Abstract
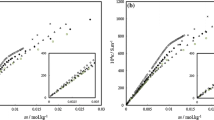
Three direct –NSO3H functionalized Brønsted acidic ionic liquids of 2-alkyl-1,3-disulfo imidazolium chloride with varied sizes of alkyl substituents (Me-, Et-, nBu-) were utilized to explore the effects of ionic liquids on aggregation behavior of anionic surfactant sodium dodecyl sulfate in aqueous media at various concentrations of ionic liquids and temperatures (288.15 K, 293.15 K, 298.15 K, 303.15 K, and 308.15 K). Critical micelle concentrations (CMCs) of the IL-surfactant systems obtained from conductivity measurement were found to be in good agreement with the CMC values of surface tension and UV–visible spectroscopy techniques. These CMCs values were used to calculate the thermodynamic parameters of IL-surfactant solutions such as standard free energy of micellization (ΔG°m), standard enthalpy of micellization (ΔH°m), and standard entropy of micellization (ΔS°m). Continuous decrease of the CMC values was observed with increasing concentrations of the ILs as well as temperatures. Packing parameters calculated from the surface tension measurement displayed small spherical shape for all the mixed micellar systems. Structural changes of the IL-surfactant solutions were also observed using FT-IR spectroscopic method. Increased positive inductive effect (+ I) of 2-alkyl substituent of the imidazolium cation of ionic liquid showed stabilizing effect on the micelle formation by lowering of more negative zeta potential values of the IL-surfactant systems.
Graphical Abstract












Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The authors declare that the data supporting the findings of this study are available within the paper and its supplementary information file.
Abbreviations
- SDS:
-
Sodium dodecyl sulfate
- CMC:
-
Critical micelle concentration
- ILs:
-
Ionic liquids
- BAILs:
-
Brønsted acidic ionic liquids (BAILs)
- BDSIM:
-
2-Butyl-1,3-disulfoimidazolium (BDSIM)
- EDSIM:
-
2-Ethyl-1,3-disulfoimidazolium
- MDSIM:
-
2-Methyl-1,3-disulfoimidazolium
References
Lombardo D, Kiselev MA, Magazù S, Calandra P (2015) Amphiphiles self-assembly: basic concepts and future perspectives of supramolecular approaches. Advances in Condensed Matter Physics 2015:1–22, Article ID 151683. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/151683
Panda A, Kumar A, Mishra S, Mohapatra SS (2020) Soapnut: a replacement of synthetic surfactant for cosmetic and biomedical applications. Sustainable Chemistry and Pharmacy 17:100297. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scp.2020.100297
Abbot V, Paliwal D, Sharma A, Sharma P (2022) A review on the physicochemical and biological applications of biosurfactants in biotechnology and pharmaceuticals. Heliyon 8:e10149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e10149
Kralova I, Sjöblom J (2009) Surfactants used in food industry: a review. J Dispersion Sci Technol 30:1363–1383. https://doi.org/10.1080/01932690902735561
Sun J, Zhang Y, Pan X, Zhu G (2018) The effects of anionic and non-ionic surfactant on anaerobic co-digestion of sludge, food wastes and green wastes. Environ Technol 40:2538–2547. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2018.1446457
Le Guenic S, Chaveriat L, Lequart V, Joly N, Martin P (2019) Renewable surfactants for biochemical applications and nanotechnology. J Surfactants Deterg 22:5–21. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsde.12216
Pan A, Rakshit S, Sahu S, Bhattacharya SC, Moulik SP (2015) Synergism between anionic double tail and zwitterionic single tail surfactants in the formation of mixed micelles and vesicles, and use of the micelle templates for the synthesis of nano-structured gold particles. Colloids Surf A 481:644–654. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2015.06.032
Mukherjee I, Dinda G, Ghosh S, Moulik SP (2012) Synthesis, characterization, and applications of microheterogeneous-templated CdS nanodispersions. J Nanopart Res 14:1–4. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-012-0997-z
Quintero L (2002) An overview of surfactant applications in drilling fluids for the petroleum industry. J Dispersion Sci Technol 23:393–404. https://doi.org/10.1080/01932690208984212
