Abstract
Objective
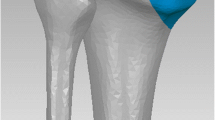
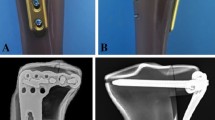
This study evaluates a proximally angulated cortical screw forming a triangular construct in lateral locking plates of comminuted intraarticular tibial plateau fractures.
Methods
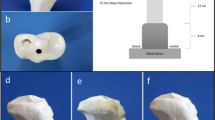
Sixteen composite tibiae were used for the fracture model and a complete articular fracture of the proximal tibia (AO 41.C2) was performed. A compression force was applied to the medial tibial plateau with an alternating, stepwise loading: 250 N–10 N–300 N–10 N–350 N–10 N–400 N. The relative motion between the different fragments of each sample was measured using a contactless, 3-dimensional digital image correlation system.
Results
Between the medial and lateral condyle, elastic as well as plastic shear was significantly lower using the triangular support screw (p < 0.05). In the metaphyseal region, elastic deformation remained identical, independent of the screw positioning. However, plastic deformation (varus collapse) was significantly reduced by 30–40% using a triangular support screw at higher compression forces (>300 N; p < 0.05).
Conclusion
Based on the results of this study, the use of a triangular support screw in metaphyseal comminuted tibial plateau fractures might enhance fracture stability. However, further studies are necessary to prove these biomechanical results in composite bone.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barei DP, Nork SE, Mills WJ et al (2004) Complications associated with internal fixation of high-energy bicondylar tibial plateau fractures utilizing a two-incision technique. J Orthop Trauma 18(10):649–657
Cole PA, Zlowodzki M, Kregor PJ (2004) Treatment of proximal tibia fractures using the less invasive stabilization system: surgical experience and early clinical results in 77 fractures. J Orthop Trauma 18(8):528–535
Horwitz DS, Bachus KN, Craig MA et al (1999) A biomechanical analysis of internal fixation of complex tibial plateau fractures. J Orthop Trauma 13(8):545–549
Koval KJ, Polatsch D, Kummer FJ et al (1996) Split fractures of the lateral tibial plateau: evaluation of three fixation methods. J Orthop Trauma 10(5):304–308
Moore TM, Patzakis MJ, Harvey JP (1987) Tibial plateau fractures: definition, demographics, treatment rationale, and long-term results of closed traction management or operative reduction. J Orthop Trauma 1(2):97–119
Young MJ, Barrack RL (1994) Complications of internal fixation of tibial plateau fractures. Orthop Rev 23(2):149–154
Gosling T, Schandelmaier P, Marti A et al (2004) Less invasive stabilization of complex tibial plateau fractures: a biomechanical evaluation of a unilateral locked screw plate and double plating. J Orthop Trauma 18(8):546–551
Karunakar MA, Egol KA, Peindl R et al (2002) Split depression tibial plateau fractures: a biomechanical study. J Orthop Trauma 16(3):172–177
Egol KA, Su E, Tejwani NC et al (2004) Treatment of complex tibial plateau fractures using the less invasive stabilization system plate: clinical experience and a laboratory comparison with double plating. J Trauma 57(2):340–346
Higgins TF, Klatt J, Bachus KN (2007) Biomechanical analysis of bicondylar tibial plateau fixation: how does lateral locking plate fixation compare to dual plate fixation? J Orthop Trauma 21(5):301–306
Gosling T, Schandelmaier P, Muller M et al (2005) Single lateral locked screw plating of bicondylar tibial plateau fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res 439:207–214
Barei DP, Nork SE, Mills WJ et al (2006) Functional outcomes of severe bicondylar tibial plateau fractures treated with dual incisions and medial and lateral plates. J Bone Joint Surg Am 88(8):1713–1721
Haidukewych G, Sems SA, Huebner D et al (2007) Results of polyaxial locked-plate fixation of periarticular fractures of the knee. J Bone Joint Surg Am 89(3):614–620
Mueller KL, Karunakar MA, Frankenburg EP et al (2003) Bicondylar tibial plateau fractures: a biomechanical study. Clin Orthop Relat Res 412:189–195
Ratcliff JR, Werner FW, Green JK et al (2007) Medial buttress versus lateral locked plating in a cadaver medial tibial plateau fracture model. J Orthop Trauma 21(7):444–448
Stoffel K, Lorenz KU, Kuster MS (2007) Biomechanical considerations in plate osteosynthesis: the effect of plate-to-bone compression with and without angular screw stability. J Orthop Trauma 21(6):362–368
Berend ME, Small SR, Ritter MA et al (2010) The effects of bone resection depth and malalignment on strain in the proximal tibia after total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 25(2):314–318
Hulet C, Sabatier JP, Souquet D et al (2002) Distribution of bone mineral density at the proximal tibia in knee osteoarthritis. Calcif Tissue Int 71(4):315–322
Acknowledgments
No other financial support was received by the authors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Implants used in this study were donated by Zimmer, Inc., Switzerland.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baumann, P., Ebneter, L., Giesinger, K. et al. A triangular support screw improves stability for lateral locking plates in proximal tibial fractures with metaphyseal comminution: a biomechanical analysis. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 131, 815–821 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-010-1243-8
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-010-1243-8