Abstract
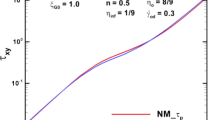
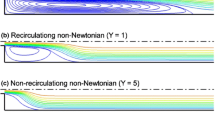
This numerical study focuses on regularised Bingham-type and viscoelastoplastic fluids, performing simulations for 4:1:4 contraction–expansion flow with a hybrid finite element–finite volume subcell scheme. The work explores the viscoplastic regime, via the Bingham–Papanastasiou model, and extends this into the viscoelastoplastic regime through the Papanastasiou–Oldroyd model. Our findings reveal the significant impact that elevation has in yield stress parameters, and in sharpening of the stress singularity from that of the Oldroyd/Newtonian models to the ideal Bingham form. Such aspects are covered in field response via vortex behaviour, pressure-drops, stress field structures and yielded–unyielded zones. With rising yield stress parameters, vortex trends reflect suppression in both upstream and downstream vortices. Viscoelastoplasticity, with its additional elasticity properties, tends to disturb upstream–downstream vortex symmetry balance, with knock-on effects according to solvent-fraction and level of elasticity. Yield fronts are traced with increasing yield stress influences, revealing locations where relatively unyielded material aggregates. Analysis of pressure drop data reveals significant increases in the viscoplastic Bingham–Papanastasiou case, O (12%) above the equivalent Newtonian fluid, that are reduced to 8% total contribution increase in the viscoelastoplastic Papanastasiou–Oldroyd case. This may be argued to be a consequence of strengthening in first normal stress effects.


















Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
To date, the concept of the yield stress and its definition remains a subject of controversy. Hence, in the literature, doubts are often expressed whether the yield stress exists in reality (as discussed in a plenary lecture by K. Walters at the YPF 2009 conference).
References
Abdali SS, Mitsoulis E, Markatos NC (1992) Entry and exit flows of Bingham fluids. J Rheol 36:389–407
Aboubacar M, Webster MF (2001) A cell-vertex finite volume/element method on triangles for abrupt contraction viscoelastic flows. J Non-Newton Fluid Mech 98:83–106
Aguayo JP, Tamaddon-Jahromi HR, Webster MF (2006) Extensional response of the pom-pom model through planar contraction flows for branched polymer melts. J Non-Newton Fluid Mech 134:105–126
Aguayo JP, Tamaddon-Jahromi HR, Webster MF (2008) Excess pressure-drop estimation in contraction and expansion flows for constant shear-viscosity, extension strain-hardening fluids. J Non-Newton Fluid Mech 153:157–176
Azouz I, Shirazi SA, Pilehvari A, Azar JJ (1993) Numerical simulation of laminar flows of yield-power-law fluids in conduits of arbitrary cross-section. J Fluids Eng 115:710–716
Balmforth NJ, Craster RV (2001) Geophysical aspects of non-newtonian fluid mechanics. In: Lecture notes in physics, vol 582/2001, Springer, Berlin/Heidelberg, pp 34–51
Baloch A, Webster MF (1995) A computer simulation of complex flows of fibre suspensions. Comput Fluids 24:135–151
Barnes HA (1999) The yield stress—a review or ‘πανταρι’–everything flows? J Non-Newton Fluid Mech 81:133–178
Barnes HA, Walters K (1985) The yield stress myth? Rheol Acta 24:323–326
Bingham EC (1922) Fluidity and plasticity. McGraw Hill, New York
Bonn D (2009) Yield stress fluids: to flow or not to flow, that is the question. Viscoplastic fluids: from theory to application, Cyprus
Burgos GR, Alexandrou AN, Entov V (1999) On the determination of yield surfaces in Herschel–Bulkley fluids. J Rheol 43:463–483
Carter RE, Warren RC (1987) Extrusion stresses, die swell, and viscous heating effects in double-base propellants. J Rheol 31:151–173
de Souza Mendes PR, Naccache MF, Varges PR, Marchesini FH (2007) Flow of viscoplastic liquids through axisymmetric expansions-contractions. J Non-Newton Fluid Mech 142:207–217
Dimakopoulos Y, Tsamopoulos J (2003) Transient displacement of viscoplastic fluids by air in straight or suddenly constricted tubes. J Non-Newton Fluid Mech 112:43–75
