Abstract
Poly(acrylamide-co-acrylic acid) hydrogels are synthesized by free-radical polymerization in a microwave oven, in a one-step procedure that provides reduction in time, energy and resources in comparison with conventional heating in aqueous solution. Hydrogel microstructures are analysed by scanning electron microscopy (SEM). Dynamic swelling tests are carried out at three pH values (3.0, 10.0 and 7.0) and two temperatures (25 and 37 °C) considering the conditions for hydrogel application. SEM pictures indicate irregular cellular and porous structure of microwave synthesized hydrogels, obtained as a result of simultaneous polymerization and water evaporation. The results of swelling measurements show that the swelling ratio at pH 7.0 and 10.0 increases with increasing in acrylic acid amount, while at pH 3.0 decreases. Swelling rate is higher at physiological temperature, and solvent diffusion is relaxation-controlled. Swelling of hydrogels follows the second-order kinetics. Rheological behaviour of hydrogels has been assessed using the results of frequency and amplitude sweep tests applied at the systems in equilibrium swollen state. Obtained data reveal a dominant elastic character and a long linear viscoelastic region (up to 2000 Pa), as well as a similar three-dimensional internal structure of investigated hydrogels.
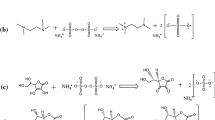
Graphical abstract



















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kostić A, Jovanović J, Adnadjević B, Popović A (2007) Comparison of the swelling kinetics of a partially neutralized poly(acrylic acid) hydrogel in distilled water. Journal of Serbian Chemical Sociaty 72:1139–1153. https://doi.org/10.2298/JSC0711139K
Kopecek J (2002) Polymer chemistry: swell gels. Nature 417:388–391. https://doi.org/10.1038/417388a
Mahkam M, Allahverdipoor M (2004) Controlled release of biomolecules from pH-sensitive network polymers prepared by radiation polymerization. J Drug Target 12:151–156. https://doi.org/10.1080/10611860410001688009
Xue W, Champ S, Huglin M (2001) Network and swelling parameters of chemically crosslinked thermoreversible hydrogels. Polymer 42:3665–3669. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0032-3861(00)00627-3
Ullah F, Othman MBH, Javed F, Ahmad Z, Akil HM (2015) Classification, processing and application of hydrogels: a review. Material Science and Engineering: C 57:414–433. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2015.07.053
Okay O, Sariisik SB, Zor SD (1998) Swelling behavior of anionic acrylamide-based hydrogels in aqueous salt solutions: Comparison of experiment with theory. J Appl Polym Sci 70:567–575. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1097-4628(19981017)70:3<567::AID-APP19>3.0.CO;2-Y
Ganji F, Vasheghani-Farahani S, Vasheghani-Farahani E (2010) Theoretical description of hydrogel swelling: a review. Iran Polym J 19:375–398
Bajpai AK, Shukla SK, Bhanu S, Kankane S (2008) Responsive polymers in controlled drug delivery. Prog Polym Sci 33:1088–1118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2008.07.005
Shah R, Saha N, Kitano T, Saha P (2014) Preparation of CaCO3-based biomineralized polyvinylpyrrolidone–carboxymethylcellulose hydrogels and their viscoelastic behavior. J Appl Polym Sci 131:40237. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.40237
Tang S, Glassman MJ, Li S, Socrate S, Olsen BD (2014) Oxidatively responsive chain extension to entangle engineered protein hydrogels. Macromolecules 47:791–799. https://doi.org/10.1021/ma401684w
Gradzielski M, Homann I (2018) Polyelectrolyte-surfactants complexes (PESCs) composed of oppositely charged components. Current Opinion in Colloid Interface and Science 35:124–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cocis.2018.01.017
Smilek J, Jarábková S, Velcer T, Pekar M (2019) Compositional and temperature effects on the rheological properties of polyelectrolyte-surfactant hydrogels. Polymers 11:927. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11050927
Mah E, Ghosh R (2013) Thermo-responsive hydrogels for stimuli-responsive membranes. Processes 1:238–262. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr1030238
Craciun G, Ighigeanu D, Manaila E, Stelescu MD (2015) Synthesis and characterization of poly(acrylamide-co-acrylic acid) flocculant obtained by electron beam irradiation. Mater Res 18:984–993. https://doi.org/10.1590/1516-1439.00871
Mutar MA, Kmal RK (2012) Preparation of copolymer of acrylamide and acrylic acid and its application for slow release sodium nitrate fertilizer 71-83. https://doi.org/10.13140/RG.2.2.26409.44647
Tomar RS, Gupta I, Singhal NAK (2007) Synthesis of poly (acrylamide-co-acrylic acid) based superabsorbent hydrogels: study of network parameters and swelling behaviour. Polym-Plast Technol Eng 46:481–488. https://doi.org/10.1080/03602550701297095
Chen J, Zhao Y (2000) Relation between water absorbency and reaction conditions in aqueous solution polymerization of polyacrylate superabsorbent polymers. J Appl Polym Sci 75:808–814. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1097-4628(20000207)75:6<808::AID-APP10>3.0.CO;2-3
Nesrinne S, Djamel A (2007) Synthesis, characterization and rheologicalbehavior of pH sensitive poly(acrylamide-co-acrylic acid) hydrogels. Arab J Chem 10:539–547. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2013.11.027
El-Sherbiny IM, Yacoub MH (2013) Hydrogel scaffolds for tissue engineering: progress and challenges. Global Cardiology Science and Practice 2013:1–27. https://doi.org/10.5339/gcsp.2013.38
