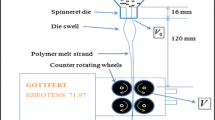
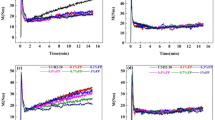
Abstract
In this study, rheological behaviors and capillary extrusion flow instabilities of ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene (UHMWPE)/high-density polyethylene (HDPE)/SiO2 composites containing modified nano-SiO2 or pure nano-SiO2 are investigated. Effects of interfacial conditions between the dispersed nano-SiO2 phase and PE matrix on rheological behaviors are analyzed. The results show that modified nano-SiO2 in the PE matrix has a relatively strong interfacial interaction with the polymer chains compared with pure nano-SiO2, thus causing a more pronounced shear thinning behavior and reducing extrudate swell during capillary extrusion. Nanocomposite extrudates experience the transition of smooth- sharkskin- oscillating distortion—overall melt fracture with the increase of shear rate (or shear stress). The interfacial interaction allows a more storage of elastic energy as the melt flow through the die, resulting in sharkskin distortion and oscillating distortion to occur prematurely at critical shear rates. It also restricts the elastic recovery of the melt after leaving the die, thus delaying sharkskin distortion under shear stress. At high shear rates, the modified nano-SiO2 particles begin to roll, and some of the unmodified particles move and embed to the wall. It is believed that the interfacial adsorption effect and the wall-slip effect of nanoparticles exist simultaneously in the whole extrusion process.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allal A, Lavernhe A, Vergnes B, Marin G (2006) Relationships between molecular structure and sharkskin defect for linear polymers. J Non-Newtonian Fluid Mech 134:127–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnnfm.2005.12.010
Ansari M, Hatzikiriakos SG, Sukhadia AM, Rohlfing DC (2012a) Melt fracture of two broad molecular weight distribution high-density polyethylenes. Polym Eng Sci 52(4):795–804. https://doi.org/10.1002/pen.22144
Ansari M, Inn YW, Sukhadia AM, DesLauriers PJ, Hatzikiriakos SG (2012b) Melt fracture of HDPEs: metallocene versus Zieglere–Natta and broad MWD effects. Polymer 53(19):4195–4201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2012.07.030
Ansari M, Derakhshandeh M, Doufas AA, Tomkovic T, Hatzikiriakos SG (2018) The role of microstructure on melt fracture of linear low density polyethylenes. Polym Test 67:266–274. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymertesting.2018.03.015
Barone J, Wang SQ (1999) Flow birefringence study of sharkskin and stress relaxation in polybutadiene melts. Rheol Acta 38:404–414. https://doi.org/10.1007/s003970050191
Barone JR, Plucktaveesak N, Wang SQ (1998) Interfacial molecular instability mechanism for sharkskin phenomenon in capillary extrusion of linear polyethylenes. J Rheol 42:813–832. https://doi.org/10.1122/1.550902
Bigio D, Meillon MG, Kharchenko SB, Morgan D, Zhou H, Oriani SR, Macosko CW, Migler KB (2005) Coating kinetics of fluoropolymer processing aids for sharkskin elimination: the role of droplet size. J Non-Newtonian Fluid Mech 131:22–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnnfm.2005.04.008
Cai LF, Huang XB, Rong MZ, Ruan WH, Zhang MQ (2006) Effect of grafted polymeric foaming agent on the structure and properties of nano-silica/polypropylene composites. Polymer 47(20):7043–7050. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2006.08.016
Chen KP, Joseph DD (1992) Elastic short wave instability in extrusion flows of viscoelastic liquids. J Non-Newtonian Fluid Mech 42(1–2):189–211. https://doi.org/10.1016/0377-0257(92)80009-M
Chen X, Yoon K, Burger C, Sics I, Fang D, Hsiao BS, Chu B (2005) In-situ X-ray scattering studies of a unique toughening mechanism in surface-modified carbon nanofiber/UHMWPE nanocomposite films. Macromolecules 38:3883–3893. https://doi.org/10.1021/ma047978r
Cogswell FN (1977) Stretching flow instabilities at the exits of extrusion dies. J Non-Newtonian Fluid Mech 2:37–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/0377-0257(77)80031-1
Denn MM (2001) Extrusion instabilities and wall slip. Annu Rev Fluid Mech 33:265–287. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.fluid.33.1.265
Hatzikiriakos SG (2012) Wall slip of molten polymers. Prog Polym Sci 37:624–643. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2011.09.004
Hatzikiriakos SG, Dealy JM (1993) Effects of interfacial conditions on wall slip and sharkskin melt fracture of HDPE. Int Polym Process 8(1):36–43. https://doi.org/10.3139/217.930036
Hatzikiriakos SG, Migler KB (2004) Polymer processing instabilities: control and understanding. Marcel Dekker, New York
Hatzikiriakos SG, Kazatchkov IB, Vlassopoulos D (1997) Interfacial phenomena in the capillary extrusion of metallocene polyethylenes. J Rheol 41:1299–1316. https://doi.org/10.1122/1.550836
Inn YW (2013) Melt fracture and wall slip of metallocene-catalyzed bimodal polyethylenes in capillary flow. J Rheol 57:393. https://doi.org/10.1122/1.4774397
Jaggi HS, Satapathy BK, Ray AR (2014) Viscoelastic properties correlations to morphological and mechanical response of HDPE/UHMWPE blends. J Polym Res 21:482. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-014-0482-8
Joseph DD (1997) Steep wave fronts on extrudates of polymer melts and solutions: lubrication layers and boundary lubrication. J Non-Newtonian Fluid Mech 70(3):187–203. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0377-0257(96)01532-7
Ketata M, Ayadi A, Elkissi N, Bradai C (2017) Effect of rheological and physical properties on mitigation of melt fracture instability during extrusion of polymer melts through a radial flow die. Rheol Acta 56(4):341–350. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00397-017-0995-2
