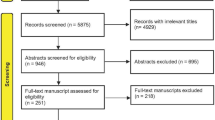
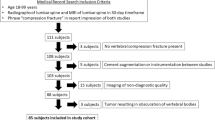
Abstract
Study design
Radiological study.
Purpose
To asses standard values, intra- and interobserver reliability and reproducibility of sacral slope (SS) and lumbar lordosis (LL) and the correlation of these parameters in patients with lumbar spinal stenosis (LSS).
Methods
Anteroposterior and lateral X-rays of the lumbar spine of 102 patients with LSS were included in this retrospective, radiologic study. Measurements of SS and LL were carried out by five examiners. Intraobserver correlation and correlation between LL and SS were calculated with Pearson’s r linear correlation coefficient and intraclass correlation coefficients (ICC) were calculated for inter- and intraobserver reliability. In addition, patients were examined in subgroups with respect to previous surgery and the current therapy.
Results
Lumbar lordosis averaged 45.6° (range 2.5°–74.9°; SD 14.2°), intraobserver correlation was between Pearson r = 0.93 and 0.98. The measurement of SS averaged 35.3° (range 13.8°–66.9°; SD 9.6°), intraobserver correlation was between Pearson r = 0.89 and 0.96. Intraobserver reliability ranged from 0.966 to 0.992 ICC in LL measurements and 0.944–0.983 ICC in SS measurements. There was an interobserver reliability ICC of 0.944 in LL and 0.990 in SS. Correlation between LL and SS averaged r = 0.79. No statistically significant differences were observed between the analyzed subgroups.
Conclusion
Manual measurement of LL and SS in patients with LSS on lateral radiographs is easily performed with excellent intra- and interobserver reliability. Correlation between LL and SS is very high. Differences between patients with and without previous decompression were not statistically significant.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arbit E, Pannullo S (2001) Lumbar stenosis: a clinical review. Clin Orthop Relat Res 384:137–143
Barrey C, Jund J, Noseda O, Roussouly P (2007) Sagittal balance of the pelvis-spine complex and lumbar degenerative diseases. A comparative study about 85 cases. Eur Spine J Off Publ Eur Spine Soc Eur Spinal Deform Soc Eur Sect Cerv Spine Res Soc 16(9):1459–1467. doi:10.1007/s00586-006-0294-6
Berthonnaud E, Labelle H, Roussouly P, Grimard G, Vaz G, Dimnet J (2005) A variability study of computerized sagittal spinopelvic radiologic measurements of trunk balance. J Spinal Disord Tech 18(1):66–71
Boulay C, Tardieu C, Hecquet J, Benaim C, Mouilleseaux B, Marty C, Prat-Pradal D, Legaye J, Duval-Beaupere G, Pelissier J (2006) Sagittal alignment of spine and pelvis regulated by pelvic incidence: standard values and prediction of lordosis. Eur Spine J Off Publ Eur Spine Soc Eur Spinal Deform Soc Eur Sect Cerv Spine Res Soc 15(4):415–422. doi:10.1007/s00586-005-0984-5
Dimar JR 2nd, Carreon LY, Labelle H, Djurasovic M, Weidenbaum M, Brown C, Roussouly P (2008) Intra- and inter-observer reliability of determining radiographic sagittal parameters of the spine and pelvis using a manual and a computer-assisted methods. Eur Spine J Off Publ Eur Spine Soc Eur Spinal Deform Soc Eur Sect Cerv Spine Res Soc 17(10):1373–1379. doi:10.1007/s00586-008-0755-1
Gardocki RJ, Watkins RG, Williams LA (2002) Measurements of lumbopelvic lordosis using the pelvic radius technique as it correlates with sagittal spinal balance and sacral translation. Spine J Off J N Am Spine Soc 2(6):421–429
Gelb DE, Lenke LG, Bridwell KH, Blanke K, McEnery KW (1995) An analysis of sagittal spinal alignment in 100 asymptomatic middle and older aged volunteers. Spine 20(12):1351–1358
Glassman SD, Bridwell K, Dimar JR, Horton W, Berven S, Schwab F (2005) The impact of positive sagittal balance in adult spinal deformity. Spine 30(18):2024–2029
Hong JY, Suh SW, Modi HN, Hur CY, Yang JH, Song HR (2010) Correlation of pelvic orientation with adult scoliosis. J Spinal Disord Tech 23(7):461–466. doi:10.1097/BSD.0b013e3181bf1a85
Jackson RP, Hales C (2000) Congruent spinopelvic alignment on standing lateral radiographs of adult volunteers. Spine 25(21):2808–2815
Jackson RP, Peterson MD, McManus AC, Hales C (1998) Compensatory spinopelvic balance over the hip axis and better reliability in measuring lordosis to the pelvic radius on standing lateral radiographs of adult volunteers and patients. Spine 23(16):1750–1767
