Abstract
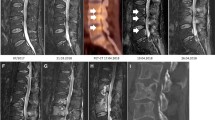
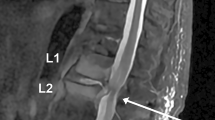
Here presented is an extremely rare case of a spinal osteomyelitis (L5–S1) with epidural empyema in a non-immunocompromised 62-year-old man caused by Yersinia enterocolitica O:9. The infection occurred acutely and required immediate surgical treatment. Y. enterocolitica was cultured from the empyema fluid, wound swabs of the intervertebral disc L5–S1 and stool cultures. Following the surgical decompression and antibiotic treatment, the patient recovered completely, without neurological deficits. A review of the literature revealed only sparse cases of spondylodiscitis due to other Y. enterocolitica serogroups. To our knowledge, we report here the first case of a spondylodiscitis of the lumbar spine caused by Y. enterocolitica serovar O:9 in a non-immunocompromised patient.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bertschinger C, Frauchiger B (1997) Therapy-resistant lumbago. Praxis 86:356–360
Cover TL, Aber RC (1989) Yersinia enterocolitica. N Engl J Med 321:16–24
Crowe M, Ashford K, Ispahani P (1996) Clinical features and antibiotic treatment of septic arthritis and osteomyelitis due to Yersinia enterocolitica. J Med Microbiol 45:302–309
Hadjipavlou AG, Mader JT, Necessary JT, Muffoletto AJ (2000) Hematogenous pyogenic spinal infections and their surgical management. Spine 25:1668–1679
Knapp W, Lysy J, Knapp C, Stille W, Goll U (1973) Clinic and diagnosis of enteritic infections in man by Yersinia enterocolitica. Infection 1:113–125
Mayrhofer S, Paulsen P, Smulders FJ, Hilbert F (2004) Antimicrobial resistance profile of five major food-borne pathogens isolated from beef, pork and poultry. Int J Food Microbiol 97:23–29
Saebø A, Nyland H, Lassen J (1993) Yersinia enterocolitica infection–An unrecognized cause of acute and chronic neurological disease? A 10-year-follow-up study on 458 hospitalized patients. Med Hypotheses 41:282–286
Sinnott JT, Multhopp H, Leo J, Rechtine G (1989) Yersinia enterocolitica causing spinal osteomyelitis and empyema in a nonimmunocompromised host. South Med J 82:399–400
Strobel E, Heesemann J, Mayer G, Peters J, Müller-Weihrich S, Emmerling P (2000) Bacteriological and serological findings in a further case of transfusion-mediated Yersinia enterocolitica sepsis. J Clin Microbiol 38:2788–2790
von Eckardstein K, Spuler A, Brauer C, Mehl M, Kiwit J (2004) Spontaneous cervical osteomyelitis due to Yersinia enterocolitica in a non-immunocompromised host. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 23:66–68
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ellenrieder, M., Zautner, A.E., Podbielski, A. et al. Spondylodiscitis of the lumbar spine in a non-immunocompromised host caused by Yersinia enterocolitica O:9. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 130, 469–471 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-009-0921-x
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-009-0921-x