Zhou C, Wang D, Cao M, Chen Y, Liu Z, Wu C, Xu H, Wang S, Wang Y (2016) Self-aggregation, antibacterial activity, and mildness of cyclodextrin/cationic trimeric surfactant complexes. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8:30811–30823. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.6b11667
Liu K, Yang L, Peng X, Wang J, Lu JR, Xu H (2020) Modulation of antimicrobial peptide conformation and aggregation by terminal lipidation and surfactants. Langmuir 36:1737–1744. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.langmuir.9b03774
Oremusová J, Vitková Z, Vitko A, Tárník M, Miklovičová E, Ivánková O, Murgaš J, Krchňák D (2019) Effect of molecular composition of head group and temperature on micellar properties of ionic surfactants with C12 alkyl chain. Molecules 24:651. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24030651
Davies TS, Ketner AM, Raghavan SR (2006) Self-assembly of surfactant vesicles that transform into viscoelastic wormlike micelles upon heating. J Am Chem Soc 128:6669–6675. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja060021e
Svenson S (2004) Controlling surfactant self-assembly. Curr Opin Colloid Interface Sci 9:201–212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cocis.2004.06.008
Kanoje B, Jangir A, Patel D, Ray D, Aswal V, Pal H, Parikh J, Kuperkar K (2018) Micellar transition (ellipsoidal to ULV) induced in aqueous Gemini surfactant (12–2-12) solution as a function of additive concentration and temperature using experimental and theoretical study. Colloids Surf, A 555:227–236. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2018.06.070
Yawen Z, Shan W, Mengdie L, Baocai X, Fu H, Li Z (2018) Effect of temperature on the organized self-assembly of SDS/β-cyclodextrin aqueous solution by dielectric relaxation behavior. J Dispersion Sci Technol 39:1056–1059. https://doi.org/10.1080/01932691.2017.1381917
Buckingham SA, Garvey CJ, Warr GG (1993) Effect of head-group size on micellization and phase behavior in quaternary ammonium surfactant systems. J Phys Chem 97:10236–10244. https://doi.org/10.1021/j100141a054
Rashidi-Alavijeh M, Javadian S, Gharibi H, Moradi M, Tehrani-Bagha AR, Shahir AA (2011) Intermolecular interactions between a dye and cationic surfactants: effects of alkyl chain, head group, and counterion. Colloids Surf, A 380:119–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2011.02.011
Jurašin D, Vinceković M, Pustak A, Šmit I, Bujan M, Filipović-Vinceković N (2013) Lamellar to hexagonal columnar liquid crystalline phase transition in a catanionic surfactant mixture: dodecylammonium chloride–sodium bis (2-ethylhexyl) sulfosuccinate. Soft Matter 9(12):3349–3360. https://doi.org/10.1039/C3SM27665A
Rao KS, Gehlot PS, Gupta H, Drechsler M, Kumar A (2015) Sodium bromide induced micelle to vesicle transitions of newly synthesized anionic surface-active ionic liquids based on dodecylbenzenesulfonate. J Phys Chem B 119:4263–4274. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp512805e
Bergström LM, Skoglund S, Edwards K, Eriksson J, Grillo I (2013) Self-assembly in mixtures of an anionic and a cationic surfactant: a comparison between small-angle neutron scattering and cryo-transmission electron microscopy. Langmuir 29:11834–11848. https://doi.org/10.1021/la401884k
Singh M, Kumar S, Aswal VK, Kang TS (2023) Mixed aggregates of surface-active ionic liquids and 14–2-14 gemini surfactants in an aqueous medium as fluid scaffolds for enzymology of cytochrome-C. Langmuir 39:11582–11595. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.langmuir.3c01050
Mukhopadhayay A, Singh D, Sharma KP (2019) Neat ionic liquid and α-chymotrypsin-polymer surfactant conjugate-based biocatalytic solvent. Biomacromol 21:867–877. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.biomac.9b01556
Dib N, Silber JJ, Correa NM, Falcone RD (2022) Amphiphilic ionic liquids capable to formulate organized systems in an aqueous solution, designed by a combination of traditional surfactants and commercial drugs. Pharm Res 39:2379–2390. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-022-03342-7
Kaur G, Kumar H, Singla M (2022) Diverse applications of ionic liquids: A comprehensive review. J Mol Liq 351:118556. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2022.118556
Correia DM, Fernandes LC, Martins PM, García-Astrain C, Costa CM, Reguera J, Lanceros-Méndez S (2020) Ionic liquid–polymer composites: a new platform for multifunctional applications. Adv Func Mater 30:1909736. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201909736
