Abstract
Introduction
Even in a well-aligned total knee arthroplasty (TKA), limb rotation at the time of radiographic assessment will alter the measurement of alignment. This could influence the radiographic outcome of TKA. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effect of limb rotation on radiographic alignment after TKA and to establish a re-calculation of this rotation by using existing radiographic landmarks.
Materials and methods
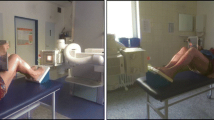
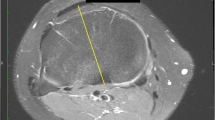
Synthetic femur and tibia (Sawbones®, Inc. Vashon Island, WA) were used to create a TKA of the Triathlon® knee prosthesis system (Stryker®, Limerick, Ireland). The femoral alignment was 6.5° valgus. The model was fixed in an upright stand. Five series of nine anteroposterior (AP) long leg radiographs were taken on a 30 cm × 120 cm plates in full extension with the limb rotated, in 5° increments, from 20° external rotation to 20° internal rotation. After digitizing each radiograph (Scanner Hewlett Packard XJ 527), an observer measured the anatomic mechanical angle of the femur [AMA (°)], the mechanical lateral proximal femur angle [mLPFA (°)], the mechanical lateral distal femur angle [mLDFA (°)], the mechanical medial proximal tibia angle [mMPTA (°)] and the mechanical lateral distal tibia angle [mLDTA (°)] using a digital measurement software (MediCAD®, Hectec, Altfraunhofen, Germany). Besides, the observer measured the geometrical distances of the femoral component figured on the long leg radiograph. A ratio of one distance to another was measured (called femoral component distance ratio).
Results
The average radiographic anatomic alignment ranged from 6.827° AMA (SD = 0.22°) in 20° internal rotation to 4.627° AMA (SD = 0.22°) in 20° external rotation. Average mLPFA (°) ranged from 101.63° (SD = 0.63) in 20° internal rotation to 93.60° (SD = 0.74°) in 20° external rotation. Average mLDFA (°) ranged from 90.59° (SD = 3.01°) in 20° internal rotation to 86.76° (SD = 0.36°) in 20° external rotation. Average mMPTA (°) ranged from 90.35° (SD = 0.81°) in 20° internal rotation to 88.49° (SD = 0.52°) in 20° external rotation. Average mLDTA (°) ranged from 98.89° (SD = 2.3°) in 20° internal rotation to 90.53° (SD = 3.39°) in 20° external rotation. Without an application of limb rotation, the femoral component distance ratio was measured to be 0.89 (SD = 0.01), in 20° internal rotation 0.63 (SD = 0.01) and in 20° external rotation 1.16 (SD = 0.01).
Discussion
Limb rotation had a highly statistically significant effect on measured anatomic alignment and mechanical angles. A correlation between limb rotation, anatomic mechanical angle, mechanical angles measured at femur and tibia and the femoral component distance ratio was established. As the anatomic mechanical angle and the femoral component distance ratio change linearly in the range of 20° internal and external limb rotation, a calculation of the femoral component distance ratio could be used to re-calculate the limb rotation at the time of radiographic assessment to evaluate the evidence of a long leg radiograph.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wright JG, Treble N, Feinstein AR (1991) Measurement of lower limb alignment using long radiographs. J Bone Joint Surg Br 73(5):721–723
Anderson KC, Buehler KC, Markel DC (2005) Computer-assisted navigation in total knee arthroplasty: comparison with conventional methods. J Arthroplasty 20(7 Suppl 3):132–138
Barrack RL, Schrader T, Bertot AJ, Wolfe MW, Myers L (2001) Component rotation and anterior knee pain after total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 392:46–55
Oswald MH, Jakob RP, Schneider E, Hoogewoud HM (1993) Radiological analysis of normal axial alignment of femur and tibia in view of total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 8(4):419–426
Chauhan SK, Clark GW, Lloyd S, Scott RG, Breidahl W, Sikorski JM (2004) Computer-assisted total knee replacement. A controlled cadaver study using a multi-parameter quantitative CT assessment of alignment (the Perth CT Protocol). J Bone Joint Surg Br 86(6):818–823
Moreland JR (1988) Mechanisms of failure in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 226:49–64
Jiang CC, Insall JN (1989) Effect of rotation on the axial alignment of the femur. Pitfalls in the use of femoral intramedullary guides in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 248:50–56
Lonner JH, Laird MT, Stuchin SA (1996) Effect of rotation and knee flexion on radiographic alignment in total knee arthroplasties. Clin Orthop Relat Res 331:102–106
Moreland JR, Bassett LW, Hanker GJ (1987) Radiographic analysis of the axial alignment of the lower extremity. J Bone Joint Surg Am 69(5):745–749
Hankemeier S, Gosling T, Richter M, Hufner T, Hochhausen C, Krettek C (2006) Computer-assisted analysis of lower limb geometry: higher intraobserver reliability compared to conventional method. Comput Aided Surg 11(2):81–86
Swanson KE, Stocks GW, Warren PD, Hazel MR, Janssen HF (2000) Does axial limb rotation affect the alignment measurements in deformed limbs? Clin Orthop Relat Res 371:246–252
Hunt MA, Fowler PJ, Birmingham TB, Jenkyn TR, Giffin JR (2006) Foot rotational effects on radiographic measures of lower limb alignment. Can J Surg 49(6):401–406
Kawakami H, Sugano N, Yonenobu K, Yoshikawa H, Ochi T, Hattori A et al (2004) Effects of rotation on measurement of lower limb alignment for knee osteotomy. J Orthop Res 22(6):1248–1253
Sparmann M, Wolke B, Czupalla H, Banzer D, Zink A (2003) Positioning of total knee arthroplasty with and without navigation support. A prospective, randomised study. J Bone Joint Surg Br 85(6):830–835
Petersen TL, Engh GA (1988) Radiographic assessment of knee alignment after total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 3(1):67–72
Paley D, Tetsworth K (1992) Mechanical axis deviation of the lower limbs. Preoperative planning of uniapical angular deformities of the tibia or femur. Clin Orthop Relat Res 280:48–64
Keppler P, Strecker W, Kinzl L (1998) Analysis of leg geometry-standard techniques and normal values. Chirurg 69(11):1141–1152
McGrory JE, Trousdale RT, Pagnano MW, Nigbur M (2002) Preoperative hip-to-ankle radiographs in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 404:196–202
Odenbring S, Berggren AM, Peil L (1993) Roentgenographic assessment of the hip-knee-ankle axis in medial gonarthrosis. A study of reproducibility. Clin Orthop Relat Res 289:195–196
Hsu RW, Himeno S, Coventry MB, Chao EY (1990) Normal axial alignment of the lower extremity and load-bearing distribution at the knee. Clin Orthop Relat Res 255:215–227
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Radtke, K., Becher, C., Noll, Y. et al. Effect of limb rotation on radiographic alignment in total knee arthroplasties. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 130, 451–457 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-009-0999-1
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-009-0999-1