Abstract
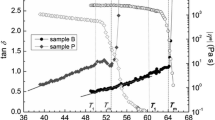
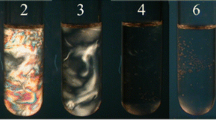
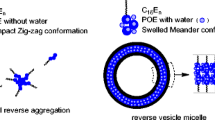
A sponge phase (L3 phase) was observed in aqueous solution of a nonionic surfactant polyethylene glycol ether of tridecyl alcohol with the average 3 of ethylene oxide (CH3(CH2)12(OCH2CH2)3OH, abbreviated as Trideceth-3) with tetradecyldimethylamino oxide (\( {\mathrm{CH}}_3{\left({\mathrm{CH}}_2\right)}_{13}\overset{\overset{\mathrm{O}}{\uparrow }}{\mathrm{N}}{\left({\mathrm{CH}}_3\right)}_2 \), abbreviated as C14DMAO). The L3 phase can be transferred to planar lamellar phase after the bilayer was protonated by the formic acid formed through the hydrolysis of methylformate. The addition of surface charge into the nonionic L3 phase through electrostatic repulsion on the ionic head groups will suppress the Helfrich undulation and induce the transition to planar lamellar phase. The planar lamellar phase can be transformed into multilamellar vesicles under shear. Rheological properties show that both of the storage modulus and the loss modulus of the lamellar phase were increased with the increment of surface charge density. The phase transition from L3 phase to vesicles was characterized by rheological measurements, 2H NMR spectra, and transmission electron microscope (TEM) observations. To our best knowledge, this is the first example of a controlled phase transition in nonionic surfactant mixtures through protonation and shear forces. The procedure provides a direction on how to achieve phase transition in surfactant solution by changing the conditions and an application of phase transition of controlled materials.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Porte G, Appel J, Bassereau P, Marignan J (1989) Lα to L3: a topology driven transition in phases of infinite fluid membranes J Phys Fr 50:1335–1347
Kaler EW, Murthy AK, Rodriguez BE, Zasadzinski J (1989) Spontaneous vesicle formation in aqueous mixtures of single-tailed surfactants Science 245:1371–1374
Zemb T, Dubois M, Deme B, Gulik-Krzywicki T (1999) Self-assembly of flat nanodiscs in salt-free catanionic surfactant solutions Science 283:816–819
Kato T (2002) Self-assembly of phase-segregated liquid crystal structures Science 295:2414–2418
Yan D, Zhou Y, Hou J (2004) Supramolecular self-assembly of macroscopic tubes Science 303:65–67
O’Leary LER, Fallas JA, Bakota EL, Kang MK, Hartgerink JD (2011) Multi-hierarchical self-assembly of a collagen mimetic peptide from triple helix to nanofibre and hydrogel Nat Chem 3:821–828
Gazeau D, Bellocq AM, Row D, Zemb T (1989) Experimental evidence for random surface structures in dilute surfactant solutions Europhys Lett 9:447–452
Mitchell DJ, Tiddy GJT, Waring L, Bostock T, McDonald MP (1983) Phase behaviour of polyoxyethylene surfactants with water J Chem Soc Faraday Trans 79(4):975–1000
Gomati R, Appell J, Bassereau P, Marignan J, Porte G (1987) Influence of the nature of the counterion and of hexanol on the phase behavior of the dilute ternary systems: cetylpyridinium bromide or chloride-hexanol-brine J Phys Chem 91:6203–6210
Porte G, Marignan J, Bassereau P, May R (1988) Shape transformations of the aggregates in dilute surfactant solutions: a small-angle neutron scattering study J Physiol Paris 49:511–519
Anderson D, Wennerström H, Olsson U (1989) Isotropic bicontinuous solutions in surfactant-solvent systems: the L3 phase J Phys Chem 93:4243–4253
Penfold J, Chen M, Thomas RK, Dong C, Smyth TJP (2011) Solution self-assembly of the sophorolipid biosurfactant and its mixture with anionic surfactant sodium dodecyl benzene sulfonate Langmuir 27:8867–8877
Roux D, Cates ME, Olsson U, Ball RC, Nallet F, Bellocq AM (1990) Light scattering from a surfactant sponge phase: evidence for a hidden symmetry Europhys Lett 11:229–234
Cates ME (1992) Sponge phases, vol 66. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg, pp. 275–280
Strey R, Schomäcker R, Roux D, Nallet F, Olsson U (1990) Dilute lamellar and L3 phases in the binary water–C12E5 system J Chem Soc Faraday Trans 86:2253–2261
Strey R, Jahn W, Porte G, Bassereau P (1990) Freeze fracture electron microscopy of dilute lamellar and anomalous isotropic (L3) phases Langmuir 6:1635–1639
Miller CA, Gradzeilski M, Hoffmann H, Kramer U, Thanic C (1991) L3 phases: their structure and dynamic properties Progr Colloid Polym Sci 84:243–249
Skouri M, Marignan J, Appell J, Porte G (1991) Fluid membranes in the “semi-rigid regime”: scale invariance J Phys B Atomic Mol Phys 1(9):1121–1132
Roux D, Coulon C, Cates ME (1992) Sponge phases in surfactant solutions J Phys Chem 96:4174–4187
Vinches C, Coulon C, Roux D (1992) Viscosity of sponge phase in porous medium J Phys B Atomic Mol Phys 2(3):453–469
Waton G, Porte G (1993) Transient behavior and relaxations of the L3 (sponge) phase: T-jumb experiments J Phys B Atomic Mol Phys 3(4):515–530