Lim JR, Chua LS, Mustaffa AA (2022) Ionic liquids as green solvent and their applications in bioactive compounds extraction from plants. Process Biochem 122:292–306. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2022.10.024
Tan JS, Lee SY, Chew KW, Lam MK, Lim JW, Ho SH, Show PL (2020) A review on microalgae cultivation and harvesting, and their biomass extraction processing using ionic liquids. Bioengineered 11:116–129. https://doi.org/10.1080/21655979.2020.1711626
Yan X, Anguille S, Bendahan M, Moulin P (2019) Ionic liquids combined with membrane separation processes: a review. Sep Purif Technol 222:230–253. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2019.03.103
Das S, Dutta T, Borah R (2019) Comparative study of the physical and electrochemical behavior of direct N-SO3H functionalized 1, 3-disulfo-2-alkyl-imidazolium trifluoroacetate ionic liquids in molecular solvents. J Mol Liq 289:111099. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2019.111099
Šarac B, Medoš Ž, Cognigni A, Bica K, Chen LJ, Bešter-Rogač M (2017) Thermodynamic study for micellization of imidazolium-based surface active ionic liquids in water: effect of alkyl chain length and anions. Colloids Surf A 532:609–617. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2017.01.062
Dai X, Qiang X, Li J, Yao T, Wang Z, Song H (2019) Design and functionalization of magnetic ionic liquids surfactants (MILSs) containing alkyltrimethylammonium fragment. J Mol Liq 277:170–174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2018.12.096
Amarasekara AS (2016) Acidic ionic liquids. Chem Rev 116:6133–6183. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.5b00763
Sarma P, Dutta AK, Borah R (2017) Design and exploration of–SO 3 H group functionalized Brønsted acidic ionic liquids (BAILs) as task-specific catalytic systems for organic reactions: a review of literature. Catal Surv Asia 21:70–93. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10563-017-9227-0
Buettner CS, Cognigni A, Schroeder C, Bica-Schröder K (2022) Surface-active ionic liquids: a review. J Mol Liq 347:118160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2021.118160
Agudelo ÁJ, Coelho YL, Ferreira GM, Ferreira GM, Hudson EA, dos Santos Pires AC, da Silva LH (2019) Solvophobic effect of 1-alkyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride on the thermodynamic of complexation between β-cyclodextrin and dodecylpyridinium cation. Colloids Surf A 582:123850. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2019.123850
Selwent A, Łuczak J (2016) Micellar aggregation of Triton X-100 surfactant in imidazolium ionic liquids. J Mol Liq 221:557–566. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2016.05.081
Lu X, Lu Z, Zhang R, Zhao L, Xie H (2021) Distribution of pigments in the aqueous two-phase system formed with piperazinium-based ionic liquid and anionic surfactant. J Mol Liq 330:115677. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2021.115677
Warsi F, Usman M, Ali M (2022) Modulating aggregation behaviour and surface properties of cationic & anionic surfactant with surface active ionic liquid 1-decyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride [C10mim][Cl]: Role of surfactant head group. J Mol Liq 365:120093. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2022.120093
Zhang Y, Marlow JB, Wood K, Wang J, Warr GG, Li H, Atkin R (2023) Phase behaviour and aggregate structures of the surface-active ionic liquid [BMIm][AOT] in water. J Colloid Interface Sci 652:749–757. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2023.08.049
Beyaz A, Oh WS, Reddy VP (2004) Ionic liquids as modulators of the critical micelle concentration of sodium dodecyl sulfate. Colloids Surf, B 35:119–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2004.02.014
Behera K (2007) Pandey S (2007) Concentration-dependent dual behavior of hydrophilic ionic liquid in changing properties of aqueous sodium dodecyl sulfate. J Phys Chem B 111:13307–13315. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp076430u
Behera K, Pandey S (2007) Modulating properties of aqueous sodium dodecyl sulfate by adding hydrophobic ionic liquid. J Colloid Interface Sci 316(2):803–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2007.07.072. Get rights and content.
