Abstract
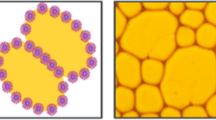
We report ultrasonically generated pH-responsive Pickering Janus emulsions of olive oil and silicone oil with controllable droplet size and engulfment. Chitosan was used as a pH-responsive emulsifier. The increase of pH from 2 to 6 leads to a transition from completely engulfed double emulsion droplets to dumbbell-shaped Janus droplets accompanied by a significant decrease of droplet diameter and a more homogeneous size distribution. The results can be elucidated by the conformational change of chitosan from a more extended form at pH 2 to a more flexible form at pH 4–5.
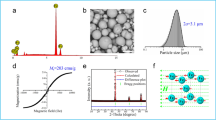
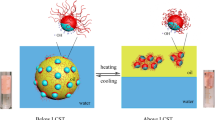
Magnetic responsiveness to the emulsion was attributed by dispersing superparamagnetic nanoparticles (Fe3O4 with diameter of 13 ± 2 nm) in the olive oil phase before preparing the Janus emulsion. Incorporation of magnetic nanoparticles leads to superior emulsion stability, drastically reduced droplet diameters, and opened the way to control movement and orientation of the Janus droplets according to an external magnetic field.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hasinovic H, Friberg SE, Rong G (2011) A one-step process to a Janus emulsion. J Colloid Interface Sci 354:424–426. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2010.10.004
Zhang Q, Savagatrup S, Kaplonek P, Seeberger PH, Swager TM (2017) Janus emulsions for the detection of bacteria. ACS Cent Sci 3:309–313. https://doi.org/10.1021/acscentsci.7b00021
Kovach I, Rumschöttel J, Friberg SE, Koetz J (2016) Janus emulsion mediated porous scaffold bio-fabrication. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 145:347–352. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2016.05.018
Nagelberg S, Zarzar LD, Nicolas N, Subramanian K, Kalow JA, Sresht V, Blankschtein D, Barbastathis G, Kreysing M, Swager TM, Kolle M (2017) Reconfigurable and responsive droplet-based compound micro-lenses. Nat Commun 8:14673. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms14673
Ge L, Lu S, Han J, Guo R (2015) Anisotropic particles templated by Janus emulsion. Chem Commun 51:7432–7434. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5CC00935A
Wei D, Ge L, Lu S, Li J, Guo R (2017) Janus particles templated by Janus emulsions and application as a Pickering emulsifier. Langmuir 33:5819–5828. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.langmuir.7b00939
Kano M, Yanagisawa N, Takahashi Y, Kondo Y (2017) Fabrication of hollow polymer particles using emulsions of hydrocarbon oil/fluorocarbon oil/aqueous surfactant solution. J Fluor Chem 197:34–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfluchem.2017.02.008
Guzowski J, Korczyk PM, Jakiela S, Garstecki P (2012) The structure and stability of multiple micro-droplets. Soft Matter 8:7269. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2sm25838b
Kovach I, Friberg SE, Koetz J (2017) A “perfect Janus emulsion”: thermodynamic factors. J Dispers Sci Technol 38:594–597. https://doi.org/10.1080/01932691.2016.1183502
Friberg SE, Kovach I, Koetz J (2013) Equilibrium topology and partial inversion of Janus drops: a numerical analysis. ChemPhysChem 14:3772–3776. https://doi.org/10.1002/cphc.201300635
Zarzar LD, Sresht V, Sletten EM, Kalow JA, Blankschtein D, Swager TM (2015) Dynamically reconfigurable complex emulsions via tunable interfacial tensions. Nature 518:520–524. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature14168
Kovach I, Koetz J, Friberg SE (2014) Janus emulsions stabilized by phospholipids. Colloids Surf A Physiochem Eng Asp 441:66–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2013.08.065
Raju RR, Kosmella S, Friberg SE, Koetz J (2017) Pickering Janus emulsions and polyelectrolyte complex-stabilized Janus gels. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 533:241–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2017.08.022
Alison L, Rühs PA, Tervoort E, Teleki A, Zanini M, Isa L, Studart AR (2016) Pickering and network stabilization of biocompatible emulsions using chitosan-modified silica nanoparticles. Langmuir 32:13446–13457. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.langmuir.6b03439
Tang J, Quinlan PJ, Tam KC (2015) Stimuli-responsive Pickering emulsions: recent advances and potential applications. Soft Matter 11:3512–3529. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5SM00247H
