Abstract
Background
Hydatidosis is a protozoal infestation which generally involves the liver and the lungs. Primary skeletal muscle hydatidosis without involving the thoracic and abdominal organs is extremely rare.
Methods
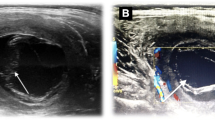
A 48-year-old farmer presented with a mass in the quadriceps muscle that had persisted for 10 years. Clinical and radiological investigations revealed a primary hydatid cyst of the vastus medialis of the quadriceps muscle. We did not find any visceral organ involvement. Wide excision was performed without destroying the cyst wall. Then 400 mg albendazole was given daily for 3 months postoperatively.
Results
At the 7th postoperative month, the patient was symptom-free, and the laboratory test results were in the normal ranges.
Conclusion
Primary muscular hydatidosis is a rare disease and should be kept in mind in the diagnostic work-up of a cystic mass of a skeletal muscle.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel-Khalig RA, Othman Y (1986) Hydatid cyst of the pectoralis major muscle. Acta Chir Scand 152:469–471
Alvarez-Sala R, Caballero P (1987) Echinococcus cyst as a cause of chest wall tumor. Ann Thorac Surg 43:689–690
Dudkiewicz I, Salai M, Apter S (1999) Hydatid cyst presenting as a soft-tissue thigh mass in a child. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 119:474–475
Duncan GJ, Tooke SMT (1990) Echinococcus infestation of the biceps brachii. Clin Orthop 261:247–250
Engin G, Acunaş B, Rozanes İ, Acunaş G (2000) Hydatid disease with unusual localization. Eur Radiol 10:1904–1912
Eroğlu A, Atabekoğlu Ş, Kocaoğlu H (1999) Primary hydatid cyst of the neck. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 256:202–204
Garcia-Diez AI, Ros Mendoza LH, Villacampa VM, Cozar M, Fuertes MI (2000) MRI evaluation of soft tissue hydatid disease. Eur Radiol 10:462–466
Prousalidis J, Tzardinoglou K, Sgouradis L, Katsohis C, Aletras H (1998) Uncommon sites of hydatid disease. World J Surg 22:17–22
Rask MR, Lattig GJ (1970) Primary intramuscular hydatidosis of the sartorius. J Bone Joint Surg Am 52:582–584
Tatari H, Baran Ö, Şanlıdağ T, Göre O, Ak D, Manisalı M, Havıtçıoğlu H (2001) Primary intramuscular hydatidosis of supraspinatus muscle. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 121:93–94
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Özkoç, G., Akpınar, S., Hersekli, M.A. et al. Primary hydatid disease of the quadriceps muscle: a rare localization. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 123, 314–316 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-003-0512-1
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-003-0512-1