Abstract
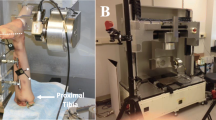
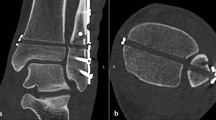
Introduction: The aim of the study was to investigate the kinematics of the distal tibiofibular syndesmosis in intact and ligament injured ankles and to assess how effective is the syndesmotic screw in restraining mortise width variations during passive foot flexion. Materials and methods: The trials were carried out on seven fresh frozen cadaver specimens. The distal tibiofibular syndesmosis widening was investigated using Roentgen stereophotogrammetric analysis, in intact and ligament injured ankles and after the fixation of the syndesmotic screw. The AO-ASIF recommendations were followed for screw implant. Results: Injury to the syndesmotic and deltoid ligaments of the ankle did not result in a significant variation of the syndesmosis behavior during passive foot flexion. The 4.5-mm diameter cortical screw used in this study proved effective in restraining mortise width variation during foot flexion. The recorded mortise widening in the flexion arc extending from the neutral to the maximally dorsiflexed position was negligible in intact and ligament injured joints. Conclusion: The result does not endorse the recommendation of placing the foot in full dorsal flexion during screw implantation. The choice of screw fixation as a treatment for ankle syndesmosis disruption should be carefully evaluated.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahl T, Dalén N, Lundberg A, Selvik G (1987) Mobility of the ankle mortise. A roentgen stereophotogrammetric analysis. Acta Orthop Scand 58:401–402
Ahl T, Dalen N, Selvik G (1989) Ankle fractures. A clinical and roentgenographic stereophotogrammetric study. Clin Orthop 246–255
Ahl T, Dalén N, Lundberg A, Wykman A (1994) Biodegradable fixation of ankle fractures. A roentgen stereophotogrammetric study of 32 cases. Acta Orthop Scand 65:166–170
Amendola A (1992) Controversies in diagnosis and management of syndesmosis injuries of the ankle. Foot Ankle 13:44–50
Barnett CH, Napier JR (1952) The axis of rotation at the ankle joint in man. Its influence upon the form of the talus and the mobility of the fibula. J Anat 86:1–9
Boden SD, Labropoulos PA, McCowin P, Lestini WF, Hurwitz SR (1989) Mechanical considerations for the syndesmosis screw. A cadaver study. J Bone Joint Surg Am 71:1548–1555
Burwell HN, Charnley AD (1965) The treatment of displaced fractures at the ankle by rigid internal fixation and early joint movement. J Bone Joint Surg Br 47:634–660
Cappozzo A, Cappello A, Della Croce U, Pensalfini F (1997) Surface-marker cluster design criteria for 3-D bone movement reconstruction. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 44:1165–1174
Close JR (1956) Some applications of the functional anatomy of the ankle joint. J Bone Joint Surg Am 38:761–781
Colton CL (1968) Fracture-diastasis of the inferior tibio-fibular joint. J Bone Joint Surg Br 50:830–835
Colton CL (1971) The treatment of Dupuytren’s fracture-dislocation of the ankle. J Bone Joint Surg Br 53:63–71
Edwards GS Jr, DeLee JC (1984) Ankle diastasis without fracture. Foot Ankle 4:305–312
Farhan MJ, Smith TW (1985) Fixation of diastasis of the inferior tibiofibular joint using the syndesmosis hook. Injury 16:309–311
Grath GB (1960) Widening of the ankle mortise. A clinical and experimental study. Acta Chir Scand 41(Suppl):263
Guise ER (1976) Rotational ligamentous injuries to the ankle in football. Am J Sports Med 4:1–6
Inman VT (1976) The joints of the ankle. Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore, MD
Karrholm J (1989) Roentgen stereophotogrammetry. Review of orthopedic applications. Acta Orthop Scand 60:491–503
Kaye RA (1989) Stabilization of ankle syndesmosis injuries with a syndesmosis screw. Foot Ankle 9:290–293
Leeds HC, Ehrlich MG (1984) Instability of the distal tibiofibular syndesmosis after bimalleolar and trimalleolar ankle fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Am 66:490–503
Lofvenberg R, Karrholm J, Selvik G, Hansson LI, Ahlgren O (1989) Chronic lateral instability of the ankle. Roentgen stereophotogrammetry of talar position. Acta Orthop Scand 60:34–39
Lofvenberg R, Karrholm J, Selvik G (1990) Fibular mobility in chronic lateral instability of the ankle. Foot Ankle 11:22–29
Lofvenberg R, Karrholm J, Ahlgren O (1994) Ligament reconstruction for ankle instability. A 5-year prospective RSA follow-up of 30 cases. Acta Orthop Scand 65:401–407
Marymont JV, Lynch MA, Henning CE (1986) Acute ligamentous diastasis of the ankle without fracture. Evaluation by radionuclide imaging. Am J Sports Med 14:407–409