Smirnova NA, Vanin AA, Safonova EA, Pukinsky IB, Anufrikov YA, Makarov AL (2009) Self-assembly in aqueous solutions of imidazolium ionic liquids and their mixtures with an anionic surfactant. J Colloid Interface Sci 336:793–802. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2009.04.004
Pal A, Chaudhary S (2013) Ionic liquid induced alterations in the physicochemical properties of aqueous solutions of sodium dodecylsulfate (SDS). Colloids Surf, A 430:58–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2013.04.001
Ferreira GM, Ferreira GM, Agudelo ÁJ, Hespanhol da Silva MC, Rezende JD, Pires AC, da Silva LH (2015) Effect of 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium halide on the relative stability between sodium dodecyl sulfate micelles and sodium dodecyl sulfate–poly (ethylene oxide) nanoaggregates. J Phys Chem B 119:15758–15768. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcb.5b09819
Kumar H, Katal A (2021) Thermodynamic analysis of micelles formation of anionic surfactant SDS in the presence of aqueous and aqueous solution of ionic liquid 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride. J Phys Org Chem 34:e4199. https://doi.org/10.1002/poc.4199
Kumar H, Kaur G (2020) Deciphering aggregation behavior and thermodynamic properties of anionic surfactant sodium hexadecyl sulfate in aqueous solutions of ionic liquids [C5mim][Br] and [C6mim][Br]. J Mol Liq 298:111949. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2019.111949
Dutta AK, Gogoi P, Borah R (2014) Synthesis of dibenzoxanthene and acridine derivatives catalyzed by 1, 3-disulfonic acid imidazolium carboxylate ionic liquids. RSC Adv 4:41287–41291. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4RA07323A
Frizzo CP, Bender CR, Salbego PR, Black G, Villetti MA, Martins MA (2016) Thermodynamic properties of the aggregation behavior of a dicationic ionic liquid determined by different methods. Colloids Surf, A 494:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2016.01.015
Zhao Y, Yue X, Wang X, Huang D, Chen X (2012) Micelle formation by N-alkyl-N-methylpiperidinium bromide ionic liquids in aqueous solution. Colloids Surf, A 412:90–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2012.07.021
Sohrabi B, Eivazzadeh S, Sharifi A, Azadbakht R (2015) Self-assembled catanionic surfactant mixtures in aqueous/ionic liquid systems. J Mol Liq 211:754–760. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2015.07.025
Warsi F, Islam MR, Alam MS, Ali M (2020) Exploring the effect of hydrophobic ionic liquid on aggregation, micropolarity and microviscosity properties of aqueous SDS solutions. J Mol Liq 310:113132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2020.113132
Inoue T, Ebina H, Dong B, Zheng L (2007) Electrical conductivity study on micelle formation of long-chain imidazolium ionic liquids in aqueous solution. J Colloid Interface Sci 314:236–241. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2007.05.052
Pal A, Punia R (2020) Self-aggregation behaviour of cationic surfactant tetradecyltrimethylammonium bromide and bi-amphiphilic surface-active ionic liquid 3-methyl-1-pentylimidazolium dodecylsulfate in aqueous solution. J Mol Liq 304:112803. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2020.112803
Agudelo ÁJ, Ferreira GM, Ferreira GM, Coelho YL, Hudson EA, dos Santos Pires AC, da Silva LH (2020) Aggregation of sodium dodecylbenzene sulfonate: weak molecular interactions modulated by imidazolium cation of short alkyl chain length. Colloids Surf, A 589:124435. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2020.124435
Cao H, Hu Y, Xu W, Wang Y, Guo X (2020) Recent progress in the assembly behavior of imidazolium-based ionic liquid surfactants. J Mol Liq 319:114354. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2020.114354
Rosen MJ (2004) Surfactants and interfacial phenomena: In emulsification by surfactant, page 303–31, 3rd edn. Wiley, New York
Hu Y, Han J, Guo R (2020) Influence of the alkyl chain length of the imidazole ionic liquid-type surfactants on their aggregation behavior with sodium dodecyl sulfate. Langmuir 36(35):10494–503. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.langmuir.0c01673
Florence AT, Attwood D (2015) Physicochemical principles of pharmacy: In Manufacture, Formulation, and Clinical Use, page 193-244, 5th edn. Pharmaceutical press.
