Abstract
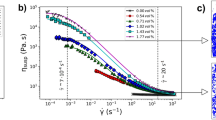
Platinum group metals (PGM) particles are generally found in nuclear borosilicate glasses resulting from the melting, at 1200 °C, of a glass precursor and fission products issued from spent fuel reprocessing. Contrary to some other elements, such as iron, nickel, and chromium, these particles are not incorporated chemically in molten glasses. During the melting step, the presence of these metals as suspended particles of a few microns has an impact on the rheological properties of the material, leading to a non-Newtonian behavior. Their impact on the process is the object of characterization and modeling of many studies that have established that the melt presents a shear-thinning and thixotropic behavior. In this work, a deeper analysis of the thixotropic behavior of a simulated nuclear glass melt containing 3.0 wt% (1.02 vol%) of PGM particles is presented. Steady and transient state rheological measurements were performed over a wide shear rate range using a stress-imposed rheometer at temperatures ranging from 1100 to 1250 °C. A mathematical modeling of the glass melt suspension thixotropic behavior is presented for the first time, using a thixotropic model akin to that proposed by Moore. This model is found to explain and predict successfully the rheological behavior of the material. In particular, it allows predicting the transient behavior of the samples from steady-state experiments, without additional adjustable parameters. The present study thus provides an important input for the modeling of the vitrification process.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Advocat T, Dussossoy JL, Petitjean V (2008) ‘Vitrification des déchets radioactifs et appareillage’. Les Techniques de l’Ingénieur 33. pp. 0–27
Akai T et al (1997) Chemical behavior of platinum-group metals in oxide glasses. J Non-Cryst Solids 222:304–309
Barnes HA (1997) Thixotropy—a review. J Nonnewton Fluid Mech 70(1–2):1–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0377-0257(97)00004-9
Barnes HA (2000) A Handbook of Elementary Rheology. The University of Wales- Institute of Non-Newtonian Fluid Mechanics, Department of Mathematics, Avaiable online
Bousmina M, Aït-Kadi A, Faisant JB (1999) Determination of shear rate and viscosity from batch mixer data: theoretical and experimental results. J Rheol 43:1999
Bousmina M et al (2010) Quantitative analysis of mixer-type rheometers using the Couette analogy. Can J Chem Eng 80(December):1166–1174. https://doi.org/10.1002/cjce.5450800618
Chavan VV, J.J.U (1973) ‘Power correlations for close clearance helical impellers in non-newtonian liquids’. Ind Eng Chem Process Des Dev 12:472–476
Cheng DCH, Evans F (1965) Phenomenological characterization of the rheological behaviour of inelastic reversible thixotropic and antithixotropic fluids. Br J Appl Phys 16(11):1599–1617. https://doi.org/10.1088/0508-3443/16/11/301
Derksen JJ (2011) Simulations of thixotropic liquids. Appl Math Model 35(4):1656–1665. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apm.2010.09.042
Dullaert K, Mewis J (2005) Thixotropy: Build-up and breakdown curves during flow. J Rheol 49(6):1213–1230. https://doi.org/10.1122/1.2039868
Estellé P et al (2008) Processing the vane shear flow data from Couette analogy. Appl Rheol 18(3):1–14
Gotoh S et al (1970) Power consumption of mixing impellers in Bingham plastic liquids. J Chem Eng Jpn 3(2):237–243. https://doi.org/10.1252/jcej.3.237
Grandjean A et al (2007) Correlation between electrical conductivity, viscosity, and structure in borosilicate glass-forming melts. Phys Rev B: Condens Matter Mater Phys 75(5):1–7. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.75.054112
Grünewald W et al (2008) The role of the platinum group elements ruthenium, rhodium and palladium in the vitrification of radioactive high level liquid waste using joule heated ceramic lined waste glass melters. Glass Technol: Eur J Glass Sci Technol Part A 49(6):266–278
Guillemin JP et al (2008) Development of a new mixing rheometer for studying rheological behaviour of concentrated energetic suspensions. J Nonnewton Fluid Mech 151(1–3):136–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnnfm.2007.12.007
