Abstract
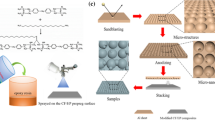
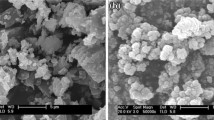
The superhydrophobic glass fiber-reinforced plastic (GFRP) surfaces are prepared by spray coating a mixture on GFRP surfaces. The mixture is comprised of EPOLAM resin 2008 (EP2008), EPOLAM curing agent 2008-S (EP2008-S), hydrophobic silica nanoparticles (HSNPs), and acetone. By simply controlling the concentration of HSNPs in the mixture, the tunable adhesive superhydrophobic surfaces can be obtained. The results confirm that the as-prepared samples not only could achieve superhydrophobicity but also present huge differences in adhesive abilities. Noticeably, the superhydrophobic GFRP surfaces can keep the excellent stability in many kinds of solvents for 3 days, such as water (25 °C), toluene, acetone, tetrahydrofuran, and ethanol. In addition, water droplets with different pH (1–14) have similar contact angles and adhesion on the surfaces, indicating that these surfaces are chemical resistant to acid and alkali. Furthermore, after being stored in ambient environment for 6 months, no obvious decrease in water contact angle (CA) was observed. In addition, the damaged surfaces could be restored completely after spray coating again. The results reported herein not only present a simple, efficient, and reproducible method to elaborate the superhydrophobic GFRP surfaces but also benefits in understanding the principle for the fabrication superhydrophobic surfaces with tunable adhesive.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Xue CH, Zhang P, Ma JZ, Ji PT, Li YR, Jia ST (2013) Long-lived superhydrophobic colorful surfaces. Chem Commun 49:3588–3590
Zhou H, Wang H, Niu H, Gestos A, Wang X, Lin T (2012) Fluoroalkyl silane modified silicone rubber/nanoparticle composite: a super durable, robust superhydrophobic fabric coating. Adv Mater 24:2409–2412
Teisala H, Tuominen M, Aromaa M, Stepien M, Mäkelä JM, Saarinen JJ, Kuusipalo J (2013) High- and low-adhesive superhydrophobicity on the liquid flame spray-coated board and paper: structural effects on surface wetting and transition between the low- and high-adhesive states. Colloid Polym Sci 291:447–455
Li XM, Reinhoudt D, Crego-Calama M (2007) What do we need for a superhydrophobic surface? A review on the recent progress in the preparation of superhydrophobic surfaces. Chem Soc Rev 36:1350–1368
Liu K, Yao X, Jiang L (2010) Recent developments in bio-inspired special wettability. Chem Soc Rev 39:3240–3255
Chen Y, Zhang Y, Shi L, Li J, Xin Y, Yang T, Guo Z (2012) Transparent superhydrophobic/superhydrophilic coatings for self-cleaning and anti-fogging. Appl Phys Lett 101:033701
Xue Z, Wang S, Lin L, Chen L, Liu M, Feng L, Jiang L (2011) A novel superhydrophilic and underwater superoleophobic hydrogel-coated mesh for oil/water separation. Adv Mater 23:4270–4273
Tsougeni K, Papageorgiou D, Tserepi A, Gogolides E (2010) “Smart” polymeric microfluidics fabricated by plasma processing: controlled wetting, capillary filling and hydrophobic valving. Lab Chip 10:462–469
Xu QF, Wang JN (2009) A superhydrophobic coating on aluminium foil with an anti-corrosive property. New J Chem 33:734–738
Krupenkin TN, Taylor JA, Wang EN, Kolodner P, Hodes M, Salamon TR (2007) Reversible wetting-dewetting transitions on electrically tunable superhydrophobic nanostructured surfaces. Langmuir 23:9128–9133
Shiu JY, Kuo CW, Chen P, Mou CY (2004) Fabrication of tunable superhydrophobic surfaces by nanosphere lithography. Chem Mater 16:561–564
Lee Y, Ju KY, Lee JK (2010) Stable biomimetic superhydrophobic surfaces fabricated by polymer replication method from hierarchically structured surfaces of Al templates. Langmuir 26:14103–14110
Lee Y, Park SH, Kim KB, Lee JK (2007) Fabrication of hierarchical structures on a polymer surface to mimic natural superhydrophobic surfaces. Adv Mater 19:2330–2335
Amigoni S, Taffin de Givenchy E, Dufay M, Guittard F (2009) Covalent layer-by-layer assembled superhydrophobic organic–inorganic hybrid films. Langmuir 25:11073–11077
Du X, Li X, He J (2010) Facile fabrication of hierarchically structured silica coatings from hierarchically mesoporous silica nanoparticles and their excellent superhydrophilicity and superhydrophobicity. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2:2365–2372
