Abstract
Background
Reliable concentric reduction of the femoral head and subsequent retention in a centred position are indispensable preconditions for the remodelling of the acetabulum in developmental dysplasia of the hip (DDH) and to prevent damage to the hip joint, i.e. avascular necrosis. The objective of this study is to evaluate the necessity of verifying the reduced position of the articulation in the plaster cast.
Method
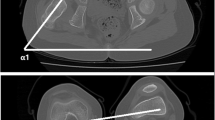
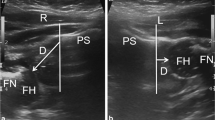
MRI was carried out in 15 infants with 21 unstable hip joints after reduction under arthrographic control and fixation in a plaster cast in the 'human' position with the hips flexed above 90° and abducted to 50° or 60°. When the reduction was found to be inadequate—the hip still partially or completely dislocated—the plaster cast was removed, reduction repeated, a new cast applied, and MRI carried out again.
Results
After primary reduction, 1 of 21 hips was dislocated, and 2 showed unsatisfactory reduction. Three hip joints out of 21 (14.3%) were not fixed in the plaster cast in the optimal centred position.
Conclusion
In view of the number of inadequate reductions in plaster casts, we recommend verifying the position of the hip joint by MRI. This MRI documentation should be established as a standard examination post-reduction.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aoki K, Mitani S, Asaumi K, Akazawa H, Inoue H (1999) Utility of MRI in detecting obstacles to reduction in developmental dysplasia of the hip: comparison with two-directional arthrography and correlation with intraoperative findings. J Orthop Sci 4:255–263
Bos CFA, Bloem JL, Obermann WR, Rozing PM (1988) Magnetic resonance imaging in congenital dislocation of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Br 70:174–178
Duffy CM, Taylor FN, Coleman L, Graham HK, Nattrass GR (2002) Magnetic resonance imaging evaluation of surgical management in developmental dysplasia of the hip in childhood. J Pediatr Orthop 22:92–100
Eggli KD, King SH, Boal DKB, Quoigue T (1994) Low-dose CT of development dysplasia of the hip after reduction: diagnostic accuracy and dosimetry. Am J Roentgenol 163:1441–1443
Fettweis E (1968) Sitz-Hock-Stellungsgips bei Hüftgelenksdysplasien. Arch Orthop Traumatol 63:38–51
Fischer R, O'Brien TS, Davis KM (1991) Magnetic resonance imaging in congenital dysplasia of the hip. J Pediatr Orthop 11:617–622
Franke J, Lazovic D, Lotz J, Rühmann O, Wirth CJ (1998) Die Magnetresonanztomografie als Therapiekontrolle nach Repositionsbehandlung bei kongenitaler Hüftluxation. Z Orthop 136:205–209
Graf R (1980) The diagnosis of congenital hip joint dislocation by ultrasonic compound treatment. Arch Orthop Traum Surg 97:117–133
Greenhill BJ, Hugosson C, Jacobsson B, Ellis RD (1993) Magnetic resonance imaging study of acetabular morphology in developmental dysplasia of the hip. J Pediatr Orthop 13:314–317
Guidera KJ, Einbecker ME, Berman CG, Ogden A, Arrington JA, Murtagh R (1990) Magnetic resonance imaging evaluation of congenital dislocation of the hips. Clin Orthop 261:96–101
Jaramillo D, Villegas-Medina OL, Doty DK, Dwek JR, Ransil BJ, Mulkern RV, Shapiro F (1995) Gadolinium-enhanced MR imaging demonstrates abduction-caused hip ischemia and its reversal in piglets. Pediatr Radiol 25:578–587
Jaramillo D, Villegas-Medina OL, Laor T, Shapiro F, Millis MB (1998) Gadolinium-enhanced MR imaging of pediatric patients after reduction of dysplastic hips: assessment of femoral head position, factors impeding reduction and femoral head ischemia. Am J Roentgenol 170:1633–1637
Kashiwagi N, Suzuki S, Kasahara Y, Seto Y (1996) Prediction of reduction in developmental dysplasia of the hip by magnetic resonance imaging. J Pediatr Orthop 16:254–258
Kawaguchi AT, Otsuka NY, Delgado ED, Genant HK, Lang P (2000) Magnetic resonance arthrography in children with developmental hip dysplasia. Clin Orthop 374:235–246
Krasny R, Casser HR, Requardt H, Botschek A (1993) A new holder and surface MRI coil for the examination of the newborn infant hip. Pediatr Radiol 23:538–540
Laor T, Roy DR, Mehlman CT (2000) Limited magnetic resonance imaging examination after surgical reduction of developmental dysplasia of the hip. J Pediatr Orthop 20:572–574
Lazovic D, Franke J, Wirth CJ (1996) Computerized tomography and magnetic resonance imaging in treatment of congenital luxation of the hip. Hip Int 6:119–123
McNally EG, Taker A, Benson MK (1997) MRI after operative reduction for developmental dysplasia of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Br 79:724–726
Ömeroglu H (1998) MRI after operative reduction for developmental dysplasia of the hip (letter). J Bone Joint Surg Br 80:556
Salter RB, Kostuik J, Dallas S (1969) Avascular necrosis of the femoral head as a complication of treatment of congenital dislocation of the hip in young children: a clinical and experimental investigation. Can J Surg 12:44–61
Smith BG, Mills MB, Hey LA, Jaramillo D, Kasser J (1997) Postreduction computed tomography in developmental dislocation of the hip. Part II. Predictive value for outcome. J Pediatr Orthop 17:631–636
Tennant S, Kinmont C, Lamb G, Gedroyc W, Hunt DM (1999) The use of dynamic interventional MRI in developmental dysplasia of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Br 81:392–397
Wientroub S, Grill F (2000) Current concepts review: ultrasonography in developmental dysplasia of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Am 82:1004–1018
Acknowledgements
No benefits in any form have been received or will be received from a commercial party related directly or indirectly to the subject of this article. This study complies with the current laws of Germany.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Westhoff, B., Wild, A., Seller, K. et al. Magnetic resonance imaging after reduction for congenital dislocation of the hip. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 123, 289–292 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-003-0518-8
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-003-0518-8