Abstract
Background
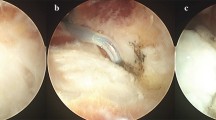
Plantar fascia release is the main procedure for plantar fasciitis which does not respond to conservative treatment. However, this procedure is sometimes accompanied by lateral column pain due to loss of the longitudinal arch height after surgery. To avoid this complication, we performed calcaneal osteotomy. The aim of this study was to clarify the efficacy of this procedure.
Methods
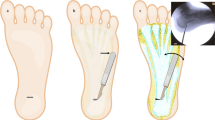
A retrospective clinical and radiographic study was conducted for 11 patients (11 feet) who had undergone calcaneal osteotomy for the treatment of intractable plantar fasciitis. Three of the patients were males and eight were females, with an average age of 46 (range 24–70) years. Calcaneal osteotomy was performed from 1 cm anterior of the calcaneal attachment of the plantar fascia to 1 cm anterior of the calcaneal attachment of the Achilles tendon, and the proximal fragment was displaced approximately 5 mm in the plantar direction. The patients with a pronated foot before surgery underwent an additional approximately 5 mm medial displacement of the proximal fragment.
Result
Significant improvement was seen between the American Orthopaedic Foot and Ankle Society Ankle-Hindfoot score before surgery and at final follow-up (P < 0.0001). With regard to the radiographic parameters which evaluated longitudinal arch height, significant improvement was seen between the talar pitch (P = 0.0002), calcaneal plantar angle (P < 0.0001) and lateral talocalcaneal angle (P = 0.0251) before and at 2 years after surgery. One patient with severe pes planus before surgery showed poor clinical and radiographic results.
Conclusions
This procedure can bring about good results in patients who do not have severe pes planus.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson DJ, Fallat LM, Savoy-Moore RT (2001) Computer-assisted assessment of lateral column movement following plantar fascia release: a cadaveric study. J Foot Ankle Surg 40:52–70
Bazaz R, Ferkel RD (2007) Results of endoscopic plantar fascia release. Foot Ankle Int 28:549–556. doi:10.3113/FAI.2007.0549
Bordelon R (1993) Heel pain. In: Mann RA (ed) Surgery of the foot and ankle. CV Mosby, St Louis, pp 837–847
Boyle RA, Slater GL (2003) Endoscopic plantar fascia release: a case series. Foot Ankle Int 24:176–179
Brugh AM, Fallat LM, Savoy-Moore RT (2002) Lateral column symptomatology following plantar fascia release: a prospective study. J Foot Ankle Surg 41:365–371
Downey MS (1998) Endoscopic plantar fasciotomy remains controversial. Biomechanics 5:33–39
Garceau DD, Dean D, Requejo SM, Thordarson DB (2003) The association between diagnosis of plantar fasciitis and windlass test results. Foot Ankle Int 24:251–255
Gill LH (1997) Plantar fasciitis: diagnosis and conservative management. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 5:109–117
Kalen V, Brecher A (1988) Relationship between adolescent bunions and flatfeet. Foot Ankle 8:331–336
Kitaoka HB, Alexander IJ, Adelaar RS, Nunley JA, Myerson MS, Sanders M (1994) Clinical rating systems for the ankle-hindfoot, midfoot, hallux, and lesser toes. Foot Ankle Int 15:349–353
Kwong PK, Kay D, Voner RT, White MW (1988) Plantar fasciitis. Mechanics and pathomechanics of treatment. Clin Sports Med 7:119–126
Leach R, Seavey M, Salter D (1986) Results of surgery in athletes with plantar fasciitis. Foot Ankle Int 7:156–161
Lemont H, Ammirati KM, Usen N (2003) Plantar fasciitis: a degenerative process (Fasciosis) without inflammation. J Am Podiatr Med Assoc 93:234–237
Lutter L (1986) Surgical decisions in athletes’ subcalcaneal pain. Am J Sports Med 14:481–486. doi:10.1177/036354658601400609
Martin RL, Irrgang JJ, Conti SF (1998) Outcome study of subjects with insertional plantar fasciitis. Foot Ankle Int 19:803–811
Murphy GA, Pneumaticos SG, Kamaric E, Noble PC, Trevino SG, Baxter DE (1998) Biomechanical consequences of sequential plantar fascia release. Foot Ankle Int 19:149–152
O’Malley MJ, Page A, Cook R (2000) Endoscopic plantar fasciotomy for chronic heel pain. Foot Ankle Int 21:505–510
Sammaro GJ, Helfrey RB (1996) Surgical treatment of recalcitrant plantar fasciitis. Foot Ankle Int 17:520–526
Wearing SC, Smeathers JE, Yates B, Sullivan PM, Urry SR, Dubois P (2004) Sagittal movement of the medial longitudinal arch is unchanged in plantar fasciitis. Med Sci Sports Exerc 176:1–1767
Wolgin M, Cook C, Graham C, Mauldin D (1994) Conservative treatment of plantar heel pain: long term follow-up. Foot Ankle 15:97–102
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miyamoto, W., Takao, M. & Uchio, Y. Calcaneal osteotomy for the treatment of plantar fasciitis. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 130, 151–154 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-009-0879-8
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-009-0879-8