Zhai L, Cebeci FC, Cohen RE, Rubner MF (2004) Stable superhydrophobic coatings from polyelectrolyte multilayers. Nano Lett 4:1349–1353
Shang Q, Gao L, Liu H, Xiao G (2011) Fabrication of superhydrophobic silica film by removing polystyrene spheres. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 59:334–337
Latthe SS, Imai H, Ganesan V, Rao AV (2009) Superhydrophobic silica films by sol–gel co-precursor method. Appl Surf Sci 256:217–222
Hao L, Chen Z, Wang R, Guo C, Zhang P, Pang S (2012) A non-aqueous electrodeposition process for fabrication of superhydrophobic surface with hierarchical micro/nano structure. Appl Surf Sci 258:8970–8973
Crick CR, Bear JC, Kafizas A, Parkin IP (2012) Superhydrophobic photocatalytic surfaces through direct incorporation of titania nanoparticles into a polymer matrix by aerosol assisted chemical vapor deposition. Adv Mater 24:3505–3508
Cengiz U, Avci MZ, Erbil HY, Sarac AS (2012) Superhydrophobic terpolymer nanofibers containing perfluoroethyl alkyl methacrylate by electrospinning. Appl Surf Sci 258:5815–5821
Shang Q, Wang M, Liu H, Gao L, Xiao G (2013) Facile fabrication of water repellent coatings from vinyl functionalized SiO2 spheres. J Coat Tech Res 10:465–473
Ogihara H, Xie J, Okagaki J, Saji T (2012) Simple method for preparing superhydrophobic paper: spray-deposited hydrophobic silica nanoparticle coatings exhibit high water-repellency and transparency. Langmuir 28:4605–4608
Su C (2012) A simple and cost-effective method for fabricating lotus-effect composite coatings. J Coat Tech Res 9:135–141
Hwang HS, Kim NH, Lee SG, Lee DY, Cho K, Park I (2011) Facile fabrication of transparent superhydrophobic surfaces by spray deposition. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 3:2179–2183
Xu L, Karunakaran RG, Guo J, Yang S (2012) Transparent, superhydrophobic surfaces from one-step spin coating of hydrophobic nanoparticles. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 4:1118–1125
Milionis A, Martiradonna L, Anyfantis GC, Cozzoli PD, Bayer IS, Fragouli D, Athanassiou A (2013) Control of the water adhesion on hydrophobic micropillars by spray coating technique. Colloid Polym Sci 291:401–407
Xue CH, Zhang ZD, Zhang J, Jia ST (2014) Lasting and self-healing superhydrophobic surfaces by coating of polystyrene/SiO2 nanoparticles and polydimethylsiloxane. J Mater Chem A 2:15001–15007
Cui Z, Ding J, Scoles L, Wang Q, Chen Q (2013) Superhydrophobic surfaces fabricated by spray-coating micelle solutions of comb copolymers. Colloid Polym Sci 291:1409–1418
Karunakaran RG, Lu CH, Zhang Z, Yang S (2011) Highly transparent superhydrophobic surfaces from the coassembly of nanoparticles (≤100 nm). Langmuir 27:4594–4602
Ogihara H, Xie J, Saji T (2015) Controlling surface energy of glass substrates to prepare superhydrophobic and transparent films from silica nanoparticle suspensions. J Colloid Interface Sci 437:24–27
Tenjimbayashi M, Shiratori S (2014) Highly durable superhydrophobic coatings with gradient density by movable spray method. J Appl Phys 116:114310
Wang C, Xiao J, Zeng J, Jiang D, Yuan Z (2012) A novel method to prepare a microflower-like superhydrophobic epoxy resin surface. Mater Chem Phys 135:10–15
Wenzel RN (1936) Resistance of solid surfaces to wetting by water. Ind Eng Chem 28:988–994
Cassie ABD, Baxter S (1944) Wettability of porous surfaces. Trans Faraday Soc 40:546–551
Neinhuis C, Koch K, Barthlott W (2001) Movement and regeneration of epicuticular waxes through plant cuticles. Planta 213:427–434
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Program for New Century Excellent Talents in University (NCET-12-0119), Qing-lan Project of Jiangsu province, Summit of the Six Top Talents Program of Jiangsu Province (2013-JY-007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, J., Wang, J. The fabrication of superhydrophobic glass fiber-reinforced plastic surfaces with tunable adhesion based on hydrophobic silica nanoparticle aggregates. Colloid Polym Sci 293, 2815–2821 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-015-3681-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-015-3681-x