Abstract
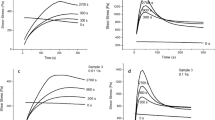
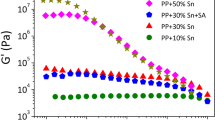
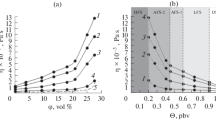
The aim of this work is to validate the use of dynamic oscillatory measurements in the melt to characterize the dispersion of a filler in a matrix after melt blending. Polyethylene oxide (PEO) is used as a polymeric matrix. Active carbon is used as a filler at a constant filler volume content of 26.4%. The melt viscosity of the polymeric matrix is varied by melt blending of two miscible POE and polyethylene glycol (PEG) species having very different molecular weight distributions. This enables to obtain various matrix viscosities and in turn various states of dispersion of the filler that were characterized by optical microscopy and image analysis. Dynamic mechanical measurements in the melt in the terminal zone show a large increase of the moduli associated to the presence of the filler. Comparison with the results of optical microscopy shows that this increase is clearly related to the dispersion. The interparticle distance is likely to be the leading parameter rather than the number of particles. Characterization of the amount of bound polymer shows that the amount of bound polymer is nearly independent of the matrix composition. Futhermore, the composition of the bound layer reflects the matrix composition though PEO is slightly preferentially bound on the active carbon.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel-Azim AA, Boutros WY, El-Sayed MA (1998) Estimation of the compatibility of poly(ethylene glycol)/poly(ethylene oxide) blends from dilute solution viscosity measurements. Polymer 39:2543–2549
Adams MJ, Edmondson B, Balachadran W (1987) Tribology in particulate technology. Adam Hilger, Bristol
Amari T, Uesugi K, Suzuki H (1997) Viscoelastic properties of carbon black suspension as a flocculated percolation system. Prog Org Coatings 31:171–178
Aranguren MI, Mora E, DeGroot JV, Macosko CW (1992) Effect of reinforced fillers on the rheology of polymer melts. J Rheol 36:1165–1182
Bar-Chaput S, Carrot C (2005) Interactions of active carbon with low and high molecular weight polyethylene glycol and polyethylene oxide. J Appl Polym Sci (in press)
Dizon ES (1976) Processing in an internal mixer as affected by carbon black properties. Rubber Chem Technol 49:12–27
Fekete E, Molnar S, Kim GM, Michler GH, Pukanszky B (1999) Aggregation, fracture initiation and strength of PP/CaCO3 composites. Morphology and micromechanics of polymers. J Macromol Sci Phys 38:885–899
Fetters LJ, Lohse DJ, Graessley WW (1999), Chain dimension and entanglement spacings in dense macromolecular systems. J Polym Sci Part B: Polym. Phys 37:1023–1033
Gahleitner M, Bernreitner K, Knogler B, Neissl W (1996) Rheology of hignly filled polypopylene compounds: measurement and applications. Macromol Symp 108:127–136
Gandhi K, Salovey R (1988) Dynamic mechanical behavior of polymers containing carbon black. Polym Eng Sci.28:877–887
Horwatt SW, Manas-Zloczower I, Feke DL (1992) Dispersion behaviour of heterogenous agglomerates at supercritical stresses. Chem Eng Sci 47:1849–1855
Jäger KM, Eggen SS (2004) Scaling of the viscoelasticity of highly filled carbon black polyethylene composites above the melting point. Polymer 45:7681–7692
Kao SV, Mason SG (1975) Dispersion of particles by shear. Nature 253:619–621
Lin L, Masuda T (1990) Effect of dispersion of particles on viscoelasticity of CaCO3- filled polypropylene melts. Polym Eng Sci 30:841–847
Powell RL, Mason SG (1982) Dispersion by laminar flow. AIChE J 28:286–293
Pukanszky B, Fekete E (1997) Eurofillers 1997, September 7–11, Manchester
Pukanszky B, Fekete E (1998) Aggregation tendency of particulate fillers: determination and consequences. Polym Polym Compos 6:313–322
Pukanszky B, Fekete E (1999) Adhesion and surface modification. Adv Polym Sci 139:109–153
Rudin A, Chee KK (1973) Zero shear viscosities of narrow and broad distribution polystyrene melts. Macromolecules 6:613–624
Rwei SP, Manas-Zloczower I, Feke DL (1991) Characterization of agglomerate dispersion by erosion in simple shear flows. Polym Eng Sci 31:558–562
Rwei SP, Manas-Zloczower I, Feke DL (1992) Analysis of dispersion of carbon black in polymeric melts and its effect on compound properties. Polym Eng Sci 32:130–135
Scott C, Ishida H, Maurer FHJ (1988) Interfacial effects on the melt state behavior of polyethylene-EPDM-calcium carbonate composites. Rheol Acta 27:273–278
Seyvet O, Navard P (2000) Collision-induced dispersion of agglomerate suspensions in a shear flow. J Appl Polym Sci 78:1130–1133
Seyvet O, Navard P (2001) In situ study of the dynamics of erosion of carbon black agglomerates. J Appl Polym Sci 80:1627–1629
Shiga S, Furuta M (1985) Processability of EPR in an internal mixer (II)— morphological changes of carbon black agglomerates during mixing. Rubber Chem Technol 58:1–22
Wu G, Asai S, Sumita M, Hattori T, Higuchi R, Washiyama J (2000) Estimation of flocculation structure in filled polymer composites by dynamic rheological measurements. Colloid Polym Sci 278:220–228
Yurekli K, Krishnamoorti R, Tse MF, McElrath KO, Tsou AH, Wang HC (2001) Structure and dynamics of carbon black-filled elastomers. J Polym Sci Part B Polym Phys 39:256–275
Zhang JF, Yi XS (2002) Dynamic rheological behavior of high-density polyethylene filled with carbon black. J Appl Polym Sci 86:3527–3531
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bar-Chaput, S., Carrot, C. Rheology as a tool for the analysis of the dispersion of carbon filler in polymers. Rheol Acta 45, 339–347 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00397-005-0045-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00397-005-0045-3