Saxena VK, Chandra U (2011) Microwave synthesis: a physical concept. In: Chandra U (ed) Microwave heating, IntechOpen. https://doi.org/10.5772/22888
Kalaleh HA, Tally M, Atassi Y (2015) Preparation of bentonite-g-poly(acrylate-co-acrylamide) superabsorbent polymer composite for agricultural applications: optimization and characterization. Polymer Science Series B 57:750–758. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1560090415060081
Erceg T, Cakić S, Cvetinov M, Dapčević-Hadnađev T, BudinskiSimendić J, Ristić I (2019) The properties of conventionally and microwave synthesized poly(acrylamide-co-acrylic acid) hydrogels. Polym Bull 77:2089–2110. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-019-02840-w
Erceg T, Ristić I, Hadnađev M, Cakić S, Budinski-Simendić J (2018) Swelling, mechanical and thermal properties of microwave–synthesized intelligent soft materials. Materials Science. Non-Equilibrium Phase Transformations 4:86–88
Kıpçak AS, Ismail O, Doymaz I, Pişkin S (2014) Modeling and investigation of the swelling kinetics of acrylamide-sodium acrylate hydrogel. Journal of Chemistry 2014:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/281063
Boztepe C, Şölener M, Yuceer M, Kunkul A, Kabasakal O (2015) Modeling of swelling behaviors of acrylamide-based polymeric hydrogels by intelligent system. J Dispers Sci Technol 36:1647–1656. https://doi.org/10.1080/01932691.2014.996892
Tanaka T, Fillmore DJ (1979) Kinetics of swelling of gels. J Chem Phys 70:1214–1218. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.437602
Li Y, Tanaka T (1990) Kinetics of swelling and shrinking of gels. J Chem Phys 92:1365–1359. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.458148
Peppas NA, Bures P, Leobandung W, Ichikawa H (2000) Hydrogels in pharmaceutical formulations. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 50:27–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0939-6411(00)00090-4
Omidian H, Hashemi SA, Sammes PG, Meldrum I (1998) A model for the swelling of superabsorbent polymers. Polymer 39:6697–6704. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0032-3861(98)00095-0
Sugahara Y, Takahisa O (2001) Synthesis of starch-graft -polyacrylonitrile hydrolyzate and its characterization. J Appl Polym Sci 82:1437–1443. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.1981
Soleimani F, Sadeghi H, Shashavari H, Soleimani A, Sadeghi F (2013) Search result studies of swelling kinetics of carboxymethyl cellulose-g-PMAAm-co-PNIPAm superabsorbent hydrogels. Asian Journal of Chemistry 25:4851–4855. https://doi.org/10.14233/ajchem.2013.14123
Quintana JR, Valderruten NE, Katime I (1999) Synthesis and swelling kinetics of poly(dimethylaminoethyl acrylate methyl chloride quaternary-co-itaconic acid) hydrogels. Langmuir 15:4728–4730. https://doi.org/10.1021/la980982
Pescosolido L, Feruglio L, Farra R, Fiorentino S, Colombo I, Coviello T, Matricardi PW, Hennink WE, Vermonden T, Grassi M (2012) Mesh size distribution determination of interpenetrating polymer network hydrogels. Soft Matter 8:7708–7715. https://doi.org/10.1039/C2SM25677K
Chavda HV, Patel RD, Modhia IP, Patel CN (2012) Preparation and characterization of superporous hydrogel based on different polymers. International Journal of Pharmaceutical Investigation 2:134–139. https://doi.org/10.4103/2230-973x.104396
Sinnwell S, Ritter H (2007) Recent advances in microwave-assisted polymer synthesis. Aust J Chem 60:729–743. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.1981
Gabriel C, Gabriel S, Grant EH, Halstead BS, Mingos DMP (1998) Dielectric parameters relevant to microwave heating. Chem Soc Rev 27:213–223. https://doi.org/10.1039/A827213Z
Braun D, Cherdron H, Ritter H (2001) Polymer synthesis: theory and practice, fundamentals, methods, experiments3rd edn. Springer Verlag, Berlin
Kolthoff IM, Miller IK (1951) The chemistry of persulfate. II The reaction of persulfate with mercaptans solubilized in solutions of saturated fatty acid soaps. The Journal of American Chemical Society 73:5118–5122. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja01155a030
Kokufuta E (2005) Polyelectrolyte gel transitions: experimental aspects of charge inhomogeneity in the swelling and segmental attractions in the shrinking. Langmuir 21:10004–10015. https://doi.org/10.1021/la050530e
Chaudhari AK, Han I, Tan JC (2015) Multifunctional supramolecular hybrid materials constructed from hierarchical self-ordering of in situ generated metal-organic framework (MOF) nanoparticles. Adv Mater 27:4438–4446. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201501448
Cuomo F, Cofelice M, Lopez F (2019) Rheological characterization of hydrogels from alginate-based nanodispersion. Polymers 11:259. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11020259
Ali W, Gebert B, Altinpinar S, Mayer-Gall T, Ulbricht M, Gutmann JS, Graf K (2018) On the potential of using dual-function hydrogels for brackish water desalination. Polymers 10:567. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10060567
Funding
The authors received financial support from the Ministry of Education, Science and Technological Development, Republic of Serbia, project number 451-03-68/2020-14/ 200134.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Erceg, T., Dapčević-Hadnađev, T., Hadnađev, M. et al. Swelling kinetics and rheological behaviour of microwave synthesized poly(acrylamide-co-acrylic acid) hydrogels. Colloid Polym Sci 299, 11–23 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-020-04763-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-020-04763-9