Khasraghi SS, Rezaei M (2015) Preparation and characterization of UHMWPE/HDPE/MWCNT melt-blended nanocomposites. J Thermoplast Compos Mater 28(3):305–326. https://doi.org/10.1177/0892705713484745
Kim J, Kim DH, Son Y (2009) Rheological properties of long chain branched polyethylene melts at high shear rate. Polymer 50:4998–5001. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2009.08.013
Lee H, Kim DH, Son Y (2006) Anomalous rheological behavior of polyethylene melts in the gross melt fracture regime in the capillary extrusion. Polymer 47:3929–3934. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2006.03.084
Li Y, Yu J, Guo ZX (2002) The influence of silane treatment on nylon 6/nano-SiO2 in situ polymerization. J Appl Polym Sci 84:827. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.10349
Li Y, Yu J, Guo ZX (2003) The influence of interphase on nylon-6/nano-SiO2 composite materials obtained from in situ polymerization. Polym Int 52:981–986. https://doi.org/10.1002/pi.1173
Li YM, Wang Y, Bai L, Zhou HLZ, Yang W, Yang MB (2011) Dynamic rheological behavior of HDPE/UHMWPE blends. J Macromol Sci B 50:1249–1259. https://doi.org/10.1080/00222348.2010.503167
Lim KLK, Mohd Ishak ZA, Ishiaku US, Fuad AMY, Yusof AH, Czigany T, Pukanszky B, Ogunniyi DS (2005) High-density polyethylene/ultrahigh-molecular-weight polyethylene blend. I. The processing, thermal, and mechanical properties. J Appl Polym Sci 97:413–425. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.21298
Miller E, Rothstein JP (2004) Control of the sharkskin instability in the extrusion of polymer melts using induced temperature gradients. Rheol Acta 44:160–173. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00397-004-0393-4
Ong HL, Akil HM, Mohd Ishak ZA (2011) Surface-activated nanosilica treated with silane coupling agents/polypropylene composites: mechanical, morphological, and thermal studies. Polym Compos 32:1568–1583. https://doi.org/10.1002/pc.21190
Palza H, Reznik B, Kappes M, Hennrich F, Naue IFC, Wilhelm M (2010) Characterization of melt flow instabilities in polyethylene/carbon nanotube composites. Polymer 51:3753–3761. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2010.06.016
Reynaud E, Jouen T, Gauthier C, Vigier G, Varlet J (2001) Nanofillers in polymeric matrix: a study on silica reinforced PA6. Polymer 42(21):8759–8768. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0032-3861(01)00446-3
Singh VP, Vimal KK, Kapur GS, Sharma S, Choudhary V (2016) High-density polyethylene/halloysite nanocomposites: morphology and rheological behaviour under extensional and shear flow. J Polym Res 23:43. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-016-0937-1
Stojanovic D, Orlovic A, Markovic S, Radmilovic V, Uskokovic PS, Aleksic R (2009) Nanosilica/PMMA composites obtained by the modification of silica nanoparticles in a supercritical carbon dioxide–ethanol mixture. J Mater Sci 44:6223–6232. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-009-3842-8
Tam TY, Aminuddin N, Young JA (2013) Melt spinning blends of UHMWPE and HDPE and fibers made therefrom. Patent 8426510, USA
Tian G, Liu J, Sun T, Wang X, Wang X, Hu H, Li C, Dong X, Wang D (2018) The effects of carbon materials with different dimensionalities on the flow instabilities of LLDPE (linear low density polyethylene). Polymer 142:144–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2018.01.085
Vega JF, Expósito MT, Otegui J, Martínez-Salazar J (2011) Eliminating sharkskin distortion in polyethylene extrusion via a molecular route. J Rheol 55:855–873. https://doi.org/10.1122/1.3589798
Wang SQ, Drda PA, Inn YW (1996) Exploring molecular origins of sharkskin, partial slip, and slope change in flow curves of linear low density polyethylene. J Rheol 40:875–897. https://doi.org/10.1122/1.550766
Wang X, Wu Q, Qi Z (2003) Unusual rheology behaviour of ultra high molecular weight polyethylene/kaolin composites prepared via polymerization-filling. Polym Int 52:1078–1082. https://doi.org/10.1002/pi.1165
Wu QY, Wu JA (2014) Polymer rheology, 2nd edn. Higher Education Press, Beijing
Wu CL, Zhang MQ, Rong MZ, Friedrich K (2005) Silica nanoparticles filled polypropylene: effects of particle surface treatment, matrix ductility and particle species on mechanical performance of the composites. Compos Sci Technol 65:635–645. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compscitech.2004.09.004
Xu H, Lele A, Rastogi S (2011) The influence of carbon-based nanofillers on the melt flow singularity of linear polyethylene. Polymer 52:3163–3174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2011.04.046
Xue Y, Wu W, Jacobs O, Schädel B (2006) Tribological behaviour of UHMWPE/HDPE blends reinforced with multi-wall carbon nanotubes. Polym Test 4:221–229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymertesting.2005.10.005
Zhang Q, Lippits DR, Rastogi S (2006) Dispersion and rheological aspects of SWNTs in ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene. Macromolecules 39:658–666. https://doi.org/10.1021/ma051031n
Funding
The authors would like to acknowledge the support of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51673021).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, L., Wang, F., Xue, P. et al. Influence of interfacial condition on rheological instability behavior of UHMWPE/HDPE/nano-SiO2 blends in capillary extrusion. Rheol Acta 58, 183–192 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00397-019-01139-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00397-019-01139-x