Abstract
Introduction
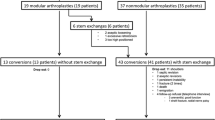
We report our experience of revision of failed stemmed shoulder hemi-arthroplasty for causes other than infection.
Material/method
Seventeen revisions were followed for a minimum of 2 years. Fifteen cases were revised for symptomatic glenoid erosion. Sixteen were revised to a total shoulder arthroplasty and one to a cuff tear arthropathy head.
Result
The mean visual analogue pain score following revision surgery was reduced from 6.7 to 3.2 (P = 0.008). However the Constant–Murley and the Association of Shoulder and Elbow Surgeons scores failed to improve significantly.
Conclusion
We conclude that revision surgery for failed stemmed shoulder hemi-arthroplasty improves pain but not function.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ravenscroft MJ, Calvert PT (2004) Utilisation of shoulder arthroplasty in the UK. Ann R Coll Surg Engl 86:25–28
Constant CR, Murley AGH (1987) A clinical method of functional assessment of the shoulder. Clin Orthop 214:160–164
Richards RR, An KN, Bigliani LU et al (1994) A standardised method for the assessment of shoulder function. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 3:347–352
Sperling JW, Cofield RH (1998) Revision total shoulder arthroplasty for the treatment of glenoid arthrosis. J Bone Joint Surg Am 80:860–867
Carroll RM, Izquierdo R, Vazquez M, Blaine TA, Levine WN, Bigliani LU (2004) Conversion of painful hemiarthroplasty to total shoulder arthroplasty: long-term results. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 13:599–603
Cheung EV, Sperling JW (2008) Cofield RH Revision shoulder arthroplasty for glenoid component loosening. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 17:371–375
Phipatanakul WP, Norris TR (2006) Treatment of glenoid loosening and bone loss due to osteolysis with glenoid bone grafting. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 15(1):84–87
Deutsch A, Abboud JA, Kelly J, Mody M, Norris T, Ramsey ML, Iannotti JP, Williams GR (2007) Clinical results of revision shoulder arthroplasty for glenoid component loosening. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 16:706–716
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ravenscroft, M., Charalambous, C.P., Haines, J.F. et al. Outcome of stemmed shoulder hemi-arthroplasty revision. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 129, 797–799 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-008-0728-1
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-008-0728-1