Abstract
The present study examines the co-micellization in different block copolymers (BCPs): P123 and F127 (with almost similar hydrophobic PO block but different hydrophilic %EO content). In varying concentration and in presence of NaCl, these BCP solutions in single and mix system displayed a variety of phases, i.e., blue point (BP), thermoreversible gel formation and cloud point (CP) with a noticeable sol–gel phase transition shift. The nanoscale micellar size distribution expressed as hydrodynamic diameter (Dh) was evaluated using dynamic light scattering (DLS). As F127 is larger than P123 and contains more EO groups, the micelle corona appears larger with greater Dh. The scattering profile from small-angle x-ray scattering (SAXS) offered information into the micellar dimensions employing SasView 4.2.2 program. The quercetin (QCT) solubilization articulated in encapsulation efficiency (EE%) and drug loading (DL%) followed the enhancement order: P123 > (P123 + F127) > F127 which was inferred from spectral and microscopy study.
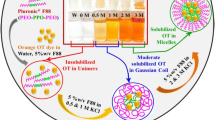
Graphical Abstract
5%w/v Pluronics® (P123 and F127) in single (pure) and mix environment depicting their micellar dimensions obtained from SAXS.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data will be made available on request.
References
Bharatiya B, Ghosh G, Aswal V, Bahadur P (2010) Effect of n-Hexanol and n-Hexylamine on the micellar solutions of Pluronic F127 and P123 in water and 1M NaCl. J Disper Sci Technol 31:660–667
Lee C, Yang C, Lin T, Bahadur P, Chen L (2019) Role of molecular weight and hydrophobicity of amphiphilic tri-block copolymers in temperature-dependent co-micellization process and drug solubility. Colloids Surf B 183:110461–110469
Barry N, Pitto-Barry A, Romero-Canelón I, Tran J, Soldevila-Barreda J, Hands-Portman I, Smith C, Kirby N, Dove A, O’Reilly R, Sadler P (2014) Precious metal carborane polymer nanoparticles: characterisation of micellar formulations and anticancer activity. Faraday Discuss 175:229–240
Chat O, Nazir N, Bhat P, Hassan P, Aswal V, Dar A (2018) Aggregation and rheological behavior of the Lavender oil- Pluronic P123 microemulsions in water-ethanol mixed solvents. Langmuir 34(3):1010–1019
Rakshit S, Sarkar A, Bhattacharya S (2017) A differential approach towards understanding the enhance demission induced superior bio-imaging and cytotoxicity within block copolymeric nanomicelles. Colloids Surf B 155:390–398
Thanitwatthanasak S, Sagis L, Chitprasert P (2019) Pluronic F127/Pluronic P123/vitamin E TPGS mixed micelles for oral delivery of mangiferin and quercetin: mixture-design optimization, micellization, and solubilization behavior. J Mol Liq 274(223–238):6
Elisseeva O, Besseling N, Koopal L, Stuart M (2005) Influence of NaCl on the behavior of PEO-PPO-PEO triblock copolymers in solution, at interfaces, and in asymmetric liquid films. Langmuir 21:4954–4963
Desai P, Jain N, Sharma R, Bahadur P (2001) Effect of additives on the micellization of PEO: PPO: PEO block copolymer F127 in aqueous solution. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng 178:57–69
Dey J, Kumar S, Nath S, Ganguly R, Aswal V, Ismail K (2014) Additive induced core and corona specific dehydration and ensuing growth and interaction of Pluronic F127 micelles. J Colloid Interface Sci 415:95–102
Branca C, Angelo G (2019) Aggregation behavior of pluronic F127 solutions in presence of chitosan/clay nanocomposites examined by dynamic light scattering. J Colloid Interface Sci 542:289–295
