Abstract
In this contribution, we reported the investigation of styrene–butadiene rubber (SBR) reinforced by kaolin-graft-polyisoprene (Mkaol). First, poly(isoprene-maleic anhydride) random copolymers (PIPMA) which was used as macromolecular surface modifiers were synthesized via reversible addition-fragmentation chain transfer polymerization (RAFT). Second, the PIPMA was sprayed onto the surface of kaolin to obtain MKaol. FTIR spectroscopy indicated that the surface of MKaol was covered with a layer of PIPMA. MKaol and kaolin were simultaneously incorporated into SBR. The storage modulus (G′) of SBR/kaolin compounds at low strains was much lower than the G′ of SBR/MKaol. The curing properties showed that the vulcanization rate of the SBR/MKaol compounds was much lower than that of the SBR/kaolin. The cross-link density of SBR/kaolin was slightly higher than those of SBR/MKaol. The SEM images revealed that kaolin microdomains in the SBR/MKaol vulcanizates were much better distributed and dispersed than in the SBR/kaolin composites. Compared to filler dispersion and filler–rubber interaction of the SBR/kaolin composites, the mechanical properties (tensile strength, elongation at break, and tear strength) of the SBR/MKaol composites were significantly improved.
Graphical abstract
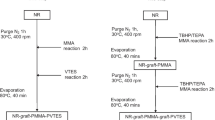
Poly(isoprene-maleic anhydride) random copolymers (PIPMA) which was used as macromolecular surface modifiers were synthesized via reversible addition-fragmentation chain transfer polymerization (RAFT). PIPMA was sprayed onto the surface of kaolin to obtain MKaol. The storage modulus (G′) of SBR/kaolin compounds at low strains was much lower than the G′ of SBR/MKaol compounds. The curing properties showed that the vulcanization rate of the SBR/MKaol compounds was much lower than that of the SBR/kaolin compounds. Kaolin microdomains in the SBR/MKaol vulcanizates were much better to disperse and distribute than in the SBR/kaolin composites. Compared to the SBR/kaolin composites, the mechanical properties of SBR/MKaol composites were greatly improved.


















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wolff S, Wang MJ, Tan EH (1993) Filler-elastomer interactions. Part VII. Study on bound rubber. Rubber Chem Technol 66:163–177. https://doi.org/10.5254/1.3538304
Dannenberg EM (1975) The effects of surface chemical interactions on the properties of filler-reinforced rubbers. Rubber Chem Technol 48:410–444. https://doi.org/10.5254/1.3547460
Frost RL, Horváth E, Makó É, Kristóf J, Cseh T (2003) The effect of mechanochemical activation upon the intercalation of a high-defect kaolinite with formamide. J Colloid Interface Sci 256:386–395. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0021-9797(03)00452-1
Cheng H, Liu Q, Yang J, Zhang J, Frost RL (2010) Thermal analysis and infrared emission spectroscopic study of halloysite–potassium acetate intercalation compound. Thermochim acta 16:124–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tca.2010.08.003
Zhang Z, Lu X, Su P (2010) Dispersion of kaolin powders in silica sols. Appl Clay Sci 49:51–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2010.04.001
Wu W, Tian L (2013) Formulation and morphology of kaolin-filled rubber composites. Appl Clay Sci 80:93–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2013.06.025
Jana SC, Jain S (2001) Dispersion of nanofillers in high performance polymers using reactive solvents as processing aids. Polymer 42:6897–6905. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0032-3861(01)00175-6
Lin Y, Zhang A, Sun J, Wang L (2013) Properties of natural rubber vulcanizates/nanosilica composites prepared based on the method of in-situ generation and coagulation. J Macromol Sci B 52:1494–1507. https://doi.org/10.1080/00222348.2013.763562
Zhang Y, Zhang A, Kang L, Zhang Y (2020) Mechanical properties and thermal stability of kaolinite/emulsion polymerization styrene butadiene rubber composite prepared by latex blending method. Polym Sci Ser 62:407–421. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0965545X20040112
Turner MR, Duguet E, Labrugere C (1997) Characterization of silane-modified ZrO2 powder surfaces. Surf Interface Anal 25:917–923. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)10969918(199711)25:12%3c917::AIDSIA314%3e3.0.CO;2-3
