Abstract
Introduction
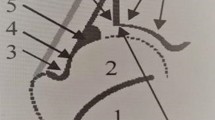
Ultrasound examination of infant hips is a widely used and accepted tool for the diagnosis and monitoring of developmental dysplasia of the hip. Its use and timing is still a focus of debate and its diagnostic accuracy has not been fully investigated.
Method
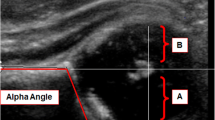
We have compared the ultrasound findings by the Graf technique with radiographic appearance (acetabular index) at 6 months of age.
Result
The negative predictive value of Ultrasound for DDH was 98% and was unaffected by the timing of the examination. The specificity and accuracy of the examination increased with age and was highest at 3 months of age.
Conclusion
Ultrasound examination of the infant hip by the static Graf technique is a safe and effective screening tool for the evaluation of DDH.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Woolacott NF, Puhan MA, Steurer J, Kleignen J (2005) Ultrasonography in the screening for developmental dysplasia of the hip in newborns: systematic review. BMJ 330:1413–1418
Graf R (1984) Classification of hip joint dysplasia by means of sonography. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 102:248–255
Harcke HT, Grisom LE (1990) Performing dynamic sonography of the infant hip. Am J Roentgenol 155:837–844
Terjesen T, Runden TO, Tangerud A (1989) Ultrasonography and radiography of the hip in infants. Acta Orthop Scand 60:651–660
General Register Office for Scotland. http://www.gro-scotland.gov.uk/
Schwend RM, Schoenecker P, Richards BS, Flynn J, Vitale M (2007) Screening the newborn for DDH: now what do we do? J Paediart Orthop 27(6):607–610
Screening for developmental dysplasia of the hip: recommendation statement. US Preventive Services Task Force. Pediatrics 2006; 117(3):898–902
Macpherson K (2006) Screening hips of newborns in Scotland. A Health Technology Assessment scoping report. NHS Quality Improvement Scotland 2006. http://www.nhshealthquality.org/nhsqis/files/HipHTA_ScopingReport.pdf
Eidelman M, Katzman A, Frieman S (1997) Management of dislocated hips with Pavlik harness treatment and ultrasound monitoring. J Paediat Orthop 17:189–198
Luhmann SJ, Bassett GS, Gordon JE, Schootman M, Schoenecker PL (2003) Reduction of a dislocation of the hip due to developmental dysplasia. Implications for the need for future surgery. J Bone Joint Surg Am 85-A(2):239–243
Grill F, Benshel H, Canadell J (1988) The Pavlik harness in the treatment of congenital dislocating hip: report on a multicenter study of the European Paediatric Orthopaedic Society. J Pediatr Orthop 8:1–8
Portinaro NM, Pelillo F, Cerutti P (2007) The role of ultrasonography in the diagnosis of developmental dysplasia of the hip. J Pediatr Orthop 27(2):247–250
Baronciani D, Atti G, Andiloro F, Bartesaghi A, Gagliardi L, Passamonti C, Petrone M, Collaborative Group DDH Project (1997) Screening for developmental dysplasia of the hip: from theory to practice. Peadiatrics 99(2):e5
Laurenson RD (1959) The acetabular index. A critical review. J Bone Joint Surg 41(B):702–710
Koven B, Koven MT (1949) Early dysplasias of the hip. Arch Paediatr 66:201
Martin HE (1951) Geometrical–Anatomical factors and their significance in the early X ray diagnosis of of hip joint disease in children. Radiology 56:842
Colonna PC (1953) Recognition and treatment of hip dysplasia in the infant. Surg Clin North Am 33:1.633
Nimityongskul P, Hudgens RA, Anderson LD, Melhem RE, Green AE, Saleeb SF (1995) Ultrasonography in the management of developmental dysplasia of the hip. J Pediatr Orthop 15(6):741–746
Hensinger RN (1995) The changing role of ultrasound in the management of developmental dysplasia of the Hip. J Pediatr Orthop 15(6):723–724