Castelletto V, Parras P, Hamley I (2007) Wormlike micelle formation and flow alignment of a pluronic block copolymer in aqueous solution. Langmuir 23:6896–6902
Kulthe S, Inamdar N, Choudhari Y, Shirolikar S, Borde L, Mourya V (2011) Mixed micelle formation with hydrophobic and hydrophilic Pluronic block copolymers: implications for controlled and targeted drug delivery. Colloids Surf B 88:691–696
Chaibundit C, Ricardo N, Costa F, Yeates S, Booth C (2007) Micellization and gelation of mixed copolymers P123 and F127 in aqueous solution. Langmuir 23(18):9229–9236
Lin T, Wang W, Zeng X, Lu X, Shih P (2022) Preparation, structural characterization of anti-cancer drugs-mediated self-assembly from the pluronic copolymers through synchrotron SAXS investigation. Materials 15:5387–5397
Zhang W, Shi Y, Chen Y, Ye J, Sha X, Fang X (2011) Multifunctional Pluronic P123/F127 mixed polymeric micelles loaded with paclitaxel for the treatment of multidrug resistant tumors. Biomaterials 32:2894–2906
Patel D, Patel D, Ray D, Kuperkar K, Aswal V, Bahadur P (2021) Single and mixed Pluronics® micelles with solubilized hydrophobic additives: underscoring the aqueous solution demeanor and micellar transition. J Mol Liq 343:117625–117637
Patel D, Ray D, Aswal V, Kuperkar K, Bahadur P (2022) Micellar assembly leading to structural growth/transition in normal and reverse Tetronics® in single and mixed solution environment. Soft Matter 18:4543–4553
Singh V, Khullar P, Dave P, Kaur N (2013) Micelles, mixed micelles, and applications of polyoxypropylene (PPO)-polyoxyethylene (PEO)-polyoxypropylene (PPO) triblock polymers. Int J Ind Chem 4(12):1–18
Castro R, Casadei B, Santana B, Lotierzo M, Oliveira N, Malheiros B, Mariani P, Kaminski R, Barbosa L (2019) SCryPTA: a web-based platform for analyzing small-angle scattering curves of lyotropic liquid crystals. bioRxiv. 79:1–17
JanssonSchillén JK, Nilsson M, Söderman O, Fritz G, Bergmann A, Glatter O (2005) O Small-angle X-ray scattering, light scattering, and NMR study of PEO-PPO-PEO triblock copolymer/cationic surfactant complexes in aqueous solution. J Phys Chem B 109:7073–7083
Ruthstein S, Raitsimring A, Bitton R, Frydman V, Godte A, Goldfar D (2009) Distribution of guest molecules in Pluronic micelles studied by double electron-electron spin resonance and small angle X-ray scattering. Phys Chem Chem Phys 11:148–160
Park M, Char K, Kim H, Lee C, Seong B, Han Y (2002) Phase behavior of a PEO-PPO-PEO triblock copolymer in aqueous solutions: two gelation mechanisms. Macromol Res 6(10):325–331
Artzner F, Geiger S, Olivier A, Allais C, Finet S, Agnely F (2007) Interactions between poloxamers in aqueous solutions: micellization and gelation studied by differential scanning calorimetry, small angle X-ray scattering, and rheology. Langmuir 23(9):5085–5092
Lee C, Yang C, Lin T, Bahadur P, Chen L (2019) Role of molecular weight and hydrophobicity of amphiphilic tri-block copolymers in temperature-dependent co-micellization process and drug solubility. Colloid Surface B 183:110461–110470
Wu Y, Sprik R, Poon W, Eiser E (2006) Effect of salt on the phase behaviour of F68 triblock PEO/PPO/PEO copolymer. J Phys Condens Matter 18:4461
Jiang J, Li C, Lombardi J, Colby R, Rigas B, Rafailovich M, Sokolov J (2008) The effect of physiologically relevant additives on the rheological properties of concentrated Pluronic copolymer gels. Polymer 49:3561–3567
Wu G, Liu L, Buu V, Chu B, Schneider D (1996) SANS and SAXS studies of Pluronic L64 in concentrated solution. Phys A Stat Mech Appl 231:73–81
