Abstract
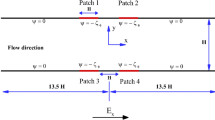
A numerical investigation is performed into the flow characteristics and mixing performance of electrokinetically driven non-Newtonian fluid in a contraction–expansion microchannel. In the study, the rheological behavior of the fluid is characterized using a power-law model. The results show that the volumetric flow rate reduces as the flow behavior index increases, and thus an improved mixing performance is obtained. Furthermore, it is shown that for all considered values of the flow behavior index, the mixing performance can be enhanced by increasing the ratio of the main channel width to the contraction channel width, extending the length of the contraction channel, assigning a smaller value to the nondimensional Debye–Hückel parameter, and applying an appropriate electric field strength. Finally, it is shown that although the mixing efficiency reduces with a reducing flow behavior index, an acceptable mixing performance can still be obtained given an appropriate specification of the flow conditions and geometry parameters.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Babaie A, Sadeghi A, Saidi MH (2011) Combined electroosmotically and pressure driven flow of power-law fluids in a slit microchannel. J Non-Newton Fluid Mech 166:792–798
Berli CLA, Olivares ML (2008) Electrokinetic flow on non-Newtonian fluids in microchannels. J Colloid Interface Sci 320:582–589
Chakraborty S (2007) Electroosmotically driven capillary transport of typical non-Newtonian biofluids in rectangular microchannels. Anal Chim Acta 605:175–184
Chen CK, Cho CC (2007) Electrokinetically-driven flow mixing in microchannels with wavy surface. J Colloid Interface Sci 312:470–480
Chen CK, Cho CC (2008) Electrokinetically driven flow mixing utilizing chaotic electric fields. Microfluid Nanofluid 5:785–793
Cho CC, Ho CJ, Chen CK (2010) Enhanced micromixing of electroosmotic flows using aperiodic time-varying zeta potentials. Chem Eng J 163:180–187
Cho CC, Chen CL, Tsai RT, Chen CK (2011) A novel microfluidic mixer using aperiodic perturbation flows. Chem Eng Sci 66:6159–6167
Cho CC, Chen CL, Chen CK (2012) Electrokinetically-driven non-Newtonian fluid flow in rough microchannel with complex-wavy surface. J Non-Newton Fluid Mech 173–174:13–20
Choudhary R, Bhakat T, Singh RK, Ghubade A, Mandal S, Ghosh A, Rammohan A, Sharma A, Bhattacharya S (2011) Bilayer staggered herringbone micro-mixers with symmetric and asymmetric geometries. Microfluid Nanofluid 10:271–286
Das S, Chakraborty S (2006) Analytical solutions for velocity, temperature and concentration distribution in electroosmotic microchannel flows of a non-Newtonian bio-fluid. Anal Chim Acta 559:15–24
Glasgow I, Aubry N (2003) Enhancement of microfluidic mixing using time pulsing. Lab Chip 3:114–120
Hadigol M, Nosrati R, Raisee M (2011) Numerical analysis of mixed electroosmotic/pressure driven flow of power-law fluids in microchannels and micropumps. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 374:142–153
Hayase T, Humphrey JAC, Greif R (1992) A consistently formulated QUICK scheme for fast and stable convergence using finite-volume iterative calculation procedures. J Comput Phys 98:108–118
Jacobson SC, Ramsey JM (1997) Electrokinetic focusing in microfabricated channel structures. Anal Chem 69:3212–3217
Knight JB, Vishwanath A, Brody JP, Austin RH (1998) Hydrodynamic focusing on a silicon chip: mixing nanoliters in microseconds. Phys Rev Lett 80:3863–3866
Lee YK, Shih C, Tabeling P, Ho CM (2007) Experimental study and nonlinear dynamic analysis of time-periodic micro chaotic mixers. J Fluid Mech 575:425–448
Liu RH, Stremler MA, Sharp KV, Olsen MG, Santiago JG, Adrian RJ, Aref H, Beeber DJ (2000) Passive mixing in a three-dimensional serpentine microchannel. J Microelectromech Syst 9:190–197
Mao WB, Xu JL (2009) Micromixing enhanced by pulsating flows. Int J Heat Mass Transfer 52:5258–5261
Masilamani K, Ganguly S, Feichtinger C, Rüde U (2011) Hybrid lattice-Boltzmann and finite-difference simulation of electroosmotic flow in a microchannel. Fluid Dyn Res 43:025501
Mengeaud V, Josserand J, Girault HH (2002) Mixing processes in a zigzag microchannel: finite element simulations and optical study. Anal Chem 74:4279–4286
Niu X, Lee YK (2003) Efficient spatial-temporal chaotic mixing in microchannels. J Micromechanics Microengineering 13:454–462
Oddy MH, Santiago JG, Mikkelsen JC (2001) Electrokinetic instability micromixing. Anal Chem 73:5822–5832
Pacheco JR (2008) Mixing enhancement in electro-osmotic flows via modulation of electric fields. Phys Fluids 20:093603
Park JM, Kim DS, Kang TG, Kwon TH (2008) Improved serpentine laminating micromixer with enhanced local advection. Microfluid Nanofluid 4:513–523
Patankar SV (1980) Numerical heat transfer and fluid flow. McGraw-Hill, New York
Patankar NA, Hu HH (1998) Numerical simulation of electroosmotic flow. Anal Chem 70:1870–1881
Phelan FR, Kutty P, Pathak JA (2008) An electrokinetic mixer driven by oscillatory cross flow. Microfluid Nanofluid 5:101–118
Stroock AD, Dertinger SKW, Ajdari A, Mezic I, Stone HA, Whitesides GM (2002) Chaotic mixer for microchannels. Science 295:647–651
Tang GH, Li XF, He YL, Tao WQ (2009) Electroosmotic flow of non-Newtonian fluid in microchannels. J Non-Newton Fluid Mech 157:133–137
Vasu N, De S (2010) Electroosmotic flow of power-law fluids at high zeta potentials. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 368:44–52
Yang C, Li D, Masliyah JM (1998) Modeling forced liquid convection in rectangular microchannels with electrokinetic effects. Int J Heat Mass Transfer 41:4229-4249
Zhao C, Zholkovskij E, Masliyah JH, Yang C (2008) Analysis of electroosmotic flow of power-law fluids in a slit microchannel. J Colloid Interface Sci 326:503–510
Zhao C, Yang C (2012) Joule heating induced heat transfer for electroosmotic flow of power-law fluids in a microcapillary. Int J Heat Mass Transfer 55:2044–2051
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the National Science Council of the Republic of China, Taiwan, for the financial support of this study under contract nos. NSC-98-2221-E-006-176-MY2, NSC-99-2811-E-006-061, and NSC 100-2811-E-006-075
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cho, CC., Chen, CL. & Chen, CK. Flow characteristics and mixing performance of electrokinetically driven non-Newtonian fluid in contraction–expansion microchannel. Rheol Acta 51, 925–935 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00397-012-0650-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00397-012-0650-x