Ramier J, Gauthier C, Chazeau L, Stelandre L, Guy L (2007) Payne effect in silica-filled styrene–butadiene rubber: influence of surface treatment. J Polym Sci, Pol Phys 45:286–298. https://doi.org/10.1002/polb.21033
Sheikh SH, Yin X, Ansarifar A, Yendall K (2017) The potential of kaolin as a reinforcing filler for rubber composites with new sulfur cure systems. J Reinf Plast Comp 36:1132–1145. https://doi.org/10.1177/0731684417712070
Hillmyer MA, Lipic PM, Hajduk DA, Almdal K, Bates FS (1997) Self-assembly and polymerization of epoxy resin-amphiphilic block copolymer nanocomposites. J Am Chem Soc 119:2749–2750. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja963622m
Hu D, Xu Z, Zeng K, Zheng S (2010) From self-organized novolac resins to ordered nanoporous carbons. Macromolecules 43:2960–2969. https://doi.org/10.1021/ma902770r
Xu Z, Zheng S (2007) Morphology and thermomechanical properties of nanostructured thermosetting blends of epoxy resin and poly (ɛ-caprolactone)-block-polydimethylsiloxane-block-poly (ɛ-caprolactone) triblock copolymer. Polymer 48:6134–6144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2007.07.072
Zhang C, Li L, Zheng S (2013) Formation and confined crystallization of polyethylene nanophases in epoxy thermosets. Macromolecules 46:2740–2753. https://doi.org/10.1021/ma4000682
Cong H, Li L, Zheng S (2014) Formation of nanostructures in thermosets containing block copolymers: from self-assembly to reaction-induced microphase separation mechanism. Polymer 55:1190–1201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2014.01.049
Xiang Y, Xu S, Zheng S (2018) Epoxy toughening via formation of polyisoprene nanophases with amphiphilic diblock copolymer. Eur Polym J 98:321–329. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2017.11.032
Rong M, Zhang M, Zheng Y, Zeng H, Walter R, Friedrich K (2001) Structure-property relationships of irradiation grafted nano-inorganic particle filled polypropylene composites. Polymer 42:167–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0032-3861(00)00325-6
Bikiaris DN, Papageorgiou GZ, Pavlidou E, Vouroutzis N, Palatzoglou P, Karayannidis GP (2006) Preparation by melt mixing and characterization of isotactic polypropylene/SiO2 nanocomposites containing untreated and surface-treated nanoparticles. J Appl Polym Sci 100:2684–2696. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.22849
Yu Y, Rong M, Zhang M (2010) Grafting of hyperbranched aromatic polyamide onto silica nanoparticles. Polymer 51:492–499. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2009.12.013
Liu C, Pan C (2007) Grafting polystyrene onto silica nanoparticles via RAFT polymerization. Polymer 48:3679–3685. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2007.04.055
Morinaga T, Ohkura M, Ohno K, Tsujii Y, Fukuda T (2007) Monodisperse silica particles grafted with concentrated oxetane-carrying polymer brushes: their synthesis by surface-initiated atom transfer radical polymerization and use for fabrication of hollow spheres. Macromolecules 40:1159–1164. https://doi.org/10.1021/ma062230p
Zhao B, Zhu L (2006) Nanoscale phase separation in mixed poly (tert-butyl acrylate)/polystyrene brushes on silica nanoparticles under equilibrium melt conditions. J Am Chem Soc 128:4574–4575. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja058560r
Wu T, Zhang Y, Wang X, Liu S (2008) Fabrication of hybrid silica nanoparticles densely grafted with thermoresponsive poly (N-isopropylacrylamide) brushes of controlled thickness via surface-initiated atom transfer radical polymerization. Chem Mater 20:101–109. https://doi.org/10.1021/cm702073f
Zong G, Chen H, Qu R, Wang C, Ji N (2011) Synthesis of polyacrylonitrile-grafted cross-linked N-chlorosulfonamidated polystyrene via surface-initiated ARGET ATRP, and use of the resin in mercury removal after modification. J Hazard Mater 186:614–621. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.11.043
Perrier S, Takolpuckdee P, Mars CA (2005) Reversible addition-fragmentation chain transfer polymerization mediated by a solid supported chain transfer agent. Macromolecules 38:6770–6774. https://doi.org/10.1021/ma0506886
Zhao Y, Perrier S (2007) Reversible addition-fragmentation chain transfer graft polymerization mediated by fumed silica supported chain transfer agents. Macromolecules 40:9116–9124. https://doi.org/10.1021/ma0716783
Rungta A, Natarajan B, Neely T, Dukes D, Schadler LS, Benicewicz BC (2012) Grafting bimodal polymer brushes on nanoparticles using controlled radical polymerization. Macromolecules 45:9303–9311. https://doi.org/10.1021/ma3018876