Bogomolova A, Hruby M, Panek J, Rabyk M, Turner S, Bals S, Steinhart M, Zhigunov A, Sedlacek O, Stepanek P, Filippov S (2013) Small-angle X-ray scattering and light scattering study of hybrid nanoparticles composed of thermoresponsive triblock copolymer F127 and thermoresponsive statistical polyoxazolines with hydrophobic moieties. J Appl Cryst 46:1690–1698
Liu Z, Liu D, Wang L, Zhang J, Zhang N (2011) Docetaxel-loaded Pluronic P123 polymeric micelles: in vitro and in vivo evaluation. Int J Mol Sci 12:1684–1696
Li Y, Li L, Dong H, Cai X, Ren T (2013) Pluronic F127 nanomicelles engineered with nuclear localized functionality for targeted drug delivery. Mater Sci Eng C 33:2698–2707
Batsberg W, Ndoni S, Trandum C, Hvidt S (2004) Effects of poloxamer inhomogeneities on micellization in water. Macromolecules 37:2965–2971
Alexandridis P, Holzwarth J, Hatton T (1994) Micellization of poly(ethylene oxide)-poly(propylene oxide)-poly(ethy1ene oxide) triblock copolymers in aqueous solutions: thermodynamics of copolymer association. Macromolecules 27:2414–2425
Yallapu M, Jaggi M, Chauhan S (2013) Curcumin nanomedicine: a road to cancer therapeutics. Curr Pharm Des 19:1994–2010
Singla P, Singh O, Chabba S, Mahajan R (2018) Pluronic-SAILs (surface active ionic liquids) mixed micelles as efficient hydrophobic quercetin drug carriers. J Mol Liq 249:294–303
Patel D, Rathod S, Tiwari S, Ray D, Kuperkar K, Aswal V, Bahadur P (2020) Self-association in EO–BO–EO triblock copolymers as a nanocarrier template for sustainable release of anticancer drugs. Phys Chem B 124(51):11750–11761
Patidar P, Pillai S, Bahadur P, Bahadur A (2017) Tuning the self-assembly of EO-PO block copolymers and quercetin solubilization in the presence of some common pharmaceutical excipients: a comparative study on a linear triblock and a starblock copolymer. J Mol Liq 241:511–519
Fraile M, Buratto R, Gómez B, Martín Á, Cocero M (2014) Enhanced delivery of quercetin by encapsulation in poloxamers by supercritical antisolvent process. Ind Eng Chem Res 53:4318–4327
Lévai G, Martín Á, Paz E, Rodríguez-Rojo S, Cocero M (2015) Production of stabilized quercetin aqueous suspensions by supercritical fluid extraction of emulsions. J Supercrit Fluids 100:34–45
Lu Z, Bu C, Hu W, Zhang H, Liu M, Lu M, Zhai G (2018) Preparation and in vitro and in vivo evaluation of quercetin-loaded mixed micelles for oral delivery. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 82(2):238–246
Parmar A, Bahadur A, Kuperkar K, Bahadur P (2013) PEO–PPO based star-block copolymer T904 as pH responsive nanocarriers for quercetin: solubilization and release study. Eur Polym J 49:12–21
Fujimori M, Kadota K, Shimono K, Shirakawa Y, Sato H, Tozuka Y (2015) Enhanced solubility of quercetin by forming composite particles with trans glycosylated materials. J Food Eng 149:248–254
Riva A, Ronchi M, Petrangolini G, Bosisio S, Allegrini P (2019) Improved oral absorption of quercetin from Quercetin Phytosome®, a new delivery system based on food grade lecithin. Eur J Drug Metab 44:169–177
Patel D, Jana R, Lin M, Kuperkar K, Seth D, Chen L, Bahadur P (2021) Revisiting the salt-triggered self-assembly in very hydrophilic triblock copolymer Pluronic® F88 using multitechnique approach. Colloid Polym Sci 299:1113–1126
Manyanga F, Sithole A, Rivera R, Karamehmedovic N, Martin N (2016) Use of differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) to study the thermodynamics of DNA-based interactions and nucleic acid-based therapeutics. J Anal Pharm 2(2):1–12