Filali M, Porte G, Appell J, Pfeuty P (1994) L3 (sponge) phase in the very dilute regime: spontaneous tearing of the membrane J Phys B Atomic Mol Phys 4(2):349–365
Porte G, Appell J, Bassereau P, Marignan M, Skouri M, Billard I (1991) Scaling laws for some physical properties of the L3 phase Progr Colloid Polym Sci 84:264–265
Granek R, Cates ME (1992) Sponge phase of surfactant solutions: an unusual dynamic structure factor Phys Rev A 46:3319–3334
Watanabe K, Nakama Y, Tanaki T, Hoffmann H (2001) Novel vesicle and sponge phase prepared in amphoteric surfactant/anionic surfactant/oleic acid/water system Langmuir 17:7219–7224
Munkert U, Hoffmann H, Thunig C, Meyer HW, Richter W (1992) From vesicles to the L3 (sponge) phase in alkyldimethylamine oxide/heptanol systems Langmuir 8:2629–2638
Thunig C, Platz G, Hoffmann H (1992) Phase behavior and light scattering of the system dodecyldimethylaminoxide, n-hexanol and water in the very dilute region Ber Bunsenges Phys Chem 96:667–667
Mahjoub HF, McGrath KM, Kléman M (1996) Phase transition induced by shearing of a sponge phase Langmuir 12:3131–3138
Yamamoto J, Tanaka H (1996) Shear-induced sponge-to-lamellar transition in a hyperswollen lyotropic system Phys Rev Lett 77:4390–4393
Nilsson PG, Lindman B (1984) Nuclear magnetic resonance self-diffusion and proton relaxation studies of nonionic surfactant solutions. Aggregate shape in isotropic solutions above the clouding temperature J Phys Chem 88:4764–4769
Dong R, Zhong Z, Hao J (2012) Self-assembly of onion-like vesicles induced by charge and rheological properties in anionic-nonionic surfactant solutions Soft Matter 8:7812–7821
Medronho B, Shafaei S, Szopko R, Miguel MG, Olsson U, Schmidt C (2008) Shear-induced transitions between a planar lamellar phase and multilamellar vesicles: continuous versus discontinuous transformation Langmuir 24:6480–6486
Nettesheim F, Zipfel J, Olsson U, Renth F, Lindner P, Richtering W (2003) Shear-induced transitions between a planar lamellar phase and multilamellar vesicles: continuous versus discontinuous transformation Langmuir 19:3603–3618
Song S, Song A (2014) Self-assembled structures of amphiphiles regulated via implanting external stimuli RSC Adv 4:41864–41875
Song S, Wang H, Song A, Dong S, Hao J (2014) Sponge phase producing porous CeO2 for catalytic oxidation of CO Chem Eur J 20:9063–9072
Wang A, Shi W, Huang J (2016) Adaptive soft molecular self-assemblies Soft Matter 12:337–357
Gentile L, Behrens MA, Porcar L, Butler P, Wagner NJ, Olsson U (2014) Multilamellar vesicle formation from a planar lamellar phase under shear flow Langmuir 30(28):8316–8325
Porcar L, Hamilton WA, Butler PD, Warr GG (2003) Scaling of structural and rheological response of L3 sponge phases in the “sweetened” cetylpyridinium/hexanol/dextrose/brine system Langmuir 19(26):10779–10794
Porcar L, Hamilton WA, Butler PD, Warr GG (2004) Topological relaxation of a shear-induced lamellar phase to sponge equilibrium and the energetics of membrane fusion Phys Rev Lett 93(19):198301
Bergmeier M, Gradzielski M, Hoffmann H, Mortensen K (1999) Behavior of ionically charged lamellar systems under the influence of a shear field J Phys Chem B 103:1605–1617
Winterhalter M, Helfrich W (1992) Bending elasticity of electrically charged bilayers: coupled monolayers, neutral surfaces, and balancing stresses J Phys Chem 96:327–330
Helfrich W (1994) Lyotropic lamellar phases J Phys Condens Matter 6:A79–A92
Friedrich H, Frederik PM, de With G, Sommerdijk NAJM (2010) Imaging of self-assembled structures: interpretation of TEM and cryo-TEM images Angew Chem Int Ed 49:7850–7858
Song A, Dong S, Jia X, Hao J, Liu W, Liu T (2005) An onion phase in salt-free zero-charged catanionic surfactant solutions Angew Chem Int Ed 44:4018–4021
Lukaschek M, Miiller S, Hansenhindl A, Grabowski DA, Schmidt C (1996) Lamellar lyomesophases under shear as studied by deuterium nuclear magnetic resonance Colloid Polym Sci 274:1–7
Zana R (1987) Surfactant solutions.New methods of investigation. Marcel Dekker, New York,
Yuan Z, Dong S, Liu W, Hao J (2009) Transition from vesicle phase to lamellar phase in salt-free catanionic surfactant solution Langmuir 25:8974–8981
Li X, Dong S, Jia X, Song A, Hao J (2007) Vesicles of a new salt-free catanionic fluoro-hydrocarbon surfactant system Chem Eur J 13:9495–9502
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (ZR2016BQ30), the Young Talents Training Program of Shandong Academy of Agricultural Sciences, and Special Agricultural Research Program (201303103).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shen, Y., Hoffmann, H., Lin, H. et al. The phase transition from L3 phase to vesicles and rheological properties of a nonionic surfactant mixture system. Colloid Polym Sci 295, 1663–1670 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-017-4144-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-017-4144-3