Abstract
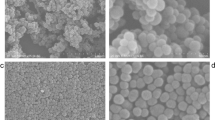
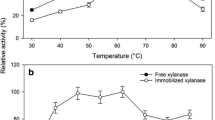
In this article, the magnetic nanospheres bonded to a polymer chelator have synthesized through a new strategy consisted of four parts: (1) synthesis and surface modification of nanoparticles with vinyl groups; (2) grafting of a water-soluble polymer having hydroxyl groups, by polymerization of the resulting monomer from the reaction of glycidyl methacrylate (GMA) and diethanolamine (DEA) on the surface of nanomagnetic particles; (3) by cerium(IV), conversion of hydroxyl groups of the synthesized polymer on the nanoparticles to radicals for subsequent grafting of the resulting monomer from reaction of GMA and iminodiacetic acid (IDA); and (4) in an ion-exchange process, nickel ions along the last synthesized polymer were immobilized. The prepared nanospheres were successfully used directly for purification of His-tagged xylanase from cell lysates. The separated proteins were subjected to enzyme assays and are observed well in the enzymatic activity.

Graphical abstract











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Renuse S, Madugundu AK, Kumar P, Nair BG, Gowda H, Prasad TS, Pandey A (2014) Proteomic analysis and genome annotation of Pichia pastoris, a recombinant protein expression host. Proteomics 14:2769–2779
Pal M, Khanal M, Marko R, Thirumalairajan S, Bearne SL (2016) Rational design and synthesis of substrate-product analogue inhibitors of alpha-methylacyl-coenzyme A racemase from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Chem Commun 52:2740–2743
Zhu X, Yang H, Guo Z, Yu W, Carney PJ, Li Y, Chen LM, Paulson JC, Donis RO, Tong S, Stevens J, Wilson IA (2012) Crystal structures of two subtype N10 neuraminidase-like proteins from bat influenza A viruses reveal a diverged putative active site. PNAS 109:18903–18908
Gaberc-Porekar V, Menart V (2005) Potential for using histidine tags in purification of proteins at large scale. Chem Eng Technol 28:1306–1314
Lata S, Reichel A, Brock R, Tampe R, Piehler J (2005) High-affinity adaptors for switchable recognition of histidine-tagged proteins. J Am Chem Soc 127:10205–10215
Xu CJ, Xu KM, Gu HW, Zhong XF, Guo ZH, Zheng RK, Zhang XX, Xu B (2004) Nitrilotriacetic acid-modified magnetic nanoparticles as a general agent to bind histidine-tagged proteins. J Am Chem Soc 126:3392–3393
Benelmekki M, Xuriguera E, Caparros C, Rodriguez-Carmona E, Mendoza R, Corchero JL, Lanceros-Mendez S, Martinez LM (2012) Design and characterization of Ni2+and Co2+ decorated porous magnetic silica spheres synthesized by hydrothermal-assisted modified-Stober method for His-tagged proteins separation. J Colloid Interface Sci 365:156–162
Kim J, Piao Y, Lee N, Park YI, Lee IH, Lee JH, Paik SR, Hyeon T (2010) Magnetic nanocomposite spheres decorated with NiO nanoparticles for a magnetically recyclable protein separation system. Adv Mater 22:57–60
Wang W, Wang DIC, Li Z (2011) Facile fabrication of recyclable and active nanobiocatalyst: purification and immobilization of enzyme in one pot with Ni-NTA functionalized magnetic nanoparticle. Chem Commun 47:8115–8117
Shukoor MI, Natalio F, Therese HA, Tahir MN, Ksenofontov V, Panthofer M, Eberhardt M, Theato P, Schroder HC, Müller WEG, Tremel W (2008) Fabrication of a silica coating on magnetic γ-Fe2O3 nanoparticles by an immobilized enzyme. Chem Mater 20:3567–3573
Shao MF, Ning FY, Zhao JW, Wei M, Evans DG, Duan X (2012) Preparation of Fe3O4@SiO2@layered double hydroxide core-shell microspheres for magnetic separation of proteins. J Am Chem Soc 134:1071–1077
Li YC, Lin YS, Tsai PJ, Chen CT, Chen WY, Chen YC (2007) Nitrilotriacetic acid-coated magnetic nanoparticles as affinity probes for enrichment of histidine-tagged proteins and phosphorylated peptides. Anal Chem 79:7519–7525
Liu Z, Li M, Yang XJ, Yin ML, Ren JS, Qu XG (2011) The use of multifunctional magnetic mesoporous core/shell hetero nanostructures in a biomolecule separation system. Biomaterials 32:4683–4690
Fang WJ, Chen XL, Zheng NF (2010) Superparamagnetic core/shell polymer particles for efficient purification of His-tagged proteins. J Mater Chem 20:8624–8630