Buckton G, Chowdhry B, Armstrong J, Leharne S, Bouwstra J, Hofland H (1992) The use of high-sensitivity differential scanning calorimetry to characterize dilute aqueous dispersions of surfactants. Int J Pharm 83:115–121
Pan K, Zhong Q, Baek S (2013) Enhanced dispersibility and bioactivity of curcumin by encapsulation in casein nanocapsules. J Agric Food Chem 61:6036–6043
Gawali S, Zhang KS, Ray D, Basu M, Aswal V, Danino DA, Hassan P (2019) Discerning the structure factor of charged micelles in water and supercooled solvent by contrast variation X-ray scattering. Langmuir 35:9867–9877
Ganguly R, Kunwar A, Dutta B, Kumar S, Barick K, Ballal A, Aswal V, Hassan P (2017) Heat-induced solubilization of curcumin in kinetically stable pluronic P123 micelles and vesicles: an exploit of slow dynamics of the micellar restructuring processes in the aqueous pluronic system. Colloid Surface B 152:176–182
Dutta B, Barick K, Verma G, Aswal V, Freilich I, Danino D, Singh B, Priyadarsini K, Hassan P (2017) PEG coated vesicles from mixtures of Pluronic P123 and L-α- phosphatidylcholine: structure, rheology and curcumin encapsulation. Phys Chem Chem Phys 19:26821–26832
Leharne S (2017) The physical chemistry of high-sensitivity differential scanning calorimetry of biopolymers. ChemTexts 3(1):1–12
Tsui H, Wang J, Hsu Y, Chen L (2010) Study of heat of micellization and phase separation or Pluronic aqueous solutions by using a high sensitivity differential scanning calorimetry. Colloid Polym Sci 288:1687–1696
Wanka G, Hoffmann H, Ulbricht W (1994) Phase diagrams and aggregation behavior of poly(oxyethylene)-poly(oxypropylene)-poly(oxyethylene) triblock copolymers in aqueous solutions. Macromolecules 27:4145–4159
Lee Y, Chung H, Yeo S, Ahn C, Lee H, Messersmith P, Park T (2010) Thermo-sensitive, injectable, and tissue adhesive sol–gel transition hyaluronic acid/pluronic composite hydrogels prepared from bio-inspired catechol-thiol reaction. Soft Matter 6:977–983
Lee S, Lee Y, Kim J, Park T, Ahn C (2009) A novel pH-sensitive PEG-PPG-PEG copolymer displaying a closed-loop sol–gel–sol transition. J Mater Chem 19:8198–8201
López-Barrón C, Li D, Wagner N, Caplan J (2014) Triblock copolymer self-assembly in ionic liquids: effect of PEO block length on the self-assembly of PEO−PPO−PEO in ethylammonium nitrate. Macromolecules 47(21):7484–7495
Chen Z, Greaves T, Caruso R, Drummond C (2014) Effect of cosolvents on the self-assembly of a non-ionic polyethylene oxide-polypropylene oxide-polyethylene oxide block copolymer in the protic ionic liquid ethylammonium nitrate. J Colloid Interface Sci 441:46–51
Albouy P, Deville S, Fulkar A, Hakouk K, Impéror-Clerc M, Klotz M, Liua Q, Marcellini M, Perez J (2017) Freezing induced self-assembly of amphiphilic molecules. Soft Matter 13:1759–1763
Golwala P, Rathod S, Patil R, Joshi A, Ray D, Aswal V, Bahadur P, Tiwari S (2020) Effect of cosurfactant addition on phase behavior and microstructure of a water dilutable microemulsion. Colloids Surf B 186:110736–110743
Patel D, Ray D, Kuperkar K, Aswal V, Bahadur P (2020) Parabens induced spherical micelle to polymersome transition in thermo-responsive amphiphilic linear and star-shaped EO-PO block copolymers. J Mol Liq 316:113897–113908
Patel D, Ray D, Kuperkar K, Pal H, Aswal V, Bahadur P (2019) Solubilization, micellar transition and biocidal assay of loaded antioxidants in Tetronic® 1304 micelles. Polym Int 11(69):1097–1104
Narvekar A, Gawali S, Hassan P, Jain R, Dandekar P (2020) pH dependent aggregation and conformation changes of rituximab using SAXS and its comparison with the standard regulatory approach of biophysical characterization. Int J Biol Macromol 164:3084–3097
