Abstract
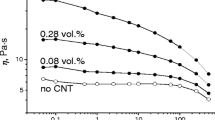
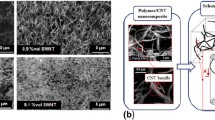
This paper describes optical observations on the way aggregates of multi-walled carbon nanotubes (CNTs) in an epoxy matrix can form unusual helical bands (HBs) that are aligned perpendicular to the shear flow. By applying specific flow conditions, HBs were formed from isotropic aggregates of CNTs suspended in an essentially Newtonian epoxy matrix. Both optical and matching rheological data are presented together with a schematic model of the way HBs are formed. It was discovered that the steady shear rheology of the CNT suspension did not substantially change during the observed micro-structure change. The HB structure may have relevance in terms of potential applications for CNTs.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ajayan PM, Stephan O, Colliex C, Trauth D (1994) Aligned carbon nanotube arrays formed by cutting a polymer resin-nanotube composite. Science 265:1212–1215
Baughman RH, Zakhidov AA, de Heer WA (2002) Carbon nanotubes—the route toward applications. Science 297:787–792
Batchelor GK (1977) The effect of Brownian motion on the block stress in a suspension of particles. J Fluid Mech 83:97–117
Bower C, Mackley MR, Smeulders BAS, Barker D, Hayes J (1998) The rheology, processing, and microstructure of complex fluids. In: Ottewill RH, Rennie AR (eds) Modern aspects of colloidal dispersions. Kluwer, Netherlands
Burgers (1938) On the motion of small particles of elongated form suspended in a viscous liquid. In: Second report on viscosity and plasticity. Nordemann, New York
Calvert P (1999) Nanotube composites: a recipe for strength. Nature 399:210–211
Degroot JV, Macosko CW, Kume T, Hashimoto T (1994) Flow-induced anisotropic SALS in silica-filled PDMS liquids. J Colloid Interface Sci 166:404–413
Dresselhaus MS, Avouris P (2001) Introduction to carbon materials research. In: Dresselhaus MS, Dresselhaus G, Avouris P (eds) carbon nanotubes, Top Appl Phys 80:1–9
Gervat L, Mackley MR, Nicholson TM, Windle AH (1995) The effect of shear on thermotropic liquid crystalline polymers. Philos Trans Phys Sci Eng 350:1–27
Grazian D, Mackley MR (1984a) Shear induced optical textures and their relaxation behaviour in thermotropic liquid crystalline polymers. Mol Cryst Liq Cryst 106:73–93
Grazian D, Mackley MR (1984b) Disclinations observed during the shear of MBBA. Mol Cryst Liq Cryst 106:103–119
Hinch EJ, Leal LG (1975) Constitutive equations in suspension mechanics. Part I. J Fluid Mech 71:481–495
Hinch EJ, Leal LG (1976) Constitutive equations in suspension mechanics. Part II. J Fluid Mech 76:187–208
Hobbie EK, Fry DJ (2006) Nonequilibrium phase diagram of sticky nanotube suspensions. Phys Rev Lett 97:036101-1–036101-4
Hobbie EK, Wang H, Kim H, Han CC, Grulke EA (2003a) Optical measurements of structure and orientation in sheared carbon-nanotube suspensions. Rev Sci Instrum 74:1244–1250
Hobbie EK, Wang H, Kim H, Lin-Gibson S, Grulke EA (2003b) Orientation of carbon nanotubes in a sheared polymer melt. Phys Fluids 15:1196–1202
Hoekstra H, Vermant J. Mewis J, Fuller GG (2003) Flow-induced anisotropy and reversible aggregation in two-dimensional suspensions. Langmuir 19:9134–9141
Huang YY, Ahir SV, Terentjev EM (2006) Dispersion rheology of carbon nanotubes in a polymer matrix. Phys Rev B 73:125422-1–125422-9
Iijima S (1991) Helical microtubules of graphitic carbon. Nature (London) 354:56–58
Lin-Gibson S, Pathak JA, Grulke EA, Wang H, Hobbie EK (2004) Elastic flow instability in nanotube suspensions. Phys Rev Lett 92:048302-1–048302-4
Mackley MR, Wannaborworn S, Gao P, Zhao F (1999) The optical microscopy of sheared liquids using a newly developed optical stage. J Microsc Anal 69:25–27
Macosko CW (1994) Rheology: principles, measurements and applications. Wiley/VCH, New York
Montesi A, Peña AA, Pasquali M (2004) Vorticity alignment and negative normal stresses in sheared attractive emulsions. Phys Rev Lett. 92:058303-1–058303-4
Morton WE, Wray GR (1962) An introduction to the study of spinning. Longmans, London
Petrie CJS (1999) The rheology of fibre suspensions. J Non-Newton Fluid Mech 87:369–402
Pignon F, Magnin A, Piau JM (1997) Butterfly light scattering pattern and rheology of a sheared thixotropic clay gel. Phys Rev Lett 79:4689–4692
Rahatekar SS, Koziol KKK, Butler SA, Elliott JA, Shaffer MSP, Mackley MR, Windle AH (2006) Optical microstructure and viscosity enhancement for an epoxy resin matrix containing multi-wall carbon nanotubes. J Rheol 50(5):599–610
Saito S (1997) Carbon nanotubes for next-generation electronics devices. Science 278:77–78
Sandler J, Shaffer MSP, Prasse T, Bauhofer W., Schulte K., Windle AH (1999) Development of a dispersion process for carbon nanotubes in an epoxy matrix and the resulting electrical properties. Polymer 40:5967–5971
Shaffer MSP, Fan X, Windle AH (1998) Dispersion and packing of carbon nanotubes. Carbon 36:1603–1612
Singh C, Shaffer MSP, Windle AH (2003) Production of controlled architectures of aligned carbon nanotubes by an injection chemical vapour deposition method. Carbon 41:359–368
Smoluchowski M (1917) Versuch einer mathematischen Theorie der Koagulationskinetik kolloider Lösungen. Z Phys Chem 92:129–168
Tans SJ, Verschueren ARM, Dekker C (1998) Room-temperature transistor based on a single carbon nanotube. Nature 393:49–52
Varadan P, Solomon MJ (2001) Shear-induced microstructural evolution of a thermoreversible colloidal gel. Langmuir 17:2918–2929
Vermant J, Solomon MJ (2005) Flow-induced structure in colloidal suspensions. J Phys Condens Matter 17:R187–R216
Warren LJ (1981) Shear flocculation. Chemtech 11:180–185
Zheng M, Jagota A, Semke ED, Diner BA, McLean RS, Lustig SR, Richardson RE, Tassi NG (2003) DNA-assisted dispersion and separation of carbon nanotubes. Nat Mater 2:338–342
Zollars RI, Ali SI (1986) Shear coagulation in the presence of repulsive interparticle forces. J Colloid Interface Sci 114:149–166
Acknowledgment
We would like to thank Prof. A.H. Windle and the Department of Materials Science and Metallurgy at the University of Cambridge for providing the base multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Anson Ma would also like to thank the Croucher Foundation Scholarship and the Overseas Research Students Awards Scheme `(ORSAS) for providing financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, A.W.K., Mackley, M.R. & Rahatekar, S.S. Experimental observation on the flow-induced assembly of Carbon nanotube suspensions to form helical bands. Rheol Acta 46, 979–987 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00397-007-0183-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00397-007-0183-x