Abstract
Introduction
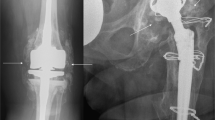
The present study investigated the incidence and risk factors of heterotopic ossification (HO) after implantation of knee prosthesis.
Materials and methods
We undertook a retrospective cohort study in 434 cases (363 patients) treated with a total knee replant using a Press-Fit-Condylar (P.F.C.®Sigma®) prosthesis. The occurrence of HO in radiograph after a follow-up period of 11.2 ± 2.4 months was correlated in a regression model with a variety of influencing factors.
Results
21 patients (4.8 %) developed heterotopic ossifications, all located in the area of the distal femur. The only risk factor found concerning the development of HO was osteoarthritis when compared to rheumatoid arthritis (OR = 4.07, 95 % CI 1.18–14.05; p = 0.0201) and postoperative wound healing problems (OR = 11.32, 95 % CI 3.26–39.33; p = 0.0001). Notching (OR = 2.22, 95 % CI 0.92–5.36; p = 0.0765) and osteophyte forming (hypertrophic) arthrosis (OR = 2.40, 95 % CI 0.97–5.95; p = 0.0596), however, were associated with the development of a bony spur in the contact area of the femoral component of the prosthesis.
Conclusions
Our study has revealed that patients with rheumatoid arthritis are at lower risk of HO than patients with osteoarthritis. An impairment of wound healing would appear to promote the development of a HO. Notching and hypertrophic arthrosis are highly likely to be associated with the development of a bony spur in the ventral contact area of the prosthesis.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nunley RM, Zhu J, Clohisy JC, Barrack RL (2011) Aspirin decreases heterotopic ossification after hip resurfacing. Clin Orthop Relat Res 469(6):1614–1620. doi:10.1007/s11999-011-1846-6 (Epub 2011/03/17)
Shields JS, Mofidi A, Ward WG, Jinnah RH (2011) Does a plastic drape reduce incidence of heterotopic ossification after hip resurfacing? Clin Orthop Relat Res 469(6):1606–1613. doi:10.1007/s11999-010-1606-z (Epub 2010/10/05)
Board TN, Karva A, Board RE, Gambhir AK, Porter ML (2007) The prophylaxis and treatment of heterotopic ossification following lower limb arthroplasty. J Bone Jt Surg Br Vol 89(4):434–440. doi:10.1302/0301-620X.89B4.18845 (Epub 2007/04/28)
Eulert J, Knelles D, Barthel T (1997) Heterotopic ossifications. Der Unfallchirurg 100(8):667–674 (Epub 1997/08/01. Heterotope Ossifikationen)
Kölbl O, Barthel T, Krödel A, Seegenschmiedt MH (2003) Prävention von heterotopen Ossifikationen nach Totalendoprothese des Hüftgelenkes. Dtsch Arztebl 100(45):2944–2954 (Epub 2003/07/28)
Hierton C (1983) Regional blood flow in experimental myositis ossificans. A microsphere study in conscious rabbits. Acta Orthop Scand 54(1):58–63 (Epub 1983/02/01)
Eggli S, Woo A (2001) Risk factors for heterotopic ossification in total hip arthroplasty. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 121(9):531–535. doi:10.1007/s004020100287 (Epub 2001/10/16)
Harwin SF, Stein AJ, Stern RE, Kulick RG (1993) Heterotopic ossification following primary total knee arthroplasty. J Arthrop 8(2):113–116 (Epub 1993/04/01)
Rader CP, Barthel T, Haase M, Scheidler M, Eulert J (1997) Heterotopic ossification after total knee arthroplasty. 54/615 cases after 1–6 years’ follow-up. Acta Orthop Scand 68(1):46–50 (Epub 1997/02/01)
Iorio R, Healy WL (2002) Heterotopic ossification after hip and knee arthroplasty: risk factors, prevention, and treatment. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 10(6):409–416 (Epub 2002/12/10)
Figgie HE 3rd, Goldberg VM, Heiple KG, Moller HS 3rd, Gordon NH (1986) The incidence and significance of heterotopic ossification following total knee arthroplasty. Adv Orthop Surg 10:12–17
Furia JP, Pellegrini VD Jr (1995) Heterotopic ossification following primary total knee arthroplasty. J Arthrop 10(4):413–419. doi:10.1016/S0883-5403(05)80139-1 (Epub 1995/08/01)
Sterner T, Saxler G, Barden B (2005) Limited range of motion caused by heterotopic ossifications in primary total knee arthroplasty: a retrospective study of 27/191 cases. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 125(3):188–192. doi:10.1007/s00402-005-0797-3 (Epub 2005/02/03)
Barrack RL, Brumfield CS, Rorabeck CH, Cleland D, Myers L (2002) Heterotopic ossification after revision total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 404:208–213 (Epub 2002/11/20)
Hasegawa M, Ohashi T, Uchida A (2002) Heterotopic ossification around distal femur after total knee arthroplasty. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 122(5):274–278. doi:10.1007/s00402-001-0377-0 (Epub 2002/06/19)
Goel A, Sharp DJ (1991) Heterotopic bone formation after hip replacement. The influence of the type of osteoarthritis. J Bone Jt Surg Br Vol 73(2):255–257 (Epub 1991/03/01)
Lovelock JE, Griffiths HJ, Silverstein AM, Anson PS (1984) Complications of total knee replacement. AJR Am J Roentgenol 142(5):985–992 (Epub 1984/05/01)
Atamaz F, Aydogdu S, Hepguler S, Sur H (2006) Heterotopic ossification after total knee arthroplasty. Acta Orthop et Traumatol Turc 40(3):202–206 (Epub 2006/08/15. Total diz artroplastisi sonrasi heterotopik ossifikasyon)
Chidel MA, Suh JH, Matejczyk MB (2001) Radiation prophylaxis for heterotopic ossification of the knee. J Arthrop 16(1):1–6. doi:10.1054/arthr.2001.16492 (Epub 2001/02/15)
Rath EM, Russell GV Jr, Washington WJ, Routt ML Jr (2002) Gluteus minimus necrotic muscle debridement diminishes heterotopic ossification after acetabular fracture fixation. Injury 33(9):751–756 (Epub 2002/10/16)
Daluga D, Lombardi AV Jr, Mallory TH, Vaughn BK (1991) Knee manipulation following total knee arthroplasty. Analysis of prognostic variables. J Arthrop 6(2):119–128 (Epub 1991/06/11)
Thienpont E, Schmalzried T, Bellemans J (2006) Ankylosis due to heterotopic ossification following primary total knee arthroplasty. Acta Orthop Belg 72(4):502–506 (Epub 2006/10/03)
Acknowledgements
We thank Prof. Kreitner, Institute for Radiology at the Mainz University Medical Centre for his support with radiological questions.
Conflict of interest
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Roth, K.E., Salzmann, G., Maier, G.S. et al. Risk factors for heterotopic ossification and spur formation after total knee arthroplasty. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 134, 991–996 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-014-1957-0
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-014-1957-0