Wu J, Ma G-H (2016) Recent studies of Pickering emulsions: particles make the difference. Small 12:4633–4648. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201600877
Montagne F, Mondain-Monval O, Pichot C, Mozzanega H, Elaı̈ssari A (2002) Preparation and characterization of narrow sized (o/w) magnetic emulsion. J Magn Magn Mater 250:302–312. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-8853(02)00412-2
Kaiser A, Liu T, Richtering W, Schmidt AM (2009) Magnetic capsules and Pickering emulsions stabilized by core—shell particles. Langmuir 25:7335–7341. https://doi.org/10.1021/la900401f
Zhou J, Qiao X, Binks BP, Sun K, Bai M, Li Y, Liu Y (2011) Magnetic Pickering emulsions stabilized by Fe 3 O 4 nanoparticles. Langmuir 27:3308–3316. https://doi.org/10.1021/la1036844
Hamman JH (2010) Chitosan based polyelectrolyte complexes as potential carrier materials in drug delivery systems. Mar Drugs 8:1305–1322
Payet L, Terentjev EM (2008) Emulsification and stabilization mechanisms of O/W emulsions in the presence of chitosan. Langmuir 24:12247–12252. https://doi.org/10.1021/la8019217
Liu H, Wang C, Zou S, Wei Z, Tong Z (2012) Simple, reversible emulsion system switched by pH on the basis of chitosan without any hydrophobic modification. Langmuir 28:11017–11024. https://doi.org/10.1021/la3021113
Wang XY, Heuzey MC (2016) Chitosan-based conventional and Pickering emulsions with long-term stability. Langmuir 32:929–936. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.langmuir.5b03556
Liu X, Ma Z, Xing J, Liu H (2004) Preparation and characterization of amino–silane modified superparamagnetic silica nanospheres. J Magn Magn Mater 270:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2003.07.006
Cao H, He J, Deng L, Gao X (2009) Fabrication of cyclodextrin-functionalized superparamagnetic Fe3O4/amino-silane core–shell nanoparticles via layer-by-layer method. Appl Surf Sci 255:7974–7980. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2009.04.199
Hasinovic H, Boggs C, Friberg SE, Kovach I, Koetz J (2014) Janus emulsions from a one-step process; optical microscopy images. J Dispers Sci Technol 35:613–618. https://doi.org/10.1080/01932691.2013.801019
Raymond L, Morin FG, Marchessault RH (1993) Degree of deacetylation of chitosan using conductometric titration and solid-state NMR. Carbohydr Res 246:331–336. https://doi.org/10.1016/0008-6215(93)84044-7
Jiang X, Chen L, Zhong W (2003) A new linear potentiometric titration method for the determination of deacetylation degree of chitosan. Carbohydr Polym 54:457–463. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2003.05.004
Tsaih ML, Chen RH (1999) Effects of ionic strength and pH on the diffusion coefficients and conformation of chitosans. J App Polym Sci 73:2041–2050. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1097-4628(19990906)73:10<2041::AID-APP22>3.0.CO;2-T
Frison R, Cernuto G, Cervellino A et al (2013) Magnetite-maghemite nanoparticles in the 5-15 nm range: correlating the core-shell composition and the surface structure to magnetic properties. A total scattering study. Chem Mater 25:4820–4827. https://doi.org/10.1021/cm403360f
Kim I, Worthen AJ, Johnston KP, DiCarlo DA, Huh C (2016) Size-dependent properties of silica nanoparticles for Pickering stabilization of emulsions and foams. J Nanopart Res 18:82. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-016-3395-0
Binks BP, Lumsdon SO (2001) Pickering emulsions stabilized by monodisperse latex particles: effects of particle size. Langmuir 17:4540–4547. https://doi.org/10.1021/la0103822
Acknowledgements
We thankfully acknowledge effective discussions and cordial help from Sibylle Rüstig and Dr. Brigitte Tiersch regarding Cryo-SEM and TEM micrographs.
Funding
This study was funded by the Polymer Science Program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interests.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 2
(DOCX 9730 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Raju, R.R., Liebig, F., Klemke, B. et al. pH-responsive magnetic Pickering Janus emulsions. Colloid Polym Sci 296, 1039–1046 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-018-4321-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-018-4321-z