Chinthamanipeta PS, Kobukata S, Nakata H, Shipp DA (2008) Synthesis of poly (methyl methacrylate)-silica nanocomposites using methacrylate-functionalized silica nanoparticles and RAFT polymerization. Polymer 49:5636–5642. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2008.10.018
Tumnantong D, Rempel GL, Prasassarakich P (2018) Preparation of poly (methyl methacrylate)-silica nanoparticles via differential microemulsion polymerization and physical properties of NR/PMMA-SiO2 hybrid membranes. Polym Eng Sci 58:759–766. https://doi.org/10.1002/pen.24611
Khani MM, Abbas ZM, Benicewicz BC (2017) Well-defined polyisoprene-grafted silica nanoparticles via the RAFT process. J Polym Sci, Pol Chem 55:1493–1501. https://doi.org/10.1002/pola.28514
Kongsinlark A, Rempel GL, Prasassarakich P (2012) Synthesis of monodispersed polyisoprene–silica nanoparticles via differential microemulsion polymerization and mechanical properties of polyisoprene nanocomposite. Chem Eng J 193:215–226. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2012.04.008
Tumnantong D, Rempel GL, Prasassarakich P (2017) Polyisoprene-silica nanoparticles synthesized via RAFT emulsifier-free emulsion polymerization using water-soluble initiators. Polymers 9:637. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9110637
Xiang Y, Shen X, Gao J, Asiri AM, Marwani HM (2019) Grafting polyisoprene onto surfaces of nanosilica via RAFT polymerization and modification of natural rubber. Polym Eng Sci 59:1167–1174. https://doi.org/10.1002/pen.25096
Lai JT, Filla D, Shea R (2002) Functional polymers from novel carboxyl-terminated trithiocarbonates as highly efficient RAFT agents. Macromolecules 35:6754–6756. https://doi.org/10.1021/ma020362m
Abd-El-Messieh SL, Abd-El-Nour KN (2003) Effect of curing time and sulfur content on the dielectric relaxation of styrene–butadiene rubber. J Appl Polym Sci 88:1613–1621. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.11686
Boopasiri S, Sae-Oui P, Lundee S, Takaewnoi S, Siriwong C (2021) Reinforcing efficiency of pyrolyzed spent coffee ground in styrene-butadiene rubber. Macromol Res 29:597–604. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13233-021-9072-x
Huang M, Li L, Zheng S (2016) Mesoporous silica with block copolymer templates: modulation of porosity via block copolymer reaction with silica. Micropor Mesopor Mat 225:9–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2015.12.008
Liew YM, Kamarudin H, Al Bakri AM, Luqman M, Nizar IK, Ruzaidi CM, Heah CY (2012) Processing and characterization of calcined kaolin cement powder. Constr Build Mater 30:794–802. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2011.12.079
Sepehri A, Razzaghi-Kashani M, Ghoreishy MHR (2012) Vulcanization kinetics of butyl rubber–clay nanocomposites and its dependence on clay microstructure. J Appl Polym Sci 125:E204–E213. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.34231
Sarkawi SS, Dierkes WK, Noordermeer JW (2014) Elucidation of filler-to-filler and filler-to-rubber interactions in silica-reinforced natural rubber by TEM Network Visualization. Eur Polym J 54:118–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2014.02.015
Ahmed NM, El-Sabbagh SH (2014) The influence of kaolin and calcined kaolin on SBR composite properties. Polym Composite 35:570–580. https://doi.org/10.1002/pc.22697
Pangamol P, Malee W, Yujaroen R, Sae-Oui P, Siriwong C (2018) Utilization of bagasse ash as a filler in natural rubber and styrene–butadiene rubber composites. Arab J Sci Eng 43(1):221–227. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-017-2859-6
Funding
This work was financially supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Anhui Province (1908085QB63), the Key Research and Development Project of Anhui Province (2022a05020009), the Foundation of Anhui Laboratory of Clean Catalytic Engineering (LCCE-02), and the Foundation of Anhui Polytechnic University of Xuancheng Institute of Industrial Technology (B2018-04).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Geng, Y., Zhao, H., Xiang, Y. et al. Grafting polyisoprene onto surfaces of kaolin by spray drying technology and modification of styrene–butadiene rubber. Colloid Polym Sci 300, 927–938 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-022-04966-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-022-04966-2