Hanotin C et al (2016) Platinum group metal particles aggregation in nuclear glass melts under the effect of temperature. J Nucl Mater 477:102–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnucmat.2016.04.033
Hartmann T, Pentinghaus H (2012) The ternary system palladium-rhodium-tellurium: a study to understand phase formation in the vitrification process of high-level waste concentrates (HLWC). J Nucl Mater 422(1–3):124–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnucmat.2011.12.029
Luckscheiter B (1991) Properties and behavior of the platinum group metals in the glass resulting from the vitrification of simulated nuclear fuel reprocessing waste. J Mater Res 6(12):2535–2546. https://doi.org/10.1557/JMR.1991.2535
Mewis J (1979) Thixotropy - a general review. J Nonnewton Fluid Mech 6(1):1–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/0377-0257(79)87001-9
Moore F (1959) The rheology of ceramic slips and bodies. Trans Br Ceram Soc 58:470–494
Mujumdar A, Beris AN, Metzner AB (2002) Transient phenomena in thixotropic systems. J Nonnewton Fluid Mech 102(2):157–178. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0377-0257(01)00176-8
Nuernberg R et al (2021) The origin of hysteresis in the electrical behavior of RuO2-glass composite melts. J Non-Cryst Solids 557:120596. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2020.120596
Pereira Machado NM (2022) Rheological study of nuclear glass melts containing Platinum Group Metal aggregates. Lorraine University, Thesis
Pflieger R et al (2009) Behaviour of ruthenium dioxide particles in borosilicate glasses and melts. J Nucl Mater 389(3):450–457. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnucmat.2009.02.034
Puig J et al (2014) Rheological properties of nuclear glass melt containing platinum group metals. Procedia Mater Sci 7:156–162. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mspro.2014.10.021
Puig J et al (2016) High temperature rheological study of borosilicate glasses containing platinum group metal particles by means of a mixer-type rheometer. J Nucl Mater 469:112–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnucmat.2015.11.053
Richmond WR, Jones RL, Fawell PD (1998) The relationship between particle aggregation and rheology in mixed silica-titania suspensions. Chem Eng J 71(1):67–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1385-8947(98)00105-3
Roth G, Weisenburger S (2000) Vitrification of high-level liquid waste: glass chemistry, process chemistry and process technology. Nucl Eng Des 202(2–3):197–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0029-5493(00)00358-7
Simonnet C, Grandjean A, Phalippou J (2005) Electrical behavior of platinum-group metals in glass-forming oxide melts. J Nucl Mater 336(2–3):243–250. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnucmat.2004.09.019
Taylor RF (1985) Chemical engineering problems of radioactive waste fixation by vitrification. Chem Eng Sci 40(4):541–569. https://doi.org/10.1016/0009-2509(85)80001-4
Uruga K et al (2014) Viscoplasticity of simulated high-level radioactive waste glass containing platinum group metal particles. J Nucl Mater 452(1–3):419–424. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnucmat.2014.05.062
Vargas S (2001) Straw and Coal Ash Rheology. Technical University of Denmark, Thesis
Vernaz É, Bruezière J (2014) History of nuclear waste glass in France. Procedia Mater Sci 7:3–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mspro.2014.10.002
Acknowledgements
The Commissariat à l’Énergie Atomique et aux Énergies Alternatives (CEA) and Orano are gratefully acknowledged for their financial support.
Funding
This study was funded by the Commissariat à l’Énergie Atomique et aux Énergies Alternatives (CEA) and Orano.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Pereira Machado, N.M., Neyret, M., Lemaître, C. et al. Thixotropic behavior of a glass melt of nuclear interest containing platinum group metal particles. Rheol Acta 61, 857–866 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00397-022-01372-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00397-022-01372-x