Abstract
Introduction
Whether biochemical markers of bone metabolism can be used in assessing the conditions of implant fixation is unknown. In this study, the serum levels of three bone markers were measured prospectively in patients undergoing total knee arthroplasty (TKA) to determine if patients with different fixation conditions of the tibial component showed any differences in the levels of the markers.
Materials and methods
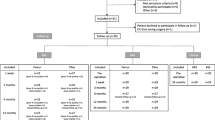
The fixation of the tibial component in 40 knees (40 patients, 14 male and 26 female, average age 71 years) was assessed by radiostereometric analysis (RSA), and based upon the pattern of migration, implants with stable fixation (n=25) and potentially unstable fixation (n=15) were identified. Serum levels of carboxyterminal propeptide of type I procollagen (PICP), osteocalcin (OC) and cross-linked carboxyterminal telopeptide of type I collagen (ICTP) were assessed and compared between the two fixation groups. Blood samples were obtained preoperatively (baseline) and repeated postoperatively at 1 week, 3, 6, 12, and 24 months.
Results
The baseline levels of the markers were statistically the same (p>0.05) between the two fixation groups. Postoperatively, ICTP levels in the unstable group were significantly higher than in the stable group from 6 to 24 months (p=0.02). Levels of OC in the unstable group were higher at 12 and 24 months compared with the stable group, reaching statistical significance only at 12 months (p=0.03). No difference in the levels of PICP was found between the two groups.
Conclusion
The findings indicate a more active bone turnover probably at the bone-cement/implant interface in knees with potentially unstable fixation. It reveals the potential value for biochemical markers in monitoring implant fixation and aseptic loosening and suggests a possibility for improving implant fixation by drugs which inhibit osteolysis.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Åkesson K, Vergnaud P, Delmas PD, Obrant KJ (1995) Serum osteocalcin increases during fracture healing in elderly women with hip fracture. Bone 16:427–430
Antoniou J, Huk O, Zukor D, Eyre D, Alini M (2000) Collagen crosslinked N-telopeptides as markers for evaluating particulate osteolysis: a preliminary study. J Orthop Res 18:64–67
Bauer TW, Schils J (1999) The pathology of total joint arthroplasty. II. Mechanisms of implant failure. Skeletal Radiol 28:483–497
Bowles SA, Kurdy N, Davis AM, France MW, Marsh DR (1996) Serum osteocalcin, total and bone-specific alkaline phosphatase following isolated tibial shaft fracture. Ann Clin Biochem 33:196–200
Chiba J, Rubash HE, Kim KJ, Iwaki Y (1994) The characterization of cytokines in the interface tissue obtained from failed cementless total hip arthroplasty with and without femoral osteolysis. Clin Orthop 300:304–312
Delmas PD (1990) Biochemical markers of bone turnover for the clinical assessment of metabolic bone disease. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am 19:1–18
Emami A, Larsson A, Petren-Mallmin M, Larsson S (1999) Serum bone markers after intramedullary fixed tibial fractures. Clin Orthop 368:220–229
Ewald FC (1989) The Knee Society total knee arthroplasty roentgenographic evaluation and scoring system. Clin Orthop 248:9–12
Garnero P, Delmas PD (1996) New developments in biochemical markers for osteoporosis. Calcif Tissue Int 59 [Suppl 1]:S2–S9
Goodman SB, Fornasier VL, Kei J (1988) The effects of bulk versus particulate polymethylmethacrylate on bone. Clin Orthop 232:255–262
Hilding M, Ryd L, Toksvig-Larsen S, Aspenberg A (2000) Clodronate prevents prosthetic migration. A randomized radiostereometric study of 50 total knee patients. Acta Orthop Scand 71:541–545
Jiranek WA, Machado M, Jasty M, Jevsevar D, Wolfe HJ, Goldring SR, Goldberg MJ, Harris WH (1993) Production of cytokines around loosened cemented acetabular components. Analysis with immunohistochemical techniques and in situ hybridization. J Bone Joint Surg Am 75:863–879
Kadoya Y, Revell PA, Kobayashi A, al-Saffar N, Scott G, Freeman MA (1997) Wear particulate species and bone loss in failed total joint arthroplasties. Clin Orthop 340:118–129
Kadoya Y, Kobayashi A, Ohashi H (1998) Wear and osteolysis in total joint replacements. Acta Orthop Scand 69 [Suppl 278]:1–16
