Abstract
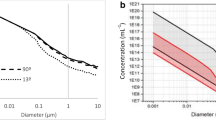
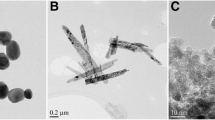
Monodisperse standard polystyrene particles were used to determine the differences between two methods for analyzing particle size based on dynamic light scattering—namely photon correlation spectroscopy (PCS) and photon cross-correlation spectroscopy (PCCS). We demonstrate that the cross-correlation technique achieves results more in line with real particle properties not only with respect to monodisperse systems, but also with respect to polydisperse standard polystyrene particle systems. In addition, suspensions of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles or PLGA (Poly(Lactide-co-Glycolide)) particles were studied by both PCS and PCCS in order to compare the measurements of non-standardized particles. Both methods were suitable for particle size distribution analysis with respect to the studied particle systems, but photon cross-correlation spectroscopy yielded more precise results and was able to distinguish particles with a diameter ratio of 4, whereas PCS showed a monomodal particle size distribution when measuring particles with a diameter ratio of 5. Measurements of non-standard samples confirmed previous findings that PCCS is more suitable for measurements of multi disperse systems.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tscharnuter W (2006) Photon correlation spectroscopy in particle sizing. In: Meyers RA (ed) Encyclopedia of analytical chemistry: applications, theory and instrumentation. Brookhaven Instruments Corporation, Holtsville 18 p
Li Y, Barron AR (2016) Dynamic light scattering. Open-Stax-CNC, http://cnx.org/contents/P8mNrZNN@1/Dynamic-Light-Scattering
Frisken BJ (2001) Revisiting the method of Cumulants for the analysis of dynamic light-scattering data. App Opt 40:4087–4091. doi:10.1364/AO.40.004087
Block ID, Scheffold F (2010) Modulated 3D cross-correlation light scattering: improving turbid sample characterization. Rev Sci Instrum 81:123107 . doi:10.1063/1.35189617 p
Medebach M, Moitzi C, Freiberger N, Glatter O (2007) Dynamic light scattering in turbid colloidal dispersions: a comparison between the modified flat-cell light-scattering instrument and 3D dynamic light-scattering instrument. J Colloid Interface Sci 305:88–93. doi:10.1016/j.jcis.2006.09.013
Urban C, Schurtenberger P (1998) Characterization of turbid colloidal suspensions using light scattering techniques combined with cross-correlation methods. J Colloid Interface Sci 207:150–158. doi:10.1006/jcis.1998.5769
LS Instruments GmbH (2011) Cross-correlation dynamic light scattering (DLS) method and system. 10156420.1. Switzerland, EP 2365313 A1. Patent application, 2011–09-14
Phillies GDJ (1981) Experimental demonstration of multiple-scattering suppression in Quasielastic-light-scattering spectroscopy by homodyne coincidence techniques. Phys Rev A: At Mol Opt Phys 24:1939–1943. doi:10.1103/PhysRevA.24.1939
Phillies GDJ (1981) Suppression of multiple scattering effects in Quasielastic light scattering by homodyne cross-correlation techniques. J Chem Phys 74:260–262. doi:10.1063/1.440884
Meyer WV, Cannell DS, Smart AE, Taylor TW, Tin P (1997) Multiple-scattering suppression by cross correlation. App Opt 36:7551–7558. doi:10.1364/AO.36.007551
Sympatec GmbH (online) Photon cross-correlation spectroscopy. https://www.sympatec.com/EN/PCCS/PCCS.html
Pusey PN (1999) Suppresion of multiple scattering by photon cross-correlation techniques. Curr Opin Colloid Interface Sci 4:177–185. doi:10.1016/S1359-0294(99)00036-9
Scheffold F, Cerbino R (2007) New trends in light scattering. Curr Opin Colloid Interface Sci 12:50–57
NanoComposix (2015) Nano composix’s guide to dynamic light scattering measurement and analysis. https://cdn.shopify.com/s/files/1/0257/8237/files/nanoComposix_Guidelines_for_DLS_Measurements_and_Analysis.pdf
Kaszuba M, Connah MT, McNeil-Watson FK, Nobbmann U (2007) Resolving concentrated particle size mixtures using dynamic light scattering. Part Part Syst Charact 24:159–162. doi:10.1002/ppsc.200601035
Fissan H, Ristig S, Kaminski H, Asbach C, Epple M (2014) Comparison of different characterization methods for nanoparticle dispersion before and after aerosolization. Anal Methods 6:7324–7334. doi:10.1039/C4AY01203H
Atashafrooz Z, Dizaj SM, Sadaghiani AS (2014) Cucurbita pepo Oil as a drug microemulsion formulation: study of phase diagram. Nanomedicine J 1:298–301. doi:10.7508/nmj.2015.05.002
Mahmoudi M, Snat S, Wang B, Laurent S, Sen T (2011) Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPIONs): development, surface modification and application in chemotherapy. Adv Drug Deliver Rev 63:24–46. doi:10.1016/j.addr.2010.05.006
Wahajuddin AS (2012) Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: magnetic nanoplatforms as drug carriers. Int J Nanomedicine 7:3445–3471. doi:10.2147/IJN.S30320
Makadia HK, Siegel SJ (2011) Poly lactic-co-glycolic acid (PLGA) as biodegradable controlled drug delivery carrier. Polymers 3:1377–1397. doi:10.3390/polym3031377
Wu L, Ding J (2004) In vitro degradation of three-dimensional porous poly(d,l-lactide-co-glycolide) scaffolds for tissue engineering. Biomaterials 25:5821–5830. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2004.01.038
Siegel SJ, Kahn JB, Metzger K, Winey KI, Werner K, Dan N (2006) Effect of drug type on the degradation rate of PLGA matrices. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 64:287–293. doi:10.1016/j.ejpb.2006.06.009
Danhier F, Ansorena E, Silva JM, Coco R, Le Breton A, Préat V (2012) PLGA-based nanoparticles: an overview of biomedical applications. J Control Release 161:505–522. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2012.01.043
Prescott JH, Shiau S, Rowell RL (1993) Characterization of polystyrene latexes by hydrodynamic and electrophoretic fingerprinting. Langmuir 9:2071–2076. doi:10.1021/la00032a027
Vo-Dinh T (2007) Nanotechnology in biology and medicine: methods, devices, and applications. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Wells MA, Abid A, Kennedy IM, Barakat AI (2012) Serums proteins prevent aggregation of Fe2O3 and ZnO nanoparticles. Nanotoxicology 6:837–846. doi:10.3109/17435390.2011.625131
Bryant G, Thomas JC (1995) Improved particle size distribution measurements using multiangle dynamic light scattering. Langmuir 11:2480–2485. doi:10.1021/la00007a028
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Project Nr. LO1211, Materials Research Centre at FCH BUT- Sustainability and Development (National Programme for Sustainability I, Ministry of Education, Youth and Sports of the Czech Republic).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 21 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Burdíková, J., Mravec, F., Wasserbauer, J. et al. A practical comparison of photon correlation and cross-correlation spectroscopy in nanoparticle and microparticle size evaluation. Colloid Polym Sci 295, 67–74 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-016-3982-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-016-3982-8