Abstract
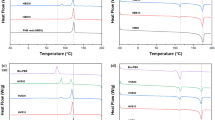
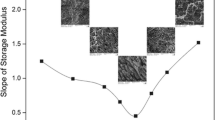
The work focuses on the detection of the co-continuity window in immiscible polymer blends. The purpose of the paper is to describe how rheological techniques can help to evaluate the composition range of the co-continuous morphology through the study of a particular system: PEO/PVDF-HFP. First, the blends were characterized by selective dissolution experiments and SEM observations. Then the ability of dynamic mechanical spectroscopy to detect the co-continuity was investigated in the melt and in the solid state. The evolution of the storage modulus of molten blends with their composition at a constant low frequency gives information about the co-continuity interval, especially as far as the onset of the continuity of the PEO phase is concerned. Then the immiscibility of the polymers and the continuity of PVDF-HFP as a function of blend composition have been highlighted by means of dynamic mechanical spectrometry below the melting point of PVDF-HFP. Comparison with results from classical methods shows fair agreement.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ajji A, Choplin L, Prudhomme RE (1991) Rheology of PS/PVME blends near the phase transition. J Polym Sci Part B 29:1573–1575
Ajroldi G, Pianca M, Fumagalli M, Moggi G (1989) Fluroelastomers-dependence of relaxation phenomena on composition. Polymer 30:2180–2187
Bourry D, Favis BD (1998) Cocontinuity and phase inversion in HDPE/PS blends: influence of interfacial modification and elasticity. J Polym Sci Part B 36:1889–1899
Bousmina M, Muller RJ (1993) Linear viscoelasticity in the melt of impact PMMA. Influence of concentration and aggregation of dispersed rubber particles. J Rheol 37:663–679
Brouillet-Fourman S, Carrot C, Mignard N, Prochazka F (2002) On the use of an internal mixer for the rheological characterization of maize starch. Appl Rheol 12:192–199
Bu W, He J (1996) The effect of mixing time on the morphology of immiscible polymer blends. J Appl Polym Sci 62:1445–1456
Castro M, Prochazka F, Carrot C (2003) Morphologie et comportement viscoélastique aux basses fréquences d’un mélange de polymères incompatibles. Proceedings of the 38th National Congress of French Rheology Group GFR
Dickie RA (1973) Heterogenous polymer-polymer composites. I. Theory of viscoelastic properties and equivalent mechanical models. J Appl Polym Sci 17:45–63
Friedrich C, Gleinser W, Korat E, Maier D, Weese J (1995) Comparison of sphere-size distributions obtained from rheology and transmission electron microscopy in PMMA/PS blends. J Rheol 39:1411–1425
Galloway JA, Macosko CW (2004) Comparison of methods for the detection of cocontinuity in poly(ethylene oxide)/polystyrene blends. Polym Eng Sci (in press)
Galloway JA, Montminy MD, Macosko CW (2002) Image analysis for interfacial area and cocontinuity detection in polymer blends. Polymer 43:4715–4722
He J, Bu W, Zeng J (1997) Co-phase continuity in immiscible binary polymer blends. Polymer 38:6347–6353
Heeschen WA (1995) A quantitative image analysis method for the determination of cocontinuity in polymer blends. Polymer 36:1835–1841
Huitric J, Médéric P, Moan M, Jarrin J (1998) Influence of composition and morphology on rheological properties of polyethylene/polyamide blends. Polymer 39:4849–4856
Kerner EH (1956) The elastic and thermo-elastic properties of composite media. Proc Phys Soc B 69:808–813
Lacroix C, Bousmina M, Carreau PJ, Favis BD, Michel A (1996) Properties of PETG/EVA blends. 1. Viscoelastic, morphological and interfacial properties. Polymer 37:2939–2947
Luciani A (1993) Mécanismes d’établissement des morphologies dans les mélanges de polymères incompatibles. Doctoral thesis. University Paris VI
Mani S, Malone MF, Winter HH (1992) Influence of phase separation on the linear viscoelastic behaviour of a miscible polymer blend. J Rheol 36:1625–1650
Marin N, Favis BD (2002) Co-continuous morphology development in partially miscible PMMA/PC blends. Polymer 43:4723–4731
Mekhilef N, Favis BD, Carreau PJ (1997) Morphological stability, interfacial tension and dual-phase continuity in polystyrene-polyethylene blends. J Polym Sci Part B 35:293–308
Palierne JF (1990) Linear rheology of viscoelastic emulsions with interfacial tension. Rheol Acta 29:204–214
Steinmann S, Gronski W, Friedrich C (2001) Cocontinuous polymer blends: influence of viscosity and elasticity ratios of the constituent polymers on phase inversion. Polymer 42:6619–6629
Steinmann S, Gronski W, Friedrich C (2002a) Quantitative rheological evaluation of phase inversion in two-phase polymer blends with cocontinuous morphology. Rheol Acta 41:77–86
Steinmann S, Gronski W, Friedrich C (2002b) Influence of selective filling on rheological properties and phase inversion of two-phase polymer blends. Polymer 43:4467–4477
Utracki LA (1991) On the viscosity-concentration dependence of immiscible polymer blends. J Rheol 35:1615–1637
Vinckier I, Laun HM (1999) Manifestation of phase separation processes in oscillatory shear: droplet-matrix systems versus co-continuous morphologies. Rheol Acta 38:274–286
Weis C, Leukel J, Borkenstein K, Maier D, Gronski W, Friedrich C, Honerkamp J (1998) Morphological and rheological detection of the phase inversion of PMMA/PS polymer blends. Polym Bull 40:235–241
Willemse RC, Posthuma de Boer A, Van Dam J, Gotsis AD (1999) Co-continuous morphologies in polymer blends: the influence of the interfacial tension. Polymer 40:827–834
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chaput, S., Carrot, C., Castro, M. et al. Co-continuity interval in immiscible polymer blends by dynamic mechanical spectroscopy in the molten and solid state. Rheol Acta 43, 417–426 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00397-004-0369-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00397-004-0369-4