Zhou L, Jiang X, Li Y, Chen Z, Hu X (2007) Synthesis and properties of a novel class of gemini pyridinium surfactants. Langmuir 23:11404–11408. https://doi.org/10.1021/la701154w
Cheng H, Zhang H, Liu X, Lin M, Qin Z, Fang Y (2015) Effect of polyoxyethylene chain length on the physicochemical properties of n, n-dimethyl-n-dodecyl polyoxyethylene amine oxide hybrid surfactants (C12EOnAO, with n= 1–4). J Surfactants Deterg 18:487–493. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11743-014-1650-x
Jaycock MJ, Parfitt GD (1981) Chemistry of interfaces, page 234-247, John Wiley & Sons. New York
Dong B, Zhao X, Zheng L, Zhang J, Li N, Inoue T (2008) Aggregation behavior of long-chain imidazolium ionic liquids in aqueous solution: micellization and characterization of micelle microenvironment. Colloids Surf, A 317:666–672. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2007.12.001
Wang X, Yu L, Jiao J, Zhang H, Wang R, Chen H (2012) Aggregation behavior of COOH-functionalized imidazolium-based surface-active ionic liquids in aqueous solution. J Mol Liq 173:103–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2012.06.023
Banjare MK, Kurrey R, Yadav T, Sinha S, Satnami ML, Ghosh KK (2017) A comparative study on the effect of imidazolium-based ionic liquid on self-aggregation of cationic, anionic, and non-ionic surfactants studied by surface tension, conductivity, fluorescence and FTIR spectroscopy. J Mol Liq 241:622–632. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2017.06.009
Tanford C (1980) The hydrophobic effect: formation of micelles and biological membranes, 232 pages, 2nd edn. John Wiley & Sons. New York
Sharma R, Mahajan S, Mahajan RK (2013) Surface adsorption and mixed micelle formation of surface-active ionic liquid in cationic surfactants: conductivity, surface tension, fluorescence and NMR studies. Colloids Surf, A 427:62–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2013.03.023
Bi Y, Zhao L, Hu Q, Gao YA, Yu L (2015) Aggregation behavior of imidazolium-based surface-active ionic liquids with photoresponsive cinnamate counterions in the aqueous solution. Langmuir 31:12597–12608. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.langmuir.5b03216
Das S, Ghosh S, Das B (2018) Formation of mixed micelle in an aqueous mixture of a surface-active ionic liquid and a conventional surfactant: experiment and modeling. J Chem Eng Data 63:3784–3800. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jced.8b00372
Noriyuki M, Mariko K, Yasuko N, Shozo M, Hitoshi S (1980) Mechanism for the inducement of the intestinal absorption of poorly absorbed drugs by mixed micelles I. Effects of various lipid—bile salt mixed micelles on the intestinal absorption of streptomycin in rat. Int J Pharm 4(4):271–279. https://doi.org/10.1016/0378-5173(80)90002-2
Seki A, Chiang K-Y, Yu C-C, Yu X, Okuno M, Hunger J, Nagata Y, Bonn M (2020) The bending mode of water: a powerful probe for hydrogen bond structure of aqueous systems. Phys Chem Lett 19:8459–8469. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpclett.0c01259
Vogel R, Pal AK, Jambhrunkar S, Patel P, Thakur SS, Reátegui E, Parekh HS, Saá P, Stassinopoulos A, Broom MF (2017) High resolution single particle zeta potential characterization of biological nanoparticles using tunable resistive pulse sensing. Sci Rep 7:17479. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-14981-x
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to Sophisticated Analytical Instrumentation Centre, Tezpur University, for providing various facilities to carry out experimental works and University Grants Commission (UGC) for providing Senior Research Fellowship to Debanga Bhusan Bora.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
D.B. B. and R. B. wrote the main manuscript text. All the prime experiments were performed by D. B. B. and B. R. B. The analysis and interpretation of experimental data were done by R.B. and D.B.B. The other co-authors S.P., S. K., and N. K. synthesized and characterized the required ionic liquids. Validation experiments were conducted by S.P., S. K., and N. K. The corresponding author R.B. initiated the original idea of manuscript and supervised the work. All authors approved the final version of manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Bora, D.B., Bora, B.R., Paul, S. et al. Variation of micellization, thermodynamic, and surface properties of sodium dodecyl sulfate in aqueous media using 1,3-disulfo-2-alkyl imidazolium chloride ionic liquids. Colloid Polym Sci (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-024-05247-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-024-05247-w