Mast JW, Teipner WA (1980) A reproducible approach to the internal fixation of adult ankle fractures: rationale, technique, and early results. Orthop Clin North Am 11:661–679
Miller CD, Shelton WR, Barrett GR, Savoie FH, Dukes AD (1995) Deltoid and syndesmosis ligament injury of the ankle without fracture. Am J Sports Med 23:746–750
Müller ME, Allgöwer M, Schneider R, Willenegger H (1995) Manual of internal fixation—techniques recommended by the AO-ASIF Group. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Olerud S (1971) Subluxation of the ankle without fracture of the fibula. A case report. J Bone Joint Surg Am 53:594–596
Olerud C (1985) The effect of the syndesmotic screw on the extension capacity of the ankle joint. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 104:299–302
Pankovich AM (1976) Maisonneuve fracture of the fibula. J Bone Joint Surg Am 58:337–342
Peter RE, Harrington RM, Henley MB, Tencer AF (1994) Biomechanical effects of internal fixation of the distal tibiofibular syndesmotic joint: comparison of two fixation techniques. J Orthop Trauma 8:215–219
Phillips WA, Schwartz HS, Keller CS, Woodward HR, Rudd WS, Spiegel PG, Laros GS (1985) A prospective, randomized study of the management of severe ankle fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Am 67:67–78
Riegels-Nielsen P, Christensen J, Greiff J (1983) The stability of the tibio-fibular syndesmosis following rigid internal fixation for type C malleolar fractures: an experimental and clinical study. Injury 14:357–360
Ryd L (1986) Micromotion in knee arthroplasty. A roentgen stereophotogrammetric analysis of tibial component fixation. Acta Orthop Scand Suppl 220:1–80
Ryd L, Yuan X, Lofgren H (2000) Methods for determining the accuracy of radiostereometric analysis (RSA). Acta Orthop Scand 71:403–408
Sclafani SJ (1985) Ligamentous injury of the lower tibiofibular syndesmosis: radiographic evidence. Radiology 156:21–27
Selvik G (1989) Roentgen stereophotogrammetry. A method for the study of the kinematics of the skeletal system. Acta Orthop Scand Suppl 232:1–51
Selvik G (1990) Roentgen stereophotogrammetric analysis. Acta Radiol 31:113–126
Selvik G, Alberius P, Aronson AS (1983) A roentgen stereophotogrammetric system. Construction, calibration and technical accuracy. Acta Radiol Diagn (Stockh) 24:343–352
Slawski DP, West C (1995) Maisonneuve fracture with an associated distal fibular fracture. A case report. Clin Orthop 193–198
Soavi R, Girolami M, Loreti I, Bragonzoni L, Monti C, Visani A, Marcacci M (2000) The mobility of the proximal tibio-fibular joint. A Roentgen stereophotogrammetric analysis on six cadaver specimens. Foot Ankle Int 21:336–342
Söderkvist I, Wedin PA (1993) Determining the movements of the skeleton using well-configured markers. J Biomech 26(12):1473–1477
Solari J, Benjamin J, Wilson J, Lee R, Pitt M (1991) Ankle mortise stability in Weber C fractures: indications for syndesmotic fixation. J Orthop Trauma 5:190–195
de Souza LJ, Gustilo RB, Meyer TJ (1985) Results of operative treatment of displaced external rotation-abduction fractures of the ankle. J Bone Joint Surg Am 67:1066–1074
Tornetta P, Spoo JE, Reynolds FA, Lee C (2001) Overtightening of the ankle syndesmosis: is it really possible? J Bone Joint Surg Am 83:489–492
Wuest TK (1997) Injuries to the distal lower extremity syndesmosis. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 5:172–181
Xenos JS, Hopkinson WJ, Mulligan ME, Olson EJ, Popovic NA (1995) The tibiofibular syndesmosis. Evaluation of the ligamentous structures, methods of fixation, and radiographic assessment. J Bone Joint Surg Am 77:847–856
Yamaguchi K, Martin CH, Boden SD, Labropoulos PA (1994) Operative treatment of syndesmotic disruptions without use of a syndesmotic screw: a prospective clinical study. Foot Ankle Int 15:407–414
Yuan X, Ryd L (2000) Accuracy analysis for RSA: a computer simulation study on 3D marker reconstruction. J Biomech 33:493–498
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank Vito Amabile, Luciano Ussia and Valentina Matti of the Radiology Department for their essential cooperation, Elettra Pignotti for her help with statistical data processing, Carmelo Carcasio for the technical support, and Silvia Bassini for her assistance with graphics.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bragonzoni, L., Russo, A., Girolami, M. et al. The distal tibiofibular syndesmosis during passive foot flexion. RSA-based study on intact, ligament injured and screw fixed cadaver specimens. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 126, 304–308 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-006-0131-8
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-006-0131-8