Xu F, Geiger JH, Baker GL, Bruening ML (2011) Polymer brush-modified magnetic nanoparticles for His-tagged protein purification. Langmuir 27:3106–3112
Dyal A, Loos K, Noto M, Chang S, Spagnoli C, Shafi KVPM, Ulman A, Cowman M, Gross RA (2003) Activity of Candida rugosa lipase immobilized on γ-Fe2O3 magnetic nanoparticles. J Am Chem Soc 125:1684–1685
Ma WF, Zhang Y, Li LL, You LJ, Zhang P, Zhang YT, Li JM, Yu M, Guo J, Lu HJ, Wang CC (2012) Tailor-made magnetic Fe3O4@mTiO2 microspheres with a tunable mesoporous anatase shell for highly selective and effective enrichment of phospho peptides. ACS Nano 6:3179–3188
Luo B, Xu S, Luo A, Wang WR, Wang SL, Guo J, Lin Y, Zhao DY, Wang CC (2011) Mesoporous biocompatible and acid-degradable magnetic colloidal nano crystal clusters with sustainable stability and high hydrophobic drug loading capacity. ACS Nano 5:1428–1435
Cho HS, Dong ZY, Pauletti GM, Zhang JM, Xu H, Gu HC, Wang LM, Ewing RC, Huth C, Wang F, Shi DL (2010) Fluorescent, super paramagnetic nanospheres for drug storage, targeting, and imaging: a multifunctional nano carrier system for cancer diagnosis and treatment. ACS Nano 4:5398–5404
Li D, Tang J, Wei C, Guo J, Wang SL, Chaudhary D, Wang CC (2012) Doxorubicin-conjugated mesoporous magnetic colloidal nano crystal clusters stabilized by polysaccharide as a smart anticancer drug vehicle. Small 8:2690–2697
Rembsum A, Dreyer W (1980) Immunomicrospheres: reagents for cell labeling and separation. Science 208:364–368
Wang D, He J, Rosenzweig N, Rosenzweig Z (2004) Rational growth of branched and hyperbranched nanowire structures. Nano Lett 4:409–413
Yang J, Lee CH, Park J, Seo S, Lim EK, Song YJ, Suh JS, Yoon HG, Huh YM, Haam S (2010) Uniform magnetic core/shell microspheres functionalized with Ni2+–iminodiacetic acid for one step purification and immobilization of His-tagged enzymes. J Mater Chem 20:8624–8630
Kim J, Piao Y, Hyeon T (2009) Multifunctional nanostructured materials for multimodal imaging, and simultaneous imaging and therapy. Chem Soc Rev 38:372–390
Shi DL, Bedford NM, Cho HS (2011) Engineered multifunctional nano carriers for cancer diagnosis and therapeutics. Small 7:2549–2567
Zhang L, Chen L, Wan QH (2008) Preparation of uniform magnetic microspheres through hydrothermal reduction of iron hydroxide nanoparticles embedded in a polymeric matrix. Chem Mater 20:3345–3353
Di Corato R, Piacenza P, Musaro M, Buonsanti R, Cozzoli PD, Zambianchi M, Barbarella G, Cingolani R, Manna L, Pellegrino T (2009) Magnetic fluorescent colloidal nanobeads: preparation and exploitation in cell separation experiments. Macromol Biosci 9:952–958
Felinto MCFC, Parra DF, Lugao AB, Batista MP, Higa OZ, Yamaura M, Camilo RL, Ribela MTCP, Sampaio LC (2005) Magnetic polymeric microspheres for protein adsorption. Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res Sect B 236:495–500
Yi DK, Selvan ST, Lee SS, Papaefthymiou GC, Kundaliya D, Ying JY (2005) Silica-coated nanocomposites of magnetic nanoparticles and quantum dots. J Am Chem Soc 127:4990–4991
Gao R, Kong XX, Wang X, He XW, Chen LX, Zhang YK (2011) Preparation and characterization of uniformly sized molecularly imprinted polymers functionalized with core–shell magnetic nanoparticles for the recognition and enrichment of protein. J Mater Chem 21:17863–17871
Lyon JL, Fleming DA, Stone B, Schiffer P, Williams ME (2004) Synthesis of Fe oxide core/Au shell nanoparticles by iterative hydroxylamine seeding. Nano Lett 4:719–723
Kim J, Park S, Lee JE, Jin SM, Lee JH, Lee IS, Yang I, Kim JS, Kim SK, Cho MH, Hyeon T (2006) Designed fabrication of multifunctional magnetic gold nano shells and their application to magnetic resonance imaging and photo thermal therapy. Angew Chem Int Ed 45:7754–7758
Xu ZC, Hou YL, Sun SH (2007) Magnetic core/shell Fe3O4/Au and Fe3O4/Au/Ag nanoparticles with tunable plasmonic properties. J Am Chem Soc 129:8698–8699
Gupta AK, Gupta M (2005) Synthesis and surface engineering of iron oxide nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Biomaterials 26:3995–4021