Kärrholm J, Malchau H, Snorrason F, Herberts P (1994) Micromotion of femoral stems in total hip arthroplasty. A randomized study of cemented, hydroxyapatite-coated, and porous-coated stems with roentgen stereophotogrammetric analysis. J Bone Joint Surg Am 76:1692–1705
Lassus J, Waris V, Xu JW, Li TF, Hao J, Nietosvaara Y, Santavirta S, Konttinen YT (2000) Increased interleukin-8 (IL-8) expression is related to aseptic loosening of total hip replacement. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 120:328–332
Mallmin H, Ljunghall S, Larsson K (1993) Biochemical markers of bone metabolism in patients with fracture of the distal forearm. Clin Orthop 295:259–263
Miller EJ, Gay S (1987) The collagens: an overview and update. Methods Enzymol 144:3–41
Nilsson KG, Kärrholm J (1993) Increased varus-valgus tilting of screw-fixated knee prostheses. Stereoradiographic study of uncemented versus cemented tibial components. J Arthroplasty 8:529–540
Nilsson KG, Kärrholm J (1996) RSA in the assessment of aseptic loosening. Editorial. J Bone Joint Surg Br 78:1–3
Nilsson KG, Kärrholm J, Carlsson LV, Dalén T (1999) Hydroxyapatite coating versus cemented fixation of the tibial component in total knee arthroplasty. Prospective randomized comparison of hydroxyapatite-coated and cemented tibial components with 5-year follow-up using radiostereometry (RSA). J Arthroplasty 14:9–20
Pandey R, Quinn JM, Sabokbar A, Athanasou NA (1996) Bisphosphonate inhibition of bone resorption induced by particulate biomaterial-associated macrophages. Acta Orthop Scand 67:221–228
Ranawat CS, Flynn WF Jr, Saddler S, Hansraj KK, Maynard MJ (1993) Long-term results of the total condylar knee arthroplasty. A 15-year survivorship study. Clin Orthop 286:94–102
Risteli J, Elomaa I, Niemi S, Novamo A, Risteli L (1993) Radioimmunoassay for the pyridinoline cross-linked carboxy-terminal telopeptide of type 1 collagen: a new serum marker of bone collagen degradation. Clin Chem 39:635–640
Rosen HN, Dresner-Pollak R, Moses AC, Rosenblatt M, Zeind AJ, Clemens JD, Greenspan SL (1994) Specificity of urinary excretion of cross-linked N-telopeptides of type 1 collagen as a marker of bone turnover. Calcif Tissue Int 54:26–29
Ryd L (1986) Micromotion in knee arthroplasty. A roentgen stereophotogrammetric analysis of tibial component fixation. Acta Orthop Scand 57 [Suppl 220]:1–80
Ryd L, Albrektsson BEJ, Carlsson L, Dansgård F, Herberts P, Lindstrand A, Regnér L, Toksvig-Larsen S (1995) Roentgen stereophotogrammetric analysis as a predictor of mechanical loosening of knee prostheses. J Bone Joint Surg Br 77:377–383
Sabokbar A, Fujikawa Y, Neale S, Murray DW, Athanasou NA (1997) Human arthroplasty derived macrophages differentiate into osteoclastic bone resorbing cells. Ann Rheum Dis 56:414–420
Schmalzried TP, Jasty M, Rosenberg A, Harris WH (1994) Polyethylene wear debris and tissue reactions in knee as compared to hip replacement prostheses. J Appl Biomater 5:185–190
Schneider U, Breusch SJ, Termath S, Thomsen M, Brocai DR, Niethard FU, Kasperk C (1998) Increased urinary crosslink levels in aseptic loosening of total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 13:687–692
Selvik G (1989) Roentgen stereophotogrammetry. A method for the study of the kinematics of the skeletal system. Acta Orthop Scand 60 [Suppl 232]:1–60
Shanbhag AS, Hasselman CT, Rubash HE (1997) The John Charnley Award. Inhibition of wear debris mediated osteolysis in a canine total hip arthroplasty model. Clin Orthop 344:33–43
Sumner DR, Kienapfel H, Jacobs JJ, Urban RM, Turner TM, Galante JO (1995) Bone ingrowth and wear debris in well-fixed cementless porous-coated tibial components removed from patients. J Arthroplasty 10:157–167
Xu JW, Konttinen YT, Lassus J, Natah S, Ceponis A, Solovieva S, Aspenberg P, Santavirta S (1996) Tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) in loosening of total hip replacement (THR). Clin Exp Rheumatol 14:643–648
Acknowledgments
This study was funded in part with grants from The Swedish Rheumatism Association (64/98) and the University of Umeå. It complied with the laws of Sweden.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, M.G., Thorsen, K. & Nilsson, K.G. Increased bone turnover as reflected by biochemical markers in patients with potentially unstable fixation of the tibial component. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 124, 404–409 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-004-0695-0
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-004-0695-0