Jang JS, Lee SH, Min JH, Han KM (2007) Lumbar degenerative kyphosis: radiologic analysis and classifications. Spine 32(24):2694–2699. doi:10.1097/BRS.0b013e31815a590b
Kim YJ, Bridwell KH, Lenke LG, Rhim S, Cheh G (2006) An analysis of sagittal spinal alignment following long adult lumbar instrumentation and fusion to L5 or S1: can we predict ideal lumbar lordosis? Spine 31(20):2343–2352. doi:10.1097/01.brs.0000238970.67552.f5
Kumar MN, Baklanov A, Chopin D (2001) Correlation between sagittal plane changes and adjacent segment degeneration following lumbar spine fusion. Eur Spine J Off Publ Eur Spine Soc Eur Spinal Deform Soc Eur Sect Cerv Spine Res Soc 10(4):314–319
Lachin JM (2004) The role of measurement reliability in clinical trials. Clin Trials 1(6):553–566
Lazennec JY, Brusson A, Rousseau MA (2011) Hip-spine relations and sagittal balance clinical consequences. Eur Spine J Off Publ Eur Spine Soc Eur Spinal Deform Soc Eur Sect Cerv Spine Res Soc 20(Suppl 5):686–698. doi:10.1007/s00586-011-1937-9
Legaye J, Duval-Beaupere G, Hecquet J, Marty C (1998) Pelvic incidence: a fundamental pelvic parameter for three-dimensional regulation of spinal sagittal curves. Eur Spine J Off Publ Eur Spine Soc Eur Spinal Deform Soc Eur Sect Cerv Spine Res Soc 7(2):99–103
Mac-Thiong JM, Labelle H, Berthonnaud E, Betz RR, Roussouly P (2007) Sagittal spinopelvic balance in normal children and adolescents. Eur Spine J Off Publ Eur Spine Soc Eur Spinal Deform Soc Eur Sect Cerv Spine Res Soc 16(2):227–234. doi:10.1007/s00586-005-0013-8
Milne JS, Lauder IJ (1974) Age effects in kyphosis and lordosis in adults. Ann Hum Biol 1(3):327–337
Rajnics P, Templier A, Skalli W, Lavaste F, Illes T (2002) The association of sagittal spinal and pelvic parameters in asymptomatic persons and patients with isthmic spondylolisthesis. J Spinal Disord Tech 15(1):24–30
Roussouly P, Gollogly S, Berthonnaud E, Dimnet J (2005) Classification of the normal variation in the sagittal alignment of the human lumbar spine and pelvis in the standing position. Spine 30(3):346–353
Roussouly P, Pinheiro-Franco JL (2011) Biomechanical analysis of the spino-pelvic organization and adaptation in pathology. Eur Spine J Off Publ Eur Spine Soc Eur Spinal Deform Soc Eur Sect Cerv Spine Res Soc 20(Suppl 5):609–618. doi:10.1007/s00586-011-1928-x
Song KS, Piyaskulkaew C, Chuntarapas T, Buchowski JM, Kim HJ, Park MS, Kang H, Riew KD (2014) Dynamic radiographic criteria for detecting pseudarthrosis following anterior cervical arthrodesis. J Bone Joint Surg Am 96(7):557–563. doi:10.2106/JBJS.M.00167
Spivak JM (1998) Degenerative lumbar spinal stenosis. J Bone Joint Surg Am 80(7):1053–1066
Stagnara P, De Mauroy JC, Dran G, Gonon GP, Costanzo G, Dimnet J, Pasquet A (1982) Reciprocal angulation of vertebral bodies in a sagittal plane: approach to references for the evaluation of kyphosis and lordosis. Spine 7(4):335–342
Vaz G, Roussouly P, Berthonnaud E, Dimnet J (2002) Sagittal morphology and equilibrium of pelvis and spine. Eur Spine J Off Publ Eur Spine Soc Eur Spinal Deform Soc Eur Sect Cerv Spine Res Soc 11(1):80–87
Vialle R, Levassor N, Rillardon L, Templier A, Skalli W, Guigui P (2005) Radiographic analysis of the sagittal alignment and balance of the spine in asymptomatic subjects. J Bone Joint Surg Am 87(2):260–267. doi:10.2106/JBJS.D.02043
Wang Z, Parent S, de Guise JA, Labelle H (2010) A variability study of computerized sagittal sacral radiologic measures. Spine 35(1):71–75. doi:10.1097/BRS.0b013e3181bc9436
Wiltse LL, Winter RB (1983) Terminology and measurement of spondylolisthesis. J Bone Joint Surg Am 65(6):768–772
Wu W, Liang J, Du Y, Tan X, Xiang X, Wang W, Ru N, Le J (2014) Reliability and reproducibility analysis of the Cobb angle and assessing sagittal plane by computer-assisted and manual measurement tools. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 15:33. doi:10.1186/1471-2474-15-33
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bredow, J., Oppermann, J., Scheyerer, M.J. et al. Lumbar lordosis and sacral slope in lumbar spinal stenosis: standard values and measurement accuracy. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 135, 607–612 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-015-2184-z
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-015-2184-z