Abstract
Background
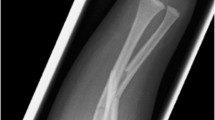
A rare type I Monteggia equivalent lesion with a posterior dislocation associated with a diaphyseal radius and ulna fracture in an adult is described. The probable mechanisms of injury are speculated to include flexion of the elbow and pronation of the forearm.
Methods and results
Early reduction of the dislocation and rigid fixation of the fractures helped to achieve excellent results.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bado JL (1967) The Monteggia lesion. Clin Orthop 50:71–86
Biyani A, Olscamp AJ, Ebraheim NA (2000) Complications in the management of complex Monteggia-equivalent fractures in adults. Am J Orthop 29:115–118
Frazier JL, Buschmann WR, Insler HP (1991) Monteggia type I equivalent lesion: diaphyseal ulna and proximal radius fracture with a posterior elbow dislocation in a child. J Orthop Trauma 5:373–375
Givon U, Pritsch M, Levy O, et al (1997) Monteggia and equivalent lesions. A study of 41 cases. Clin Orthop 337:208–215
Letts M, Locht R, Wiens J (1985) Monteggia fracture-dislocations in children. J Bone Joint Surg Br 67:724–727
Olney BW, Menelaus MB (1989) Monteggia equivalent lesions in childhood. J Pediatr Orthop 9:219–233
Papavasiliou VA, Nenopoulos JP (1988) Monteggia-type elbow fractures in childhood. Clin Orthop 233:230–233
Ramsey RH, Pederson HE (1962) The Monteggia fracture-dislocation in children. JAMA 182:1091–1094
Reckling FW (1982) Unstable fracture-dislocations of the forearm (Monteggia and Galeazzi lesions). J Bone Joint Surg Am 64:857–863
Reckling FW, Cordell LD (1968) Unstable fracture-dislocations of the forearm. The Monteggia and Galeazzi lesions. Arch Surg 96:999–1007
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hung, SC., Huang, CK., Chiang, CC. et al. Monteggia type I equivalent lesion: diaphyseal ulna and radius fractures with a posterior elbow dislocation in an adult. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 123, 311–313 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-003-0526-8
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-003-0526-8