10.2106/JBJS.E.00208
Berry GE, Adams S, Harris MB, Boles CA, McKernan MG, Collinson F et al (2005) Are plain radiographs of the spine necessary during evaluation after blunt trauma? Accuracy of screening torso computed tomography in thoracic/lumbar spine fracture diagnosis. J Trauma 59:1410–1413 (discussion 1413)
Hauser CJ, Visvikis G, Hinrichs C, Eber CD, Cho K, Lavery RF et al (2003) Prospective validation of computed tomographic screening of the thoracolumbar spine in trauma. J Trauma 55:228–234. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.TA.0000076622.19246.CF (discussion 234–235)
Ballock RT, Mackersie R, Abitbol JJ, Cervilla V, Resnick D, Garfin SR (1992) Can burst fractures be predicted from plain radiographs? J Bone Jt Surg Br 74:147–150
Campbell SE, Phillips CD, Dubovsky E, Cail WS, Omary RA (1995) The value of CT in determining potential instability of simple wedge-compression fractures of the lumbar spine. Am J Neuroradiol 16:1385–1392
Dai L-Y, Wang X-Y, Jiang L-S, Jiang S-D, Xu H-Z (2008) Plain radiography versus computed tomography scans in the diagnosis and management of thoracolumbar burst fractures. Spine 33:E548–E552
Abdel MP, Bodemer WS, Anderson PA (2012) Supine thoracolumbar sagittal spine alignment: comparing computerized tomography and plain radiographs. Spine 37:340–345. https://doi.org/10.1097/BRS.0b013e31821946d1
Epstein O, Ludwig S, Gelb D, Poelstra K, O’Brien J (2009) Comparison of computed tomography and plain radiography in assessing traumatic spinal deformity. J Spinal Disord Tech 22:197–201
Vaccaro AR, Oner C, Kepler CK, Dvorak M, Schnake K, Bellabarba C et al (2013) AOSpine thoracolumbar spine injury classification system: fracture description, neurological status and key modifiers. Spine 38:2028–2037. https://doi.org/10.1097/BRS.0b013e3182a8a381
Kuklo TR, Polly DW, Owens BD, Zeidman SM, Chang AS, Klemme WR (2001) Measurement of thoracic and lumbar fracture kyphosis: evaluation of intraobserver, interobserver, and technique variability. Spine 26:61–65 (discussion 66)
Shrout PE, Fleiss JL (1979) Intraclass correlations: uses in assessing rater reliability. Psychol Bull 86:420–428
Adam CJ, Izatt MT, Harvey JR, Askin GN (2005) Variability in Cobb angle measurements using reformatted computerized tomography scans. Spine 30:1664–1669
Farcy JP, Weidenbaum M, Glassman SD (1990) Sagittal index in management of thoracolumbar burst fractures. Spine 15:958–965
Malcolm BW, Bradford DS, Winter RB, Chou SN (1981) Post-traumatic kyphosis. A review of forty-eight surgically treated patients. J Bone Jt Surg Am 63:891–899
McAfee PC, Yuan HA, Fredrickson BE, Lubicky JP (1983) The value of computed tomography in thoracolumbar fractures. An analysis of one hundred consecutive cases and a new classification. J Bone Jt Surg Am 65:461–473
Lee JY, Vaccaro AR, Schweitzer KM, Lim MR, Baron EM, Rampersaud R et al (2007) Assessment of injury to the thoracolumbar posterior ligamentous complex in the setting of normal-appearing plain radiography. Spine J 7:422–427. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spinee.2006.07.014
Rihn JA, Yang N, Fisher C, Saravanja D, Smith H, Morrison WB et al (2010) Using magnetic resonance imaging to accurately assess injury to the posterior ligamentous complex of the spine: a prospective comparison of the surgeon and radiologist: clinical article. J Neurosurg Spine 12:391–396
Funding
There is no funding source.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, YM., Choi, SM. & Ahn, MY. Comparison of sagittal values between lateral decubitus plain radiography and supine computed tomography in thoracolumbar fractures: a greater degree of kyphosis is observed in plain radiography than CT. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 138, 745–755 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-018-2889-x
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-018-2889-x