Grishaev A, Anthis N, Clore G (2012) Contrast-matched small-angle X-ray scattering from a heavy-atom labeled protein in structure determination: application to a lead substituted calmodulin−peptide complex. J Am Chem Soc 134:14686–14689
Vercelino R, Cunha T, Ferreira E, Cunha F, Ferreira S, Oliveira M (2013) Skin vasodilation and analgesic effect of a topical nitric oxide-releasing hydrogel. J Mater Sci Mater Med 24:2157–2169
Khimani M, Rao U, Bahadur P (2014) Calorimetric and scattering studies on micellization of pluronics in aqueous solutions: effect of the size of hydrophilic PEO end blocks, temperature, and added salt. J Disper Sci Technol 35:1599–1610
Kubiak A, Bielan Z, Bartkowiak A, Gabała E, Piasecki A, Zalas M, Zielińska-Jurek A, Janczarek M, Siwińska-Ciesielczyk K, Jesionowski T (2020) Synthesis of titanium dioxide via surfactant- assisted microwave method for photocatalytic and dye-sensitized solar cells applications. Catalysts 10(5):586–610
Lin J, Chen J, Huang S, Ko J, Wang Y, Chen T, Wang L (2009) Folic acid–Pluronic F127 magnetic nanoparticle clusters for combined targeting, diagnosis, and therapy applications. Biomaterials 30:5114–5124
Thapa R, Cazzador F, Grønlien K, Tønnesen H (2020) Effect of curcumin and cosolvents on the micellization of Pluronic F127 in aqueous solution. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 195:111250–111259
Li Z, Xiong X, Peng S, Chen X, Liu W, Liu C (2019) Novel floated Pluronic F127 modified liposomes for delivery of curcumin: preparation, release and cytotoxicity. J Microencapsul 3(37):220–229
Zeng Z, Peng Z, Chen L, Chen Y (2014) Facile fabrication of thermally responsive Pluronic F127-based nanocapsules for controlled release of doxorubicin hydrochloride. Colloid Polym Sci 292(7):1521–1530
Layek R, Uddin M, Kim N, Lau A, Lee J (2017) Noncovalent functionalization of reduced graphene oxide with pluronic F127 and its nanocomposites with gum Arabic. Compos B Eng 128:155–163
Lindman B, Medronho B, Karlström G (2016) Clouding of nonionic surfactants. Curr Opin Colloid Interface Sci 22:23–29
Piazza R, Campello M, Buzzaccaro S, Sciortino F (2021) Phase behavior and microscopic dynamics of a thermosensitive gel-forming. Macromolecules 54:3897–3906
Gentile L, Luca G, Antunes F, Rossi C, Ranieri G (2010) Thermogelation analysis of F127-water mixtures by physical chemistry techniques. Appl Rheol 20(5):52081–52090
Wan F, Zhang J, Lau A, Tan S, Burger C, Chu B (2008) Nanostructured copolymer gels for dsDNA separation by CE. Electrophoresis 29:4704–4713
Kuperkar K, Patel D, Atanase L, Bahadur P (2022) Amphiphilic block copolymers: their structures, and self-assembly to polymeric micelles and polymersomes as drug delivery vehicles. Polymers 14(21):4702–4723
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge Sardar Vallabhbhai National Institute of Technology (SVNIT), Gujarat, India for providing the instrumentation facilities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
No human or animal subjects were used in this research.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Patel, D., Gawali, S.L., Kuperkar, K. et al. Co-micellization conduct and structural dynamics of block copolymers in water and salt solution environment for drug solubilization enhancement. Colloid Polym Sci 301, 919–931 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-023-05109-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-023-05109-x