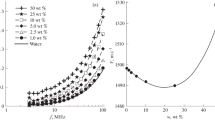
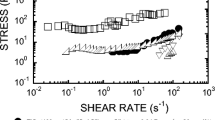
Abstract
The viscosity of aqueous suspensions of 25 nm titanium dioxide nano-particles was studied as a function of shear rate, temperature, and particle concentration. It is suggested that the complex behaviour of the material could be explained by the interplay of three factors, each having activation energy and activation entropy components. These are the intrinsic viscosity which was shown to obey a semi-empirical form of DLVO equation plus two shear rate–dependent mechanisms, one (thinning) changing the structure from an ordered to a disordered state, the other (thickening) an activation action term due to energy dissipated in particle collisions.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atkins PW (1998) Physical Chemistry, 6th edn. Oxford University Press, Oxford, UK
Bergstrom L (1998) Shear thinning and shear thickening of concentrated ceramic suspensions. Colloids Surf A 133:151–155
Chadwick MD, Goodwin JW, Vincent B, Lawson EJ, Mills PDA (2002) Rheological behaviour of titanium dioxide (uncoated anatase) in ethylene glycol. Colloids Surf A 196(235):245
Chandler HD (2013) Activation energy and entropy for viscosity of wormlike micelle solutions. J Colloid Interface Sci 409:98–103
Chandler HD (2017) Activation entropy and anomalous temperature dependence of viscosity in aqueous suspensions of Fe2O3. Powder Technol 305:572–577
Chandler HD (2019) A Physical Basis for Non-Newtonian Power Law Viscosity: Soft Mater 17:137–142
Cottrell AH, The mechanical properties of matter, J.Wiley, London, UK, 1964.
Duangthonusk WS, Wongwies S (2009) Measurement of temperature-dependent thermal conductivity and viscosity of TiO2-water nanofluids. Exptl Thermal and Fluid Sci 33:706–714
Fedele L, Colla L, Bobbo S (2012) Viscosity and thermal conductivity measurements of water-based nanofluids containing titanium dioxide nanoparticles. Int J Refrig 35:1359–1366
Frost HJ, Ashby M.F Deformation-mechanism maps, Pergamon Press, Oxford, UK, 1982.
Garoosi F (2020) Presenting two new empirical models for calculating the effective dynamic viscosity and thermal conductivity of nanofluids. Powder Technol 366:788–820
Gomez –Merino AI, Arjona-Escudero JL, Santos-Raez IM, Rubio-Hernandez FJ, (2019) Microstructure and thermodynamic properties of aqueous alumina nanofluids. Powder Technol 353:509–515
Gomez –Merino AI, Rubio-Hernandez FJ, Velazquez –Navarro JF, Aguiar J, Jimenez –Agredano C, (2014) Study of the aggregation state of anatase water nanofluids using rheological and DLS methods. Ceram Int 40:14045–14050
Hanamann T (2008) Influence of particle properties on the viscosity of polymer-alumina composites. Ceram Int 34:2099–2015
He Y, Jin Y, Chen H, Ding Y, Cang D, Liu H (2007) Heat transfer and flow behaviour of aqueous suspensions of TiO2 nanoparticles (nanofluids) flowing upward through a vertical pipe. Int J Heat and Mass Transfer 50:2272–2281
Hoffman RL (1974) Discontinuous and dilatant viscosity behaviour in concentrated suspensions, II. Theory and experimental tests. J Colloid Interface Sci 46:491–506
Krieger IM, Dougherty TJ (1959) A mechanism for non-Newtonian flow in a suspension of rigid spheres. Trans Soc Rheol 3:137–152
Mikulasek P, Wakeman RJ, Marchant JQ (1997) The influence of pH and temperature on the rheology and stability of aqueous titanium dioxide dispersions. Chem Eng J 67:97–102
Morris GE, Skinner WA, Self PG, Smart RStC, (1999) Surface chemistry and rheological behaviour of titania pigment suspensions. Colloids Surf A 155:27–41
Ree RFH, T, Eyring H, (1958) Relaxation theory of transport problems in condensed systems. Ind Eng Chem 50:1036–1040
Silambarasan M, Manikandan S, Rajan KS (2012) Viscosity and thermal conductivity of sub-micron TiO2 particles in water prepared by stirred bead milling and ultrasonication. Int J Heat and Mass Transfer 55:7991–8002
Taylor ML, Morris GE, Smart RStC (2003) Influence of aluminium doping on titania pigment structural and dispersion properties. J Colloid Interface Sci 262:81–88
Tseng WJ, Lin K-C (2003) Rheology and colloidal structure of aqueous TiO2 nanoparticle suspensions. Mater Sci Eng A 355:186–192
Turian RM, Ma TW, Hsu FLG, Sung DJ (1997) Characterization, settling, and rheology of concentrated fine particulate mineral slurries. Powder Technol 93:219–233
Yang H-G, Li C-Z, Gu H-C, Fang T-N Rheological behaviour of titanium dioxide suspensions (2001) J. Colloid Interface Sci 236:96–103.
Zhou Z, Scales PJ, Boger DV (2001) Chemical and physical control of the rheology of concentrated metal oxide suspensions. Chem Eng Sci 56:2901–2920
Zupancic A, Lapasin R, Zumer M (1997) Rheological characterisation of shear thickening TiO2 suspensions in low molecular polymer solutions. Prog Organic Coatings 30:67–78
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chandler, H.D. Viscosity of aqueous suspensions of titanium dioxide (anatase) nano-particles. Rheol Acta 61, 473–481 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00397-022-01348-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00397-022-01348-x