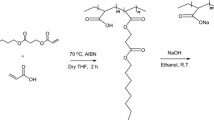
Abstract
The surface organization of the enol units of polyacryloylacetone (PAA) monolayer at the air–water interface is examined using surface pressure and surface potential measurements and theoretical calculations based on molecular models.
The mechanism and kinetics of the photochemical enol–keto tautomerization is studied by measuring the increase of the surface area at constant surface pressure. The effect is due to the increase of the area per monomer units during the consecutive enol-to-keto photoconversion and slow interfacial reorganization of these forms to a more favorable state.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 9 March 1998 Accepted: 29 May 1998
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Balashev, K., Panaiotov, I. & Petkov, I. Interfacial photochemical tautomerization in polyacryloylacetone monolayers. Colloid Polym Sci 276, 984–991 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s003960050337
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s003960050337