Dimakopoulos Y, Tsamopoulos J (2007) Transient displacement of Newtonian and viscoplastic liquids by air from complex conduits. J Non-Newton Fluid Mech 142:162–182
Donea J (1984) A Taylor-Galerkin method for convective transport problems. Int J Numer Methods Eng 20:101–119
Ellwood KRJ, Georgiou GC, Papanastasiou TC, Wilkes JO (1990) Laminar jets of Bingham-plastic liquids. J Rheol 34:787–812
Frigaard IA, Nouar C (2005) On the usage of viscosity regularization methods for viscoplastic fluid flow computation. J Non-Newton Fluid Mech 127:1–26
Hartnett JP, Hu RYZ (1989) Technical note: the yield stress—an engineering reality. J Rheol 33:671–679
Hawken DM, Tamaddon-Jahromi HR, Townsend P, Webster MF (1990) A Taylor-Galerkin based algorithm for viscous incompressible flow. Int J Numer Methods Fluids 10:327–351
Matallah H, Townsend P, Webster MF (1998) Recovery and stress-splitting schemes for viscoelastic flows. J Non-Newton Fluid Mech 75:139–166
Mitsoulis E (2007) Annular extrude swell of pseudoplastic and viscoelastic fluids. J Non-Newton Fluid Mech 141:138–147
Mitsoulis E, Huilgol RR (2004) Entry flows of Bingham plastics in expansions. J Non-Newton Fluid Mech 122:45–54
Mitsoulis E, Abdali SS, Markatos NC (1993) Flow simulation of Herschel-Bulkley fluids through extrusion dies 71:147–160
Møllera PCF, Mewisb J, Bonn D (2006) Yield stress and thixotropy: on the difficulty of measuring yield stresses in practice. Soft Matter 2:274–283
Papanastasiou TC (1987) Flows of materials with yield. J Rheol 31:385–404
Rothstein JP, McKinley GH (1999) Extensional flow of a polystyrene Boger fluid through a 4:1:4 axisymmetric contraction/expansion. J Non-Newton Fluid Mech 86:61–88
Rothstein JP, McKinley GH (2001) The axisymmetric contraction-expansion: the role of extensional rheology on vortex growth dynamics and the enhanced pressure drop. J Non-Newton Fluid Mech 98:33–63
Saramito P (2007) A new constitutive equation for elastoviscoplastic fluid flows. J Non-Newton Fluid Mech 145:1–14
Szabo P, Rallison JM, Hinch EJ (1997) Start-up of flow of a FENE-fluid through a 4:1:4 constriction in a tube. J Non-Newton Fluid Mech 72:73–86
Tamaddon-Jahromi HR, Webster MF, Walters K (2010) Predicting numerically the large increases in extra pressure drop when Boger fluids flow through axisymmetric contractions. J Nat Sci 2:1–11
Walters K (2009) The yield stress concept—then and now. Plenary lecture given at the YPF 2009 Conference
Walters K, Webster MF, Tamaddon-Jahromi HR (2009a) The numerical simulation of some contraction flows of highly elastic liquids and their impact on the relevance of the Couette correction in extensional rheology. Chem Eng Sci 64:4632–4639
Walters K, Webster MF, Tamaddon-Jahromi HR (2009b) The White-Metzner model—then and now. The 25th annual meeting of the polymer processing society, Goa
Walters K, Tamaddon-Jahromi HR, Webster MF, Tomé MF, McKee S (2009c) The competing roles of extensional viscosity and normal stress differences in complex flows of elastic liquids. In: 20th anniversary symp., Korean society of rheology, Korea, pp 3–32
Wapperom P, Webster MF (1998) A second-order hybrid finite-element/volume method for viscoelastic flows. J Non-Newton Fluid Mech 79:405–431
Wapperom P, Webster MF (1999) Simulation for viscoelastic flow by a finite volume/element method. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 180:281–304
Webster MF, Tamaddon-Jahromi HR, Aboubacar M (2004) Transient viscoelastic flows in planar contractions. J Non-Newton Fluid Mech 118:83–101
Webster MF, Tamaddon-Jahromi HR, Aboubacar M (2005) Time-dependent algorithm for viscoelastic flow-finite element/volume schemes. Numer Methods Partial Differ Equ 21:272–296
Zienkiewicz OC, Morgan K, Peraire J, Vandati M, LÄohner R (1985) Finite elements for compressible gas flow and similar systems. In: 7th int. conf. comput. meth. appl. sci. eng., Versailles, France
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Belblidia, F., Tamaddon-Jahromi, H.R., Webster, M.F. et al. Computations with viscoplastic and viscoelastoplastic fluids. Rheol Acta 50, 343–360 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00397-010-0481-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00397-010-0481-6