Oh JK, Park JM (2011) Iron oxide-based superparamagnetic polymeric nanomaterials: design, preparation, and biomedical application. Prog Polym Sci 36:168–189
Lin ZA, Zheng JN, Lin F, Zhang L, Cai ZW, Chen GN (2011) Synthesis of magnetic nanoparticles with immobilized amino phenyl boronic acid for selective capture of glycoproteins. J Mater Chem 21:518–524
Zhang M, Zhang XH, He XW, Chen LX, Zhang YKA (2012) Self-Assembled polydopamine film on the surface of magnetic nanoparticles for specific capture of protein. Nanoscale 4:3141–3147
Lin ZA, Xia ZW, Zheng JN, Zheng D, Zhang L, Yang HH, Chen GN (2012) Synthesis of uniformly sized molecularly imprinted polymer-coated silica nanoparticles for selective recognition and enrichment of lysozyme. J Mater Chem 22:17914–17922
Lin ZA, Zheng JN, Xia ZW, Yang HH, Zhang L, Chen GN (2012) One-pot synthesis of phenylboronic acid-functionalized core-shell magnetic nanoparticles for selective enrichment of glycoproteins. RSC Adv 2:5062–5065
Muller WJ (1990) New ion exchangers for the chromatography of biopolymers. Chromatogr 510:133–140
Massart T (1981) Preparation of aqueous magnetic liquids in alkaline and acidic media. IEEE Trans Magn MAG 17:1247
Chen CY, Chen CYJ (2002) Stability constants of polymer-bound iminodiacetate-type chelating agents with some transition-metal ions. J Appl Polym Sci 86:1986–1994
Rahimian Gavaseraei H, Hasanzadeh R, Afsharnezhad M, Foroutan Kalurazi A, Shahangian SH, Aghamaali MR, Aminzadeh S (2020) A novel cellulase-free xylanase B from the thermophilic bacterium Chonella sp.A01; cloning, purification and biochemical characterization. [Submitted]
Miller GL (1959) Use of dinitrosalicylic acid reagent for determination of reducing sugar. Anal Chem 31(3):426–428
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Ma ZY, Guan YP, Liu XQ, Liu HZ (2005) Synthesis of magnetic chelator for high-capacity immobilized metal affinity adsorption of protein by cerium initiated graft polymerization. Langmuir 21:6987–6994
Philips AP, Van Brugen MPB, Pathmamanoharan C (1994) Magnetic silica dispersions: preparation and stability of surface-modified silica particles with a magnetic core. Langmuir 10:92–99
Deng Y, Wang C, Hu J, Yang W, Fu S (2005) Investigation of formation of silica-coated magnetite nanoparticles via sol–gel approach. Colloids Surf 262:87–93
Lu Y, Yin Y, Mayers BT, Xia Y (2002) Modifying the surface properties of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles through a sol-gel approach. Nano Lett 2:183–186
Sachnin A, Kulkarni P, Sawadh S, Prakash K (2014) Synthesis and characterization of superparamagnetic Fe3O4@SiO2 nanoparticles. J Korean Chem Soc 58:100–104
Zou X, Li K, Zhao Y, Zhang Y, Li B, Song C (2013) Ferroferric oxide/L-cysteine magnetic nanospheres for capturing histidine-tagged proteins. J Mater Chem B 1:5108–5113
Zhang Y, Yang Y, Ma W, Guo J, Lin Y, Wang C (2013) Uniform magnetic core/shell microspheres functionalized with Ni2 + –iminodiacetic acid for one step purification and immobilization of His-tagged enzymes. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 5:2626–2633
Fenga G, Hu D, Yang L, Cui Y, Cui X, Li H (2010) Immobilized-metal affinity chromatography adsorbent with paramagnetism and its application in purification of histidine-tagged proteins. Sep Purif Technol 74:253–260
Zhang L, Zhu X, Jiao D, Sun Y, Sun H (2013) Efficient purification of His-tagged protein by superparamagnetic Fe3O4/Au–ANTA–Co2+ nanoparticles. Mater Sci Eng C 33:1989–1992
Acknowledgments
We thank the support of the Chemistry Department of the Islamic Azad University of Central Tehran Branch and the Iranian Polymer and Petrochemical Institute.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shirzadi, Z., Baharvand, H., Nezhati, M.N. et al. Synthesis of nonlinear polymer brushes on magnetic nanoparticles as an affinity adsorbent for His-tagged xylanase purification. Colloid Polym Sci 298, 1597–1607 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-020-04749-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-020-04749-7