Stein-Zamir C, Volovik I, Rishpon S, Sabi R (2008) Developmental dysplasia of the hip: risk markers, clinical screening and outcome. Paediatr Int 50(3):341–345
Tonnis D (1976) Nornal values of the hip jint for the evaluation of X rays in children and adults. Clin Orthop Relat Res 19:39–47
Graf R (1980) The diagnosis of congenital hip-joint dislocation by the ultrasound compound treatment. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 97:117–133
Committee on Quality Improvement, Subcommittee on Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip. American Academy of Paediatrics (2000) Clinical practice guideline: early detection of developmental dysplasia of the hip. Paediatrics 105(4):896–905
Patel H (2001) Preventive health care, 2001 update: screening and management of developmental dysplasia of the hip in newborns. Can Med Assoc J 164(12):1669–1677
Elbourne D, Dezteux C, Arthur R, Clarke NM, Gray A, King A, Quinn A, Gardner F, Russell G (2002) Ultrasonography in the diagnosis and management of developmental hip dysplasia (UK Hip Trial): clinical and economic results of a multicentre randomised controlled trial. UK Collaborative Hip Trial Group. Lancet 360(9350):2009–2017
Dezteux C, Brown J, Arthur R, Karnon J, Parnaby A (2003) Performance, treatment pathways and effects of alternative policy options for screening for DDH in UK. Arch Dis Child 88:753–759
Roovers EA, Boere-Boonekamp MM, Castelein RM, Zielhuis GA, Kerkhoff TH (2005) Effectiveness of ultrasound screening for developmental dysplasia of the hip. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed 90:F25–F30
Koureas G, Wicart P, Seringe R (2007) Etiology of developmental hip dysplasia or dislocation: review article. Hip Int 17(2 suppl. 5):S1–S8
Arumilli BRB, Keneru P, Garg NK, Davies R, Saville S, Sampath J, Bruce C (2006) Is secondary radiological follow-up of infants with a family history of developmental dysplasia of the hip necessary? J Bone Joint Surg 88B(9):1224–1227
Tschauner C, Klapsch W, Baumgartner A, Graf R (1994) Maturation curve of the ultrasonographic alpha angle according to Graf’s untreated hip joint in the first year of life. Z Orthop Ihre Grenzgeb 132(6):502–504
von Kries R, Ihme N, Oberle D, Lorani A, Stark R, Altenhofen L, Niethard FU (2003) Effect of ultrasound screening on the rate of first operative procedures for developmental hip dysplasia in Germany. Lancet 362(9399):1883–1887
Ihme N, Altenhofen L, von Kries R, Niethard FU (2008) Hip ultrasound screening in Germany. Results and comparison with other screening procedures. Orthopade 37(6):541–6, 548–9
Graf R, Tschauner, Klapsch W (1993) Progress in prevention of late DDH by sonographic newborn screening-results of comparative follow up study. J Pead Orthop B, 2:115–21
Schilt M (2001) Optimaler Zeitpunkt des Huftsonographie-Screenings. Ultraschall in Med 22:39–47
Graf R (2002) Huftsonographie-Ein Update. Orthopade 31:181–189
Portinaro NMA, Murray DW, Bhullar TPS, Benson MKD (1995) Errors in measurement of Acetabular index. J Pead Orthop 15:780–784
Spatz D, Reiger M, Klaumann M, Miller F, Stanton R, Lipton G (1997) Measurement of acetabular index. Intraobserver and Interobserver variation. J Paediatr Orthop 17(2):174–175
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pillai, A., Joseph, J., McAuley, A. et al. Diagnostic accuracy of static graf technique of ultrasound evaluation of infant hips for developmental dysplasia. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 131, 53–58 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